Wildcat
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Mammals
| Wildcat | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 European Wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris)
|
||||||||||||||
| Conservation status | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Felis silvestris Schreber, 1775 |
||||||||||||||
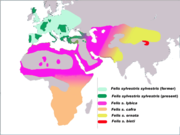 The five subspecies of Felis silvestris according to a 2007 DNA study.
|
||||||||||||||
| subspecies | ||||||||||||||
|
See text |
The Wildcat (Felis silvestris), sometimes Wild Cat or Wild-cat, is a small felid native to Europe, the western part of Asia, and Africa. It is a hunter of small mammals, birds, and other creatures of a similar size. There are several subspecies distributed in different regions. Sometimes included is the ubiquitous domestic cat (Felis silvestris catus), which has been introduced to every habitable continent and most of the world's larger islands, and has become feral in many of those environments.
In its native environment, the Wildcat is adaptable to a variety of habitat types: savanna, open forest, and steppe. Although domesticated breeds show a great variety of shapes and colours, wild individuals are medium-brown with black stripes, between 45 and 80 cm (18–32 inches) in length, and weigh between 3 and 8 kilograms (6–17.6 pounds). Shoulder height averages about 35 cm (14 in) and tail length is about 30 cm (12 in). The African subspecies tends to be a little smaller and a lighter brown in colour.
The Wildcat is extremely timid. It avoids approaching human settlements. It lives solitarily and holds a territory of about 3 km².
A study by the National Cancer Institute suggests that all current house cats in the world are descendants from a group of self-domesticating Wildcats 10,000 years ago, somewhere in the Near East. The closest relative of the Wildcat is the Sand Cat (Felis margarita).
Diet
It is an obligate carnivore, like all felines, and consumes almost every part of any kill it makes; the coat providing roughage, the bones calcium, and the meat everything else, in fact they rarely need to drink because meat has such a high water content. The Wildcat often carries parasitic worms in its gut and will eat long blades of grass to help clear out its system and probably also to obtain certain necessary acids not present in meat.
Subspecies
According to the 2007 DNA analysis, there are only 5 subspecies:
- Felis silvestris silvestris (Europe and Turkey).
- Felis silvestris lybica (North Africa, Middle East and Western Asia, to the Aral Sea).
- Felis silvestris cafra (Southern Africa).
- Felis silvestris ornata (Pakistan, north east of India, Mongolia and northern China).
- Felis silvestris bieti (China).
Older texts separated out many more subspecies:
- African subspecies
- Felis silvestris cafra (Southern Africa)
- Felis silvestris foxi ( West Africa)
- Felis silvestris griselda ( Central Africa)
- Felis silvestris lybica African wildcat (North Africa)
- Felis silvestris ocreata (East Central Africa)
- Felis silvestris mellandi (West Central Africa)
- Asian subspecies
- Felis silvestris caudata (Caspian Sea area)
- Felis silvestris ornata Indian desert cat (India to Iran)
- Felis silvestris bieti Chinese mountain cat (possible subspecies)
- European subspecies
- Felis silvestris cretensis ( Crete) (extinct, though some sightings have been reported).
- Felis silvestris caucasica Caucasian wildcat ( Caucasus Mountains and Turkey)
- Felis silvestris grampia Scottish wildcat (northern and western Scotland)
- Felis silvestris jordansi Balearic wildcat ( Balearic Islands)
- Felis silvestris reyi Corsican wildcat ( Corsica) (Possibly Extinct)
- Felis silvestris silvestris European wildcat (Europe)
- Unknown distribution:
- Felis silvestris chutuchta
- Felis silvestris gordoni
- Felis silvestris haussa
- Felis silvestris iraki
- Felis silvestris nesterovi
- Felis silvestris rubida
- Felis silvestris tristrami
- Felis silvestris ugandae
- Felis silvestris vellerosa