Area
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Mathematics
Area is a quantity expressing the two- dimensional size of a defined part of a surface, typically a region bounded by a closed curve. The term surface area refers to the total area of the exposed surface of a 3-dimensional solid, such as the sum of the areas of the exposed sides of a polyhedron.
Units
Units for measuring surface area include:
- Metric
- square metre (m²) = SI derived unit
- are (a) = 100 square metres (m²)
- hectare (ha) = 10,000 square metres (m²)
- square kilometre (km²) = 1,000,000 square metres (m²)
- square megametre (Mm²) = 1012 square metres (m²)
- are (a) = 100 square metres (m²)
- US & Imperial Units
- square foot = 144 square inches = 0.09290304 square metres (m²)
- square yard = 9 square feet = 0.83612736 square metres (m²)
- square perch = 30.25 square yards = 25.2928526 square metres (m²)
- acre = 160 square perches or 4,840 square yards or 43,560 square feet = 4046.8564224 square metres (m²)
- square mile = 640 acres = 2.5899881103 square kilometres (km²)
- square yard = 9 square feet = 0.83612736 square metres (m²)
- square metre (m²) = SI derived unit
Useful formulas
| Shape | Equation | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Square | 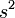 |
s is the length of the side of the square. |
| Regular triangle | 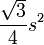 |
s is the length of one side of the triangle. |
| Regular hexagon | 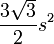 |
s is the length of one side of the hexagon. |
| Regular octagon | 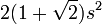 |
s is the length of one side of the octagon. |
| Any regular polygon | 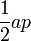 |
a is the apothem, or the radius of an inscribed circle in the polygon, and p is the perimeter of the polygon. |
| Any regular polygon | 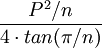 |
P is the Perimeter and n is the number of sides. |
| Any regular polygon (using degree measure) | 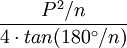 |
P is the Perimeter and n is the number of sides. |
| Rectangle | 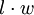 |
l and w are the lengths of the rectangle's sides (length and width). |
| Parallelogram (in general) | 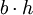 |
b and h are the length of the base and the length of the perpendicular height, respectively. |
| Rhombus | 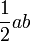 |
a and b are the lengths of the two diagonals of the rhombus. |
| Triangle | 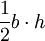 |
b and h are the base and altitude (measured perpendicular to the base), respectively. |
| Triangle | 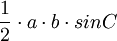 |
a and b are any two sides, and C is the angle between them. |
| Circle | 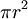 , or , or 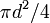 |
r is the radius and d the diameter. |
| Ellipse | 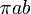 |
a and b are the semi-major and semi-minor axes, respectively. |
| Trapezoid | 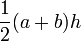 |
a and b are the parallel sides and h the distance (height) between the parallels. |
| Total surface area of a Cylinder | 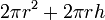 |
r and h are the radius and height, respectively. |
| Lateral surface area of a cylinder | 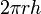 |
r and h are the radius and height, respectively. |
| Total surface area of a Cone | 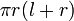 |
r and l are the radius and slant height, respectively. |
| Lateral surface area of a cone | 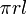 |
r and l are the radius and slant height, respectively. |
| Total surface area of a Sphere | 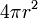 or or 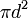 |
r and d are the radius and diameter, respectively. |
| Total surface area of an ellipsoid | See the article. | |
| Circular sector | 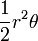 |
r and θ are the radius and angle (in radians), respectively. |
| Square to circular area conversion | 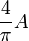 |
A is the area of the square in square units. |
| Circular to square area conversion | 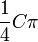 |
C is the area of the circle in circular units. |
All of the above calculations show how to find the area of many shapes.