Guyana
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Americas; Countries
|
Co-operative Republic of Guyana
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "One people, one nation, one destiny" | ||||||
|
|
||||||
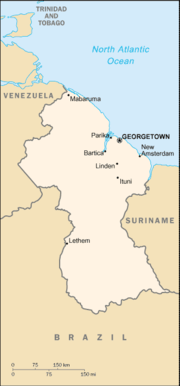
| Capital (and largest city) |
Georgetown |
|||||
| Official languages | English | |||||
| Recognised regional languages | Guyanese Creole, Akawaio, Hindi, Macushi, Wai-Wai, Arawakan, Cariban | |||||
| Demonym | Guyanese | |||||
| Government | Semi-presidential republic | |||||
| - | President | Bharrat Jagdeo | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Sam Hinds | ||||
| Independence | ||||||
| - | from the United Kingdom | May 26, 1966 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 214,970 km² ( 84th) 83,000 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 8.4 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | March 2008 estimate | 751,0001 ( 162nd) | ||||
| - | 2007 census | 769,095 | ||||
| - | Density | 3.5/km² ( 217th) 9.1/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $1.378 billion ( 157th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $4,612 ( 106th) | ||||
| HDI (2007) | ▲ 0.750 (medium) ( 97th) | |||||
| Currency | Guyanese dollar ( GYD) |
|||||
| Time zone | ( UTC-4) | |||||
| Internet TLD | .gy | |||||
| Calling code | +592 | |||||
| 1 | Population includes excess mortality caused by AIDS. Around one-third of the population (230,000) live in the capital, Georgetown. | |||||
Guyana (pronounced /ɡaɪˈænə/ or /ɡuyːˈɑːnə/), officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana and previously known as British Guiana, is the only nation state of the Commonwealth of Nations on the mainland of South America. Bordered to the east by Suriname, to the south and southwest by Brazil and to the west by Venezuela, it is the third-smallest country on the mainland of South America. It is one of four non-Spanish-speaking territories on the continent, along with the countries of Brazil (Portuguese), Suriname (Dutch) and the French overseas region of French Guiana (French). Culturally, Guyana associates primarily with the English-speaking Caribbean countries such as Jamaica, or Trinidad and Tobago.
History
The first Europeans arrived in the area around 1500. Guyana was inhabited by the Arawak and Carib tribes of Amerindians. Although Christopher Columbus sighted Guyana during his third voyage (in 1498), the Dutch were first to establish colonies: Essequibo (1616), Berbice (1627), and Demerara (1752). The British assumed control in the late 18th century, and the Dutch formally ceded the area in 1814. In 1831 the three separate colonies became a single British colony known as British Guiana.
Escaped slaves formed their own settlements known as Maroon communities. With the abolition of slavery in 1834 many of the former enslaved people began to settle in urban areas. Indentured labourers from modern day Portugal (1834), Germany (first in 1835), Ireland (1836), Scotland (1837), Malta (1839), China and India (beginning in 1838) were imported to work on the sugar plantations.
In 1889 Venezuela claimed the land up to the Essequibo. Ten years later an international tribunal ruled the land belonged to British Guiana.
During World War II the United States arranged for its air force to use British airports in South America, including those in British Guiana.
Guyana achieved independence from the United Kingdom in 1966 and became a republic on 23 February 1970, remaining a member of the Commonwealth. The United States State Department and the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), along with the British government, played a strong role in influencing who would politically control Guyana during this time. They provided secret financial support and political campaign advice to pro-western Guyanese of African descent, especially Forbes Burnham's People's National Congress to the detriment of the Cheddi Jagan-led People's Progressive Party, mostly supported by Guyanese of Indian descent, which had ties with the Soviet Union. In 1978, Guyana received considerable international attention when 918 almost entirely American members of the Peoples Temple died in Jonestown, Georgetown and at a Temple attack at a small airstrip which resulted in the murder of five people, including the only Congressman murdered in the line of duty in U.S. history, Leo Ryan.
Geography
Guyana can be divided into four natural regions: a narrow and fertile marshy plain along the Atlantic (low coastal plain) coast where most of the population lives, then a white sand belt more inland (hilly sand and clay region), containing most of Guyana's mineral deposits, the dense rainforests (Forested Highland Region) across the middle of the country, the grassy flat savannah in the south and finally the larger interior highlands (interior savannah) consisting mostly of mountains that gradually rise to the Brazilian border.
Guyana's main mountains are contained here, including Mount Ayanganna (6,699 ft (2,042 m)) and on Mount Roraima (9,301 ft (2,835 m) – the highest mountain in Guyana) on the Brazil-Guyana-Venezuela tripoint, part of the Pakaraima range. Roraima and Guyana's tepuis are said to have been the inspiration for Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 novel The Lost World. There are also many steep escarpments and waterfalls, including the famous Kaieteur Falls. Between the Rupununi River and the border with Brazil lies the Rupununi savannah, south of which lie the Kanuku Mountains.
There are many rivers in the country, the three main ones being (west to east) the Essequibo, the Demerara, and the Berbice. There is also the Corentyne along the border with Suriname. At the mouth of the Essequibo are several large islands. The 90- mile (145 km) Shell Beach along the north-west coasts. Guyana is a major breeding area for sea turtles (mainly Leatherbacks) and other wildlife.
The local climate is tropical and generally hot and humid, though moderated by northeast trade winds along the coast. There are two rainy seasons, the first from May to mid-August, the second from mid-November to mid-January.
Boundary disputes
Guyana was in a border dispute with both Suriname, which claimed the land east of the Corentyne River in southeastern Guyana, and Venezuela which claims the land west of the Essequibo River as part of Guayana Esequiba. The dispute with Suriname was arbitrated by the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea and a ruling in favour of Guyana was announced in September, 2007.
When the British surveyed British Guiana in 1840, they included the entire Cuyuni River basin within the colony. Venezuela did not agree with this as it claimed all lands west of the Essequibo River. In 1898, at Venezuela's request, an international arbitration tribunal was convened and in 1899 they issued an award giving about 94% percent of the disputed territory to British Guiana. Venezuela and Great Britain accepted the award by treaty in 1905, but Venezuela raised the issue again at the time of Guyana's independence, and continues to claim Guayana Esequiba..
Demographics
The present population of Guyana is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, composed chiefly of the descendants of immigrants who came to the country either as enslaved people or as indentured labourers. The population therefore comprises groups of persons with nationality backgrounds from Europe (especially the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Portugal), Africa, China, India, and the Middle East, with the Aboriginal Indians as the indigenous population. These groups of diverse nationality backgrounds have been fused together by a common language, i.e., English and Creole.
The largest nationality sub-group is that of the descendants of India, also known as East Indians (Indo-Guyanese), comprising 43.5 percent of the population in 2002. They are followed by people of African heritage (Afro-Guyanese) (30.2 percent). The third in number are those of mixed heritage (16.7 percent), while the Aboriginal Indians are fourth with 9.2 percent. The smallest groups are European, including Portuguese, (0.06 percent or 476 persons) and the Chinese (0.19 percent or 1395). A small group (0.01 percent or 112 persons) did not identify their race/ethnic background.
The population distribution in 2002 was determined by nationality background. The distribution pattern has been similar to those of the 1980 and 1991 censuses, but the share of the two main groups has declined. The East Indians were 51.9 percent of the total population in 1980, but by 1991 had fallen to 48.6 percent, and then 43.5 percent in 2002 census. Those of African descent increased slightly from 30.8 to 32.3 percent during the first period (1980 and 1991) before falling to 30.2 percent in the 2002 census. With small growth in the population, the decline in the shares of the two larger groups has resulted in the relative shares of the ‘Mixed’ and Amerindian groups. The Amerindian population rose by 22,097 persons between 1991 and 2002. This represents an increase of 47.3 percent or annual growth of 3.5 percent. Similarly, the ‘Mixed’ population increased by 37,788 persons, representing a 43.0 percent increase or annual growth rate of 3.2 percent from the base period of 1991 census. The whites and Chinese populations which declined between 1980 and 1991 regained in numbers by the 2002 census by 54.4 percent (168 persons) and 8.1 percent (105 persons) respectively. However, because of their relatively small sizes, the increase has effectively a zero effect on the overall change. The Portuguese group has declined constantly over the decades.
Languages
English is the official language of Guyana. In addition, Amerindian languages are spoken by a small minority, while Guyanese Creole (an English-based creole with African and Indian syntax) is widely spoken. Grammar is not standardized.
In addition to English, other languages of Guyana include Guyanese Creole, Akawaio, Wai-Wai, Arawak and Macushi.
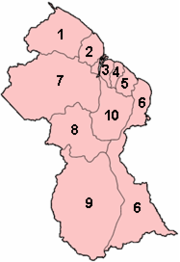
Regions and neighbourhood councils
Guyana is divided into 10 regions:
| No | Region | Area km² | Population | Population per km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barima-Waini | 20 339 | 24 275 | 1,2 |
| 2 | Pomeroon-Supenaam | 6 195 | 49 253 | 8,0 |
| 3 | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 3 755 | 103 061 | 27,5 |
| 4 | Demerara-Mahaica | 2 232 | 310 320 | 139,0 |
| 5 | Mahaica-Berbice | 4 190 | 52 428 | 12,5 |
| 6 | East Berbice-Corentyne | 36 234 | 123 695 | 3,4 |
| 7 | Cuyuni-Mazaruni | 47 213 | 17 597 | 0,4 |
| 8 | Potaro-Siparuni | 20 051 | 10 095 | 0,5 |
| 9 | Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo | 57 750 | 19 387 | 0,3 |
| 10 | Upper Demerara-Berbice | 17 040 | 41 112 | 2,4 |
| Guyana | 214 999 | 751 223 | 3,5 |
The regions are divided into 27 neighbourhood councils.
Politics
Politics of Guyana takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Guyana is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly of Guyana. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The 2006 national elections were the first peaceful elections in recent times. The elections were free and fair and were a welcome departure from the turmoil of previous elections.
Historically, politics is a source of tension in the country and violent riots have often broken out during elections. During the 1970s and 1980s, the political landscape was dominated by the People's National Congress, who retained their power by skewing election results. In 1992, the first "free and fair" elections were overseen by former American president Jimmy Carter, and the People's Progressive Party has led the country since. The two parties are principally organized along ethnic lines and as a result often clash on issues related to the allocation of resources.
Economy
Guyana's economy depends on agriculture. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labour and a deficient infrastructure. Until recently, the government was juggling a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. Low prices for key mining and agricultural commodities combined with troubles in the bauxite and sugar industries had threatened the government's tenuous fiscal position and dimmed prospects for the future. However, the Guyanese economy has rebounded slightly and exhibited moderate economic growth since 1999, based on an expansion in the agricultural and mining sectors, a more favorable atmosphere for business initiatives, a more realistic exchange rate, fairly low inflation, and the continued support of international organizations. Exports of Guyana include rice, sugar, molasses, bauxite, gold, furniture, electrical and household appliances, alcoholic beverages, chemicals and pharmeceuticals, wood, wood products, processed food, spices, fish, fruits, vegetables, hides, skins, leather and leather products, flowers and plants, textiles, yarns, fabrics, gold jewelry, toys and games, travel goods, stationery, paper products, ceramics, handicrafts, wildlife, packaged foods, and tobacco.
The main economic activities in Guyana are agriculture (producing rice and Demerara sugar), bauxite mining, gold mining, timber, shrimp fishing and minerals. The sugar industry, which accounts for 28% of all export earnings, is largely run by Guysuco, which employs more people than any other industry. Many industries have a large foreign investment. The mineral industry, for example, is heavily invested in by the American company Reynolds Metals, the Canadian Alcan and the Korean/Malaysian Barama Company has a large stake in the logging industry.
The production of balatá (natural latex) was once big business in Guyana. Most of the balata bleeding in Guyana took place in the foothills of the Kanuku Mountains in the Rupununi. Early exploitation also took place in the North West District, but most of the trees in the area were destroyed by illicit bleeding methods that involved cutting down the trees rather than making incisions in them.
Folk uses of balatá included the making of homegrown cricket balls, the temporarily filling of troublesome tooth cavities, and the crafting of figurines and other decorative items (particularly by the Macushi people of the Kanuku mountains).
Major private sector organizations include the Private Sector Commission (PSC) and the Georgetown Chamber of Commerce & Industry (GCCI); See a list of companies in Guyana.
In addition, the government initiated a major overhaul of the tax code with the start of 2007. The Value Added Tax (VAT) was brought into effect, replacing six different taxes. Prior to the implementation of the VAT it had been relatively easy to evade sales tax and many businesses were in violation of tax code. Many businesses were very opposed to VAT introduction because of the extra paperwork required; however, the Government has remained firm on the VAT. By replacing several taxes with one flat tax rate, it will also be easier for government auditors to spot embezzlement. While the adjustment to VAT has been a tough one, it may improve day-to-day life because of the significant additional funds the government will have available for public spending.
President Bharrat Jagdeo has made debt relief a foremost priority of his administration. He has been quite successful, getting US$800 million8 of debt written off by the IMF, the World Bank and the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), in addition to millions more from other industrial nations. Mr.Jagdeo was lauded by IDB President Moreno for his strong leadership and negotiating skills in pursuing debt relief for Guyana and several other regional countries.
Summary
|
|
|
Communications
- Telephones
- 110,100 main lines ( ITU, 2005)
400,000 mobile cellular (2007) - Radio broadcast stations
- 1 (government-owned, broadcasting on AM, FM, and shortwave)
- Television broadcast stations
- 21 (in 2007; one government-owned station; the rest are private stations which relay a variety of American programmes via satellite services)
- Internet hosts
- 3,000 (ITU, 2006)
- Internet users
- 160,000 (ITU, 2005)
Transport
- Railways
- Total 116 miles (187 km), all dedicated to ore transport (2001 estimate)
- Highways
- Total 4,952 miles (7,970 km), of which 367 miles (590 km) paved and 4,586 miles (7,380 km) unpaved (1999 estimate)
- Waterways
- 669 miles (1,077 km)
- Ports and harbors
- Georgetown, Port Kaituma
- Airports
- 1 international airport ( Cheddi Jagan International Airport, Timehri); 1 regional int'l airport ( Ogle Airport); and about 90 airstrips, 9 of which have paved runways (2006 estimate).
Culture
| Date | Name |
|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day |
| February 23 | Mashramani-Republic Day |
| variable | Phagwah |
| variable | Eid-ul-Fitr |
| variable | Youm Un Nabi |
| variable | Good Friday |
| variable | Easter Monday |
| May 1 | Labour Day |
| May 5 | Indian Arrival Day |
| May 26 | Independence Day |
| First Monday in July | CARICOM Day |
| August 1 | Emancipation Day |
| variable | Diwali |
| December 25 | Christmas |
| December 26 or 27 | Boxing Day |
Guyana, along with Suriname, French Guiana, and Brazil, is one of the four non-Hispanic nations in South America. Guyana's culture is very similar to that of the English-speaking Caribbean, to the extent that Guyana is included and accepted as a Caribbean nation and is a founding member of the Caricom (Caribbean Community) economic bloc and also the home of the Bloc's Headquarters, the CARICOM Secretariat. Its geographical location, its sparsely populated rain forest regions, and its substantial Amerindian population differentiate it from English-speaking Caribbean countries. Its blend of Indo-Guyanese (East Indian) and Afro-Guyanese (African) cultures gives it similarities to Trinidad and distinguishes it from other parts of the Americas. Guyana shares similar interests with the islands in the West Indies, such as food, festive events, music, sports, etc. Guyana plays international cricket as a part of the West Indies cricket team, and the Guyana team plays first class cricket against other nations of the Caribbean. In addition to its CARICOM membership, Guyana is a member of CONCACAF, the international football federation for North and Central America and the Caribbean. Another aspect of Guyanese culture is its rich folklore about Jumbees.
Religion
According to the 2002 Census, Guyana's religions breakdown is 28.4% Hindu, 16.9% Pentecostal, 8.1% Roman Catholic, 7.3% Muslim, 6.9% Anglican, 3% Seventh-day Adventist, 16.5% other Christian denominations, 4.3% no religion, 0.5% Rastafarian, 0.1% Bahá'í, and 2.2% other faiths. Most Guyanese Christians are either Protestants or Roman Catholics and include a mix of all races. Hinduism is dominated by the Indians who came to the country in the early 1800s, while Islam varies between the Afro-Guyanese, and Indian-Guyanese.
Events
Mashramani (Mash) · Phagwah ( Holi) · Deepavali (Diwali)
Education
Guyana's educational system was at one time considered to be among the best in the Caribbean, but it significantly deteriorated in the 1980s because of the emigration of highly educated citizens and the lack of appropriate funding. Although the education system has recovered somewhat in the 1990s, it still does not produce the quality of educated students necessary for Guyana to modernize its workforce. The country lacks a critical mass of expertise in many of the disciplines and activities on which it depends.
The educational system does not sufficiently focus on the training of Guyanese in science and technology, technical and vocational subjects, business management, nor computer sciences. The Guyanese education system is modeled after the former British education system. Students are expected to write SSEE (secondary school entrance exam) by grade 6 for entrance into High School in grade 7. They write CXC at the end of high school. Recently they have introduced the CAPE exams which all other Caribbean countries have now introduced. The A-level system left over from the British era has all but disappeared and is now offered only in a few schools (current as at January 2007). The reason for the insufficient focus or various disciplines can be directly attributed to the common choices made by students to specialize in areas that are similar (math/chemistry/physics or geography/history/economics). With the removal of the old A-level system that encouraged this specialization, it is thought that it will be more attractive for students to broaden their studies.
There are wide disparities among the geographical regions of the country in the availability of quality education, and the physical facilities which are provided are in poor condition.
Further adding to the problems of the educational system, many of the better-educated professional teachers have emigrated to other countries over the past two decades, mainly because of low pay, lack of opportunities and crime. As a result, there is a lack of trained teachers at every level of Guyana's educational system.
There are however several very good Private schools that have sprung up over the last fifteen years. Those schools offer a varied and balanced curriculum.
Public health
Service delivery
The delivery of health services is provided at five different levels in the public sector:
- Level I: Local Health Posts (166 in total) that provide preventive and simple curative care for common diseases and attempt to promote proper health practices. Community health workers staff them.
- Level II: Health Centres (109 in total) that provide preventive and rehabilitative care and promotion activities. These are ideally staffed with a medical extension worker or public health nurse, along with a nursing assistant, a dental nurse and a midwife.
- Level III: Nineteen District Hospitals (with 473 beds) that provide basic in-patient and outpatient care (although more the latter than the former) and selected diagnostic services. They are also meant to be equipped to provide simple radiological and laboratory services, and to be capable of gynecology, providing preventive and curative dental care. They are designed to serve geographical areas with populations of 10,000 or more.
- Level IV: Four Regional Hospitals (with 620 beds) that provide emergency services, routine surgery and obstetrical and gynecological care, dental services, diagnostic services and specialist services in general medicine and pediatrics. They are designed to include the necessary support for this level of medical service in terms of laboratory and X-ray facilities, pharmacies and dietetic expertise. These hospitals are located in Regions 2, 3, 6 and 10.
- Level V: The National Referral Hospital (937 beds) in Georgetown that provides a wider range of diagnostic and specialist services, on both an in-patient and out-patient basis; the Psychiatric Hospital in Canje; and the Geriatric Hospital in Georgetown. There is also one children’s rehabilitation centre.
This system is structured so that its proper functioning depends intimately on a process of referrals. Except for serious emergencies, patients are to be seen first at the lower levels, and those with problems that cannot be treated at those levels are referred to higher levels in the system. However, in practice, many patients by-pass the lower levels.
The health sector is currently unable to offer certain sophisticated tertiary services and specialized medical services, the technology for which is unaffordable in Guyana, or for which the required medical specialists simply do not exist. Even with substantial improvements in the health sector, the need for overseas treatment for some services might remain. The Ministry of Health provides financial assistance to patients requiring such treatment, priority being given to children whose condition can be rehabilitated with significant improvements to their quality of life.
In addition to the facilities mentioned above, there are 10 hospitals belonging to the private sector and to public corporations, plus diagnostic facilities, clinics and dispensaries in those sectors. These ten hospitals together, provide for 548 beds.
Eighteen clinics and dispensaries are owned by GUYSUCO.
The Ministry of Health and Labour is responsible for the funding of the National Referral Hospital in Georgetown, which has recently been made a public corporation managed by an independent Board. Region 6 is responsible for the management of the National Psychiatric Hospital. The Geriatric Hospital, previously administered by the Ministry of Labour, became the responsibility of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security in December 1997.
Health conditions
One of the most unfortunate consequences of Guyana's economic decline in the 1970s and 1980s was that it led to very poor health conditions for a large part of the population. Basic health services in the interior are primitive to non-existent and some procedures are not available at all. The U.S. State Department Consular Information Sheet warns "Medical care is available for minor medical conditions. Emergency care and hospitalization for major medical illnesses or surgery is limited, because of a lack of appropriately trained specialists, below standard in-hospital care, and poor sanitation. Ambulance service is substandard and may not routinely be available for emergencies." Many Guyanese seek medical care in the United States, Trinidad or Cuba.
Compared with other neighboring countries, Guyana ranks poorly in regard to basic health indicators. In 1998, life expectancy at birth was estimated at 66.0 years for Guyana, 71.6 for Suriname, 72.9 for Venezuela; 73.8 for Trinidad and Tobago, 74.7 for Jamaica, and 76.5 for Barbados. In Guyana, the infant mortality rate in 1998 was 24.2, in Barbados 14.9; in Trinidad and Tobago 16.2; in Venezuela 22; in Jamaica 24.5; and in Suriname 25.1.
Maternal mortality rates in Guyana are also relatively high, being estimated at 124.6/1000 for 1998. Comparable figures for other Caribbean countries are 50/1000 for Barbados, 75/1000 for Trinidad and 100/1000 for Jamaica.
It must be emphasized, however, that although Guyana's health profile still falls short in comparison with many of its Caribbean neighbours, there has been remarkable progress since 1988, and the Ministry of Health is constantly upgrading conditions, procedures, and facilities. Open heart surgery is now available in the country, and in the second half of 2007 an ophthalmic centre will open.
The leading causes of mortality for all age groups are cerebrovascular diseases (11.6%); ischemic heart disease (9.9%); immunity disorders (7.1%); diseases of the respiratory system (6.8%); diseases of pulmonary circulation and other forms of heart disease (6.6%); endocrine and metabolic diseases (5.5%); diseases of other parts of the Digestive System (5.2%); violence (5.1%); certain condition originating in the prenatal period (4.3%); and hypertensive diseases (3.9%).
The picture in regard to morbidity patterns differs. The ten leading causes of morbidity for all age groups are, in decreasing order: malaria; acute respiratory infections; symptoms, signs and ill defined or unknown conditions; hypertension; accident and injuries; acute diarrhoeal disease; diabetes mellitus; worm infestation; rheumatic arthritis; and mental and nervous disorders.
This morbidity profile indicates that it can be improved substantially through enhanced preventive health care, better education on health issues, more widespread access to potable water and sanitation services, and increased access to basic health care of good quality.
Guyana also suffers from the highest suicide rate of any South America country. The Guyana Health Minister, Leslie Ramsammy, estimates that at least 200 people commit suicide each year in Guyana, or 27.2 people for each 100,000 people each year.
Environment and biodiversity
Guyana abounds with plant and animal life. Each region boasts unique species.
The following habitats have been categorized for Guyana: coastal, marine, littoral, estuarine palustrine, mangrove, riverine, lacustrine, swamp, savannah, white sand forest, brown sand forest, montane, cloud forest, moist lowland and dry evergreen scrub forests (NBAP, 1999). About 14 areas of biological interest have been identified as possible hotspots for a National Protected Area System.
More than 80% of Guyana is still covered by forests, ranging from dry evergreen and seasonal forests to montane and lowland evergreen rain forests. These forests are home to more than a thousand species of trees. Guyana's tropical climate, unique geology, and relatively pristine ecosystems support extensive areas of species-rich rain forests and natural habitats with high levels of endemism. Approximately eight thousand species of plants occur in Guyana, half of which are found nowhere else.
Guyana is one of the countries with the highest biodiversity in the world. Guyana, with 1,168 vertebrate species, 1600 bird species, boasts one of the richest mammalian fauna assemblages of any comparably sized area in the world.
The Guiana Shield region is little known and extremely rich biologically. Unlike other areas of South America, over 70% of the natural habitat remains pristine.
The rich natural history of British Guiana was described by early explorers Sir Walter Raleigh and Charles Waterton and later by naturalists Sir David Attenborough and Gerald Durrell.
Ecology and World Heritage Site status
Countries interested in the conservation and protection of natural and cultural heritage sites of the world accede to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage that was adopted by UNESCO in 1972. Guyana is no exception, and signed the treaty in 1977. In fact, Guyana was the first Caribbean State Party to sign the treaty. Sometime in the latter half of the mid-1990s, Guyana seriously began the process of selecting sites for World Heritage nomination and three sites were considered: Kaieteur National Park, Shell Beach and Historic Georgetown. By 1997, work on Kaieteur National Park was started and in 1998 work on Historic Georgetown was begun. To date, however, Guyana has not made a successful nomination.
In 2000, Guyana submitted the Kaieteur National Park, including the Kaieteur Falls, to UNESCO as its first World Heritage Site nomination. The proposed area and surrounds have some of Guyana's most diversified life zones with one of the highest levels of endemic species found anywhere in South America. The Kaieteur Falls is the most spectacular feature of the park falling a distance of 226 m and exceeding the height of Niagara Falls (USA/Canada) five times. Unfortunately, the nomination of Kaieteur Park as a World Heritage Site was not successful, primarily because the area was seen by the evaluators as being too small, especially when compared with the Central Suriname Nature Reserve that had just been nominated as a World Heritage Site (2000). The dossier was thus returned to Guyana for revision.
Guyana continues in its bid for a World Heritage Site. Work continues, after a period of hiatus, on the nomination dossier for Historic Georgetown. A Tentative List indicating an intention to nominate Historic Georgetown was submitted to UNESCO in December 2004. There is now a small committee put together by the Guyana National Commission for UNESCO to complete the nomination dossier and the management plan for the site. Recently, in April 2005, two Dutch experts in conservation spent two weeks in Georgetown supervising architecture staff and students of the University of Guyana in a historic building survey of the selected area. This is part of the data collection for the nomination dossier.
Meanwhile, as a result of the Kaieteur National Park being considered too small, there is a proposal to prepare a nomination for a Cluster Site that will include the Kaieteur National Park, the Iwokrama Forest and the Kanuku Mountains. The Iwokrama Rain Forest, an area rich in biological diversity, has been described by Major General (Retired) Joseph Singh as “a flagship project for conservation.” The Kanuku Mountains area is in a pristine state, and is home to more than four hundred species of birds and other animals.
There is much work to be done for the successful nomination of these sites to the World Heritage List. The State, the private sector and the ordinary Guyanese citizens each have a role to play in this process and in the later protection of the sites. Inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage will open Guyana to more serious tourists thereby assisting in its economic development.
Guyana exhibits two of the World Wildlife Fund's Global 200 eco-regions most crucial to the conservation of global biodiversity, Guianan moist forests and Guyana Highlands moist forests and is home to several endemic species including the tropical hardwood Greenheart (Chlorocardium rodiei).
Landmarks
- St. George's Anglican Cathedral
- One of the tallest wooden structures in the world, and the second tallest wooden church after the Todaiji Temple in Japan.
- Demerara Harbour Bridge
- The world's fourth-longest floating bridge (formerly the longest).
- Kaieteur Falls
- One of the most spectacular waterfalls in the world.
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM) Building
- Houses the largest and most powerful political union in the Caribbean.
- Providence Stadium
- Situated in Providence on the east bank of the Demerara River and built in time for the ICC World Cup 2007, it is the largest sports stadium in the country. It is also near the Providence Mall, forming a major spot for leisure in Guyana.
- Guyana International Conference Centre
- Presented as a gift from the People's Republic of China to the Government of Guyana. It is the only one of its kind in the country.
- Stabroek Market
- A large cast-iron colonial structure that looked like a statue was located next to the Demerara River.
- The City Hall
- A beautiful wooden structure also from the colonial era.
- Queen's College
- Top educational institution in Guyana
Military
- Forces
- Guyana Defence Force (GDF; includes Ground Forces, Coast Guard, and Air Corps) · Guyana People's Militia (now Defunct);(GPM) · Guyana National Service (now defunct);(GNS) · Guyana Police Force
- Available manpower
- 206,199 males aged 15 to 49, of which 155,058 are fit for service (2002 estimates)