Bangladesh
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Asia; Asian Countries
| গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ Gônoprojatontri Bangladesh People's Republic of Bangladesh
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Amar Shonar Bangla My Golden Bengal |
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Dhaka |
|||||
| Official languages | Bengali (Bangla) | |||||
| Demonym | Bangladeshi | |||||
| Government | Parliamentary republic | |||||
| - | President | lajuddin Ahmed | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | vacant | ||||
| - | Chief Adviser (Interim Caretaker Government) |
Fakhruddin Ahmed |
||||
| Independence | from Pakistan | |||||
| - | Declared | March 26, 1971 | ||||
| - | Victory Day | December 16 1971 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 144,000 km² ( 94th) 55,599 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 7.0 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2007 estimate | 150,448,340 ( 7th) | ||||
| - | Density | 1045/km² ( 11th) 2,706/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | US$360.9 billion ( 31st) | ||||
| - | Per capita | US$2,270 ( 144th) | ||||
| Gini (2000) | 31.8 (medium) | |||||
| HDI (2007) | ▲ 0.547 (medium) ( 140th) | |||||
| Currency | Taka ( BDT) |
|||||
| Time zone | BDT ( UTC+6) | |||||
| - | Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC+6) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .bd | |||||
| Calling code | +880 | |||||
| 1 | Adjusted population, p.4, Population Census 2001, Preliminary Report. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (2001-08). | |||||
Bangladesh (Bengali: বাংলাদেশ [ˈbaŋlad̪eʃ] Bangladesh), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh (Bengali: গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ Gônoprojatontri Bangladesh), is a country in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Myanmar to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south. Together with the Indian state of West Bengal, it makes up the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal. The name Bangladesh means "Country of Bengal" in the official Bengali language.
The borders of the region that constitutes present-day Bangladesh were established in the 1947 Partition of India when the region became the eastern wing of newly formed Pakistan. The pairing, based on their common religion (Islam), proved geographically awkward since an expanse of foreign Indian territory, 1 600 km (1 000 mi) wide, separated the two wings. Subjected to political and linguistic discrimination as well as economic neglect at the hands of West Pakistan, the Bengalis of East Pakistan declared independence in 1971. After a liberation war, with help from India and the Soviet Union, Bangladesh was born. In spite of its liberation narrative, Bangladesh's development has since been marred by political turmoil, with fourteen different heads of government and at least four military coups.
Bangladesh is among the most densely populated countries in the world and has a high poverty level. Geographically the country straddles the fertile Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta and is subject to annual monsoon floods and cyclones. The government is a parliamentary democracy which has been suspended under emergency law since 11 January 2007. Bangladesh is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, SAARC, BIMSTEC, the OIC, and the D-8.
History
Remnants of civilisation in the greater Bengal region date back four thousand years, when the region was settled by Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, and Austro-Asiatic peoples. The exact origin of the word "Bangla" or "Bengal" is unknown, though it is believed to be derived from Bang, the Dravidian-speaking tribe that settled in the area around the year 1000 BC.
After the arrival of Indo-Aryans, the kingdom of Gangaridai was formed from at least the seventh century BC, which later united with Bihar under the Magadha and Maurya Empires. Bengal was later part of the Gupta Empire from the third to the sixth centuries CE. Following its collapse, a dynamic Bengali named Shashanka founded an impressive yet short-lived kingdom. Shashanka is considered as the first independent king in the history of Bangladesh.After a period of anarchy, the Buddhist Pala dynasty ruled the region for four hundred years, followed by a shorter reign of the Hindu Sena dynasty. Islam was introduced to Bengal in the twelfth century by Sufi missionaries, and subsequent Muslim conquests helped spread Islam throughout the region. Bakhtiar Khilji, a Turkish general, defeated Lakshman Sen of the Sena dynasty and conquered large parts of Bengal. The region was ruled by dynasties of Sultans and feudal lords for the next few hundred years. By the 16th century, the Mughal Empire controlled Bengal, and Dhaka became an important provincial centre of Mughal administration.
European traders arrived late in the 15th century, and their influence grew until the British East India Company gained control of Bengal following the Battle of Plassey in 1757. The bloody rebellion of 1857, known as the Sepoy Mutiny, resulted in transfer of authority to the crown, with a British viceroy running the administration. During colonial rule, famine racked the Indian subcontinent many times, including the Great Bengal famine of 1943 that claimed 3 million lives.
Between 1905 and 1911, an abortive attempt was made to divide the province of Bengal into two zones, with Dhaka being the capital of the eastern zone. When India was partitioned in 1947, Bengal was partitioned along religious lines, with the western part going to India and the eastern part joining Pakistan as a province called East Bengal (later renamed East Pakistan), with its capital at Dhaka.
In 1950, land reform was accomplished in East Bengal with the abolishment of the feudal zamindari system However, despite the economic and demographic weight of the east, Pakistan's government and military were largely dominated by the upper classes from the west. The Bengali Language Movement of 1952 was the first sign of friction between the two wings of Pakistan. Dissatisfaction with the central government over economic and cultural issues continued to rise through the next decade, during which the Awami League emerged as the political voice of the Bengali-speaking population. It agitated for autonomy in the 1960s, and in 1966, its president Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was jailed; he was released in 1969 after an unprecedented popular uprising.

In 1970, a massive cyclone devastated the coast of East Pakistan, and the central government responded poorly. The Bengali population's anger was compounded when Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, whose Awami League won a majority in Parliament in the 1970 elections, was blocked from taking office. After staging compromise talks with Mujib, President Yahya Khan arrested him on the night of March 25, 1971, and launched Operation Searchlight, a sustained military assault on East Pakistan. Yahya's methods were extremely bloody, and the violence of the war resulted in many civilian deaths. Chief targets included intellectuals and Hindus, and about ten million refugees fled to neighbouring India (LaPorte, p. 103). Estimates of those massacred range from three hundred thousand to 3 million.
Most of the Awami League leaders fled and set up a government-in-exile in Calcutta, India. The Bangladesh Liberation War lasted for nine months. The guerrilla Mukti Bahini and Bengali regulars eventually received support from the Indian Armed Forces in December 1971. Under the command of Lt. General J.S. Arora, the Indian Army achieved a decisive victory over Pakistan on 16 December, 1971, taking over 90,000 prisoners of war in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971.
After its independence, Bangladesh became a parliamentary democracy, with Mujib as the Prime Minister. In the 1973 parliamentary elections, the Awami League gained an absolute majority. A nationwide famine occurred during 1973 and 1974, and in early 1975, Mujib initiated a one-party socialist rule with his newly formed BAKSAL. On August 15, 1975, Mujib and his family were assassinated by mid-level military officers.
A series of bloody coups and counter-coups in the following three months culminated in the ascent to power of General Ziaur Rahman, who reinstated multi-party politics and founded the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). Zia's rule ended when he was assassinated in 1981 by elements of the military. Bangladesh's next major ruler was General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, who gained power in a bloodless coup in 1982 and ruled until 1990, when he was forced to resign under western donor pressure in a major shift in international policy after the end of communism when anti-communist dictators were no longer felt necessary. Since then, Bangladesh has reverted to a parliamentary democracy. Zia's widow, Khaleda Zia, led the Bangladesh Nationalist Party to parliamentary victory at the general election in 1991 and became the first female Prime Minister in Bangladesh's history. However, the Awami League, headed by Sheikh Hasina, one of Mujib's surviving daughters, clinched power at the next election in 1996 but lost to the Bangladesh Nationalist Party again in 2001. These two female ex-prime ministers are now in imprisonment in a sub-jail due to their suspected attachment with corruption.
In 11 January of 2007, following widespread violence, a caretaker government was appointed to administer the next general election. The country had suffered from extensive corruption, disorder and political violence. The new caretaker government has made it a priority to root out corruption from all levels of government. To this end, many notable politicians and officials, along with large numbers of lesser officials and party members, have been arrested on corruption charges. The caretaker government claims to be paving the way for free and fair elections to be held before the end of 2008.
Government and politics
| Anthem | Amar Shonar Bangla |
| Animal | Royal Bengal Tiger |
| Bird | Oriental Magpie Robin |
| Fish | Hilsa |
| Flower | White Water Lily |
| Fruit | Jackfruit |
| Sport | Kabadi |
| Calendar | Bengali calendar |
Bangladesh is a parliamentary democracy with Islam as the state religion. Direct elections involving all citizens over the age 18 are held every five years for the unicameral parliament. The parliament building is known as the Jatiyo Sangshad designed by architect Louis Kahn and currently has 300 seats, elected from single-member constituencies. The Prime Minister, as the head of government, forms the cabinet and runs the day-to-day affairs of state. While the Prime Minister is formally appointed by the President, he or she must be an MP who commands the confidence of the majority of parliament. The President is the head of state, a largely ceremonial post elected by the parliament.
However the President's powers are substantially expanded during the tenure of a caretaker government, which is responsible for the conduct of elections and transfer of power. The officers of the caretaker government must be non-partisan and are given three months to complete their task. This transitional arrangement is an innovation that was pioneered by Bangladesh in its 1991 election and then institutionalised in 1996 through its 13th constitutional amendment.
The Constitution of Bangladesh was drafted in 1972 and has undergone fourteen amendments. The highest judicial body is the Supreme Court. Justices are appointed by the President. The judicial and law enforcement institutions are weak. Separation of powers, judicial from executive was finally implemented on the 1st of November, 2007. It is expected that this separation will make the judiciary stronger and impartial. Laws are loosely based on English common law, but family laws such as marriage and inheritance are based on religious scripts, and therefore differ between religious communities.
The two major parties in Bangladesh are the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and the Bangladesh Awami League. BNP is led by Khaleda Zia and finds its allies among Islamist parties like Jamaat-e-Islami Bangladesh and Islami Oikya Jot, while Sheikh Hasina's Awami League aligns with leftist and secularist parties. Hasina and Zia are bitter rivals who have dominated politics for 15 years; both are women and each is related to one of the leaders of the independence movement. Another important player is the Jatiya Party, headed by former military ruler Ershad. The Awami League-BNP rivalry has been bitter and punctuated by protests, violence and murder. Student politics is particularly strong in Bangladesh, a legacy from the liberation movement era. Almost all parties have highly active student wings, and students have been elected to the Parliament.
Two radical Islamist parties, Jagrata Muslim Janata Bangladesh (JMJB) and Jama'atul Mujahideen Bangladesh (JMB), were banned in February 2005. Bomb attacks taking place since 1999 have been blamed on those groups, and hundreds of suspected members have been detained in numerous security operations, including the head of those two parties in 2006. The first recorded case of a suicide bomb attack in Bangladesh took place in November 2005.
The 2006 election was postponed indefinitely and emergency law declared in January 2007 as the caretaker government of Fakhruddin Ahmed aims to revise the voter list and crack down on corruption. The government aims to hold new elections by 2008 but lack of coordination between Election Commission and the Government, and their recent activities have created uncertainty about Election while the two leading candidates, Khaleda Zia and Sheikh Hasina, are facing criminal charges in court and the banned indoor politics is yet to be exercised.
Meanwhile the Bangladesh Military has expressed their interest in controlling the country with statements like "own brand of Democracy" and making changes in the constitution to allow military participation in politics. They are also assisting the interim Government of Bangladesh in a drive against corruption which seems to be mostly targeted against the politicians. The military has also imposed censorship of the national media and closing down/hampering private TV stations.
Foreign policy and military
Bangladesh pursues a moderate foreign policy that places heavy reliance on multinational diplomacy, especially at the United Nations. In 1974 Bangladesh joined both the Commonwealth of Nations and the United Nations and has since been elected to serve two terms on the Security Council in 1978-1979 and 2000–2001. In the 1980s, Bangladesh played a lead role in founding the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) in order to expand relations with other South Asian states. Since the founding of SAARC 1985, a Bangladeshi has held the post of Secretary General on two occasions.
Bangladesh's most important and complex foreign relationships are with India and Pakistan. These relationships are informed by historical and cultural ties and form an important part of the domestic political discourse.
Bangladesh's relationship with India began on a positive note because of India's assistance in the independence war and reconstruction. Throughout the years, relations between both countries have fluctuated for a number of reasons. The Washington Post reported on a major source of tension between Bangladesh and India, the Farakka Dam (article titled “India’s Major Gains and Losses in World Affairs” by M.M. Ali, March 1997, pg. 25). In 1975, India defied international law and the rights of Bangladeshi people by building a dam on the Ganges River 11 miles (18 km) from the Bangladeshi border. The dam diverts much needed water from Bangladesh and adds a man-made disaster to the country plagued by natural disasters. The dam also has terrible ecological consequences. Bangladesh claims that India feels too comfortable in playing the role of "Big Brother" to smaller, weaker nations. India has voiced concerns about anti-Indian separatists and Islamic militants allegedly being harboured across their 2,500-mile (4,000 km) border, as well as the flow of illegal migrants, and is building a fence along most of it. But at the 2007 SAARC meeting both nations pledged to work cooperatively on security, economic and border issues.
The current strength of the army is around 200,000, the air force 7,000, and navy 14,950. In addition to traditional defense roles, the military has been called on to provide support to civil authorities for disaster relief and internal security during periods of political unrest. Bangladesh is not currently active in any ongoing war, but it did contribute 2,300 troops to the coalition that fought in the 1991 Gulf War and Bangladesh is consistently a top contributor to UN peacekeeping forces around the world. As of May 2007, Bangladesh had major deployments in Democratic Republic of Congo, Liberia, Sudan, Timor-Leste and Cote d'Ivoire.
Bangladesh enjoys relatively warm ties with the People's Republic of China which has, particularly in the past decade, increased economic cooperation with the South Asian nation. Between 2006-07, trade between the two nations rose by 28.5% and there have been agreements to grant various Bangladeshi commodities tariff-free access to the Chinese market. Military cooperation between the Military of Bangladesh and the People's Liberation Army is also increasing, with joint military agreements signed and Bangladesh procuring Chinese arms which range from small arms to large naval surface combatants such as the Chinese Jiangwei Class Missile Frigate.
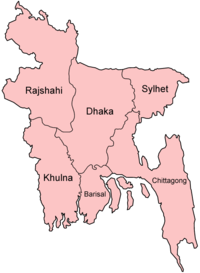
Divisions, districts, and upazilas
Bangladesh is divided into six administrative divisions, each named after their respective divisional headquarters: Barisal (বরিশাল), Chittagong (চট্টগ্রাম), Dhaka (ঢাকা), Khulna (খুলনা), Rajshahi (রাজশাহী), and Sylhet (সিলেট).
Divisions are subdivided into districts (zila). There are 64 districts in Bangladesh, each further subdivided into upazila (subdistricts) or thana ("police stations"). The area within each police station, except for those in metropolitan areas, is divided into several unions, with each union consisting of multiple villages. In the metropolitan areas, police stations are divided into wards, which are further divided into mahallas. There are no elected officials at the divisional, district or upazila levels, and the administration is composed only of government officials. Direct elections are held for each union (or ward), electing a chairperson and a number of members. In 1997, a parliamentary act was passed to reserve three seats (out of twelve) in every union for female candidates.
Dhaka is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. Other major cities include Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, and Barisal.These metropolitan cities have mayoral elections, while other municipalities elect a chairperson. Mayors and chairpersons are elected for a span of five years.
| City | City population | Metro population |
|---|---|---|
| Dhaka | 6,969,458 | 11,918,442 |
| Chittagong | 3,920,222 | 3,920,222 |
| Khulna | 1,400,689 | 1,400,689 |
| Rajshahi | 727,083 | 727,083 |
| Sylhet | 339,368 | 339,368 |
| Barisal | 291,769 | 291,769 |
Geography and climate
Bangladesh is located in the low-lying Ganges-Brahmaputra River Delta or Ganges Delta. This delta is formed by the confluence of the Ganges (local name Padma or Pôdda), Brahmaputra ( Jamuna or Jomuna), and Meghna rivers and their respective tributaries. The Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna to eventually empty into the Bay of Bengal. The alluvial soil deposited by these rivers has created some of the most fertile plains in the world. Bangladesh has 58 trans-boundary rivers, making water issues politically complicated to resolve - in most cases as the lower riparian state to India. Most parts of Bangladesh are less than 12 metres (39 ft) above the sea level, and it is believed that about 50% of the land would be flooded if the sea level were to rise by 1 metre (3 ft).
The highest point in Bangladesh is in Mowdok range at 1,052 metres (3,451 ft) in the Chittagong Hill Tracts to the southeast of the country. A major part of the coastline comprises a marshy jungle, the Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest in the world and home to diverse flora and fauna, including the Royal Bengal Tiger. In 1997, this region was declared endangered.
Straddling the Tropic of Cancer, Bangladeshi climate is tropical with a mild winter from October to March, a hot, humid summer from March to June. A warm and humid monsoon season lasts from June to October and supplies most of the country's rainfall. Natural calamities, such as floods, tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and tidal bores occur almost every year, combined with the effects of deforestation, soil degradation and erosion. Cox's Bazar, south of the city of Chittagong, has a beach that stretches uninterrupted over 120 kilometres (75 mi).
In September 1998 Bangladesh saw the most severe flooding the modern world has seen. As the Brahmaputra, Ganges and Meghna split over and swallowed 300,000 houses, 6,000 miles (9,700 km) of road and 1,600 miles (2,600 km) of embankmennt1,000 people were killed and 30 million more were made homeless with 130,000 cattle killed, 50 square kilometres of land destroyed and 11,000 km of roads damaged or destroyed. 66% of the country was underwater. There were several reasons for the severity of the flooding. Firstly, there were unusually high monsoon rains. Secondly, the Himalayas shed off an equally unusually high amount of melt water that year. Lastly, trees that usually intercept rain water were cut down for fire wood or to make space for animals.
Economy
Despite sustained domestic and international efforts to improve economic and demographic prospects, Bangladesh remains a developing nation, in part due to its large population. Its per capita income in 2006 was US$2300 (on purchasing power parity basis) compared to the world average of $10,200. Yet, as the World Bank notes in its July 2005 Country Brief, the country has made significant progress in human development in the areas of literacy, gender parity in schooling, and reduction of population growth.
Jute was once the economic engine of the country. Its share of the world export market peaked in the Second World War and the late 1940s at 80% and even in the early 1970s accounted for 70% of its export earnings. However, polypropylene products began to substitute for jute products worldwide and the jute industry started to decline. Bangladesh grows very significant quantities of rice(chal), tea (Cha) and mustard. Although two-thirds of Bangladeshis are farmers, more than three quarters of Bangladesh’s export earnings come from the garment industry, which began attracting foreign investors in the 1980s due to cheap labour and low conversion cost. In 2002, the industry exported US$5 billion worth of products. The industry now employs more than 3 million workers, 90% of whom are women. A large part of foreign currency earnings also comes from the remittances sent by expatriates living in other countries.
Obstacles to growth include frequent cyclones and floods, inefficient state-owned enterprises, mismanaged port facilities, a growth in the labour force that has outpaced jobs, inefficient use of energy resources (such as natural gas), insufficient power supplies, slow implementation of economic reforms, political infighting and corruption. According to the World Bank, "among Bangladesh’s most significant obstacles to growth are poor governance and weak public institutions."
Despite these hurdles, the country has achieved an average annual growth rate of 5% since 1990, according to the World Bank. Bangladesh has seen expansion of its middle class, and its consumer industry has also grown. In December 2005, four years after its report on the emerging " BRIC" economies (Brazil, Russia, India, and China), Goldman Sachs named Bangladesh one of the " Next Eleven," along with Egypt, Indonesia, Pakistan and seven other countries. Bangladesh has seen a dramatic increase in foreign direct investment. A number of multinational corporations, including Unocal Corporation and Tata, have made major investments, with the natural gas sector being a priority. In December 2005, the Central Bank of Bangladesh projected GDP growth around 6.5%.
One significant contributor to the development of the economy has been the widespread propagation of microcredit by Muhammad Yunus (awarded the Nobel peace prize in 2006) through the Grameen Bank. By the late 1990s, Grameen Bank had 2.3 million members, along with 2.5 million members of other similar organisations.
In order to enhance economic growth, the government set up several export processing zones to attract foreign investment. These are managed by the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority.
Demographics
Recent (2005-2007) estimates of Bangladesh's population range from 142 to 159 million, making it the 7th most populous nation in the world. With a land area of 144,000 square kilometers, ranked 94th), the population density is remarkable. A striking comparison is offered by the fact that Russia's population is slightly smaller. Indeed Bangladesh has the highest population density in the world, excluding a handful of city-states. Bangladesh's population growth was among the highest in the world in the 1960s and 1970s, when the count grew from 50 to 90 million, but with the promotion of birth control in the 1980s, the growth rate slowed. The total fertility rate is now 3.1 children per woman, compared with 6.2 thirty years ago. The population is relatively young, with the 0–25 age group comprising 60%, while 3% are 65 or older. Life expectancy is 63 years for both males and females.
Bangladesh is ethnically homogeneous, with Bengalis comprising 98% of the population. The remainder are mostly Bihari migrants and indigenous tribal groups. There are thirteen tribal groups located in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, the most populous of the tribes are the Chakmas. The region has been a source for ethnic tension since the inception of Bangladesh. The largest tribal groups outside the Hill Tracts are the Santhals and the Garos (Achiks). There are also Kaibartta, Mundas, Oraons, and Zomi ethnic groups. Human trafficking has been a lingering problem in Bangladesh and illegal immigration has remained a cause of friction with Myanmar and India..
The official and most widely used language in Bangladesh, as in West Bengal, is Bangla (Bengali) , an Indo-Aryan language of Sanskrit origin with its own script. English is used as second language among the middle and upper classes and in higher education. Since a President Order in 1987, Bangla is used for all official correspondence except those that are to foreign recipients.
Health and education levels have recently improved as poverty levels have decreased. Most Bangladeshis are rural, living on subsistence farming. Health problems abound, ranging from surface water contamination, to arsenic in the groundwater, and diseases including malaria, leptospirosis and dengue. The literacy rate in Bangladesh is approximately 41%. There is gender disparity, though, as literacy rates are 50% among men and 31% among women, according to a 2004 UNICEF estimate. Literacy has gone up due to many programmes introduced in the country. Among the most successful ones are the Food for education (FFE) programme introduced in 1993, and a stipend programme for women at the primary and secondary levels.
The two major religions practiced in Bangladesh are Islam (89.7%) and Hinduism (9.2%). About 96% of the Muslims are Sunni while over 3% are Shi'a and remainders are Ahmadis. Ethnic Biharis are predominantly Shia Muslims. Other religious groups include Buddhists (0.7% and mostly of Theravada sect), Christians (0.3% amd mostly of Catholic denomination), and Animists (0.1%). Bangladesh ranks fourth after Indonesia and Pakistan among Muslim majority nations. As India has a higher Muslim population, Bangladesh ranks fourth in this category.
Culture
A new state for an old nation, Bangladesh has a culture that encompasses elements both old and new. The Bengali language boasts a rich literary heritage, which Bangladesh shares with the Indian state of West Bengal. The earliest literary text in Bangla is the eighth century Charyapada. Bangla literature in the medieval age was often either religious (e.g. Chandidas), or adaptations from other languages (e.g. Alaol). Bangla literature matured in the nineteenth century. Its greatest icons are the poets Rabindranath Tagore and Kazi Nazrul Islam. Bangladesh also has a long tradition in folk literature, evidenced by Maimansingha Gitika, Thakurmar Jhuli or stories related to Gopal Bhar.
The musical tradition of Bangladesh is lyrics-based (Baniprodhan), with minimal instrumental accompaniment. The Baul tradition is a unique heritage of Bangla folk music, and there are numerous other musical traditions in Bangladesh, which vary from one region to the other. Gombhira, Bhatiali, Bhawaiya are a few of the better-known musical forms. Folk music of Bengal is often accompanied by the ektara, an instrument with only one string. Other instruments include the dotara, dhol, flute, and tabla. Bangladesh also has an active heritage in North Indian classical music. Similarly, Bangladeshi dance forms draw from folk traditions, especially those of the tribal groups, as well as the broader Indian dance tradition. Bangladesh produces about 80 films a year. Mainstream Hindi films are also quite popular, as are films from Kolkata, which has its own thriving Bengali-language movie industry. Around 200 dailies are published in Bangladesh, along with more than 1800 periodicals. However, regular readership is low, nearly about 15% of the population. Bangladeshis listen to a variety of local and national radio programmes from Bangladesh Betar, as well as Bangla services from the BBC and Voice of America. There is a state-controlled television channel, but in the last few years, privately owned channels have grown considerably.
The culinary tradition of Bangladesh has close relations to Indian and Middle Eastern cuisine as well as having many unique traits. Rice and curry are traditional favourites. Bangladeshis make distinctive sweetmeats from milk products; some common ones are Rôshogolla, Chômchôm and Kalojam.
The sari (shaŗi) is by far the most widely worn dress by Bangladeshi women. However, the salwar kameez (shaloar kamiz) is also quite popular, and in urban areas some women wear Western attire. Among men, European dressing has greater acceptance. Men also use the kurta-paejama combination, often on religious occasions. The lungi, a kind of long skirt, is widely worn by Bangladeshi men.
The two Eids, Eid ul-Fitr and Eid ul-Adha are the largest festivals in the Islamic calendar. The day before Eid ul-Fitr is called Chãd Rat (the night of the Moon), and is often marked by firecrackers. Other Muslim holidays are also observed. Major Hindu festivals are Durga Puja and Saraswati Puja. Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, is one of the most important Buddhist festivals while Christmas, called Bôŗodin (Great day) in Bangla is celebrated by the minority Christian population. The most important secular festival is Pohela Baishakh or Bengali New Year, the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Other festivities include Nobanno, Poush parbon (festival of Poush) and observance of national days like Shohid Dibosh.
Cricket is one of the most popular sports in Bangladesh. In 2000, the Bangladesh cricket team was granted Test cricket status and joined the elite league of national teams permitted by the International Cricket Council to play test matches. Other popular sports include football (soccer), field hockey, tennis, badminton, handball, volleyball, chess, carom, and kabadi, a seven-a-side team-sport played without a ball or any other equipment, which is the national sport of Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Sports Control Board regulates twenty-nine different sporting federations.