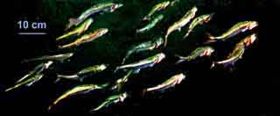
Atlantic herring
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Insects, Reptiles and Fish
| Atlantic herring | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Clupea harengus Linnaeus, 1758 |
Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) is the one of the most abundant species of fish on the planet. They can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean congregating together in large schools (or swarms). They can grow up to 45 centimeters (approximately 18 inches) in length and weigh more than half a kilogram. They feed on copepods, krill and small fish, and their natural predators are seals, whales, cod and other larger fish.
The Atlantic herring fishery has long been an important part of the economy of New England and the Canadian Maritime provinces. This is because the fish congregate relatively near to the coast in massive schools, notably in the cold waters of the semi-enclosed Gulf of Maine and Gulf of St. Lawrence. North Atlantic herring schools have been measured up to 4 cubic kilometers in size, containing an estimated 4 billion fish.
Morphology
Atlantic herring have a fusiform body. Gill rakers are present in their mouths to filter incoming water, trapping any zooplankton, or phytoplankton.
Ecological importance
Herring-like fish are the most important fish group on the planet, Clupea harengus the most frequent fish ( Guinness Book of Records). They are the dominant converter of the enormous production of zooplankton, utilizing the biomass of copepods, mysids and krill in the pelagic zone. They are on the other side a central prey item for higher trophic levels. The reasons for its success is still enigmatic; one speculation is attributing their dominance to the outstanding way of living in huge, extremely fast cruising schools.
Geographical distribution
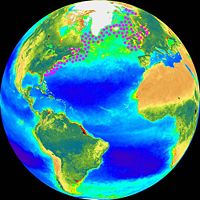
Atlantic herring can be found on both sides of the Atlantic ocean. they have an extensive range that covers the North Atlantic waters such as the Gulf of Maine, the Gulf of St Lawrence, the Bay of Fundy, the Labrador Sea, the Davis Straits, the Beaufort Sea, the Denmark Straits, the Norwegian Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea (a sub-species known as strömming in Swedish), the English Channel, the Celtic Sea the Irish Sea, and the Bay of Biscay. Although Atlantic herring are found in the northern waters surrounding the Arctic they are however, not considered to be an Arctic species.
Biological specialities
Herring are amongst the most spectacular schoolers (" obligate schooler" under the old definitions), they aggregate together in groups that consist of thousands to hundreds of thousands of individuals these schools traverse the open oceans. A school of herring in general has a very precise arrangement thus allowing the school to maintain a relatively constant cruising speed. Schools that are made up of an individual stock generally travel in a triangular pattern between their spawning grounds e.g. Southern Norway, their feeding grounds (Iceland) and also their nursery grounds (Northern Norway). Such wide triangular journeys are probably important because herring feast efficiently on their own offspring. A school of herring can react very quickly to evade predators; they have excellent hearing. Around SCUBA divers and ROVs they can form a vacuole ("fountain effect"). The phenomenon of schooling is however, far from understood, especially the implications on swimming and feeding-energetics. Many hypotheses have been put forward to explain the function of schooling, such as predator confusion, reduced risk of being found, better orientation, and synchronized hunting. However, schooling can also have some disadvantages such as: oxygen- and food-depletion, excretion buildup in the breathing media. The school-array probably gives advantages in energy saving although this is a highly controversial and much debated field.
Schools of herring can on calm days sometimes be detected at the surface from more than a mile away by the little waves they form, or from a few meters at night when they trigger the bioluminescence of surrounding plankton ("firing"). All underwater recordings show herring constantly cruising with high speeds up to 108 cm per second, and much higher escape speeds.
Habitat requirements
Atlantic herring are in general very tender and fragile fish. They have extraordinarly large and delicate gill surfaces, and upon contact with foreign matter they can lose their large scales. They have retreated from many of the estuaries worldwide due to high pollution content within the water although in some of the estuaries that have been cleaned up herring have been observed returning. The appearance of their larvae is used as bioindicator for cleaner and better oxygenated waters.
Because of their feeding habits, cruising desire, collective behaviour and fragility they are only on display in very few aquaria worldwide, this despite their natural abundance in the ocean. Even with the best facilities that these aquaria can offer they appear slim and slow compared to a quivering school in the wild.
Predators
Orca, cod, dolphins, porpoises, sharks, Rockfish, seabird, Whale, squid, Sea Lion, Seal
Life history
There is at least one herring stock spawning in any one month of the year, each race having a different spawning time and place (spring, summer, autumn and winter herrings) in 0 to 5 m off Greenland down to 200 m in autumn (bank) herrings of the North Sea. Eggs are laid on the sea bed, on rock, stones, gravel, sand or beds of algae. "...the fish were darting rapidly about, and those who have opportunity to see the fish spawning in more shallow water ... state that both males and females are in constant motion, rubbing against one another and upon the bottom, apparently by pressure aiding in the discharge of the eggs and milt" (Moore at Cross Island, Maine).
A female herring may deposit from 20,000 up to 40,000 eggs, according to her age and size, averaging about 30000. In sexually mature herrings, the genital organs are so large just before spawning commences that they make up about one-fifth of the total weight of the fish.
The eggs sink to the bottom, where they stick in layers or clumps to gravel, seaweeds or stones, by means of their coating mucus, or to any other objects on which they chance to settle.
If the layers get too thick they suffer from oxygen depletion and often die, entangled in a maze of fucus. They need a fair amount of water microturbulence, generally provided by wave action or coastal currents. Survival is highest in crevices and behind solid structures, because many predators feast on openly disposed eggs. The individual eggs are 1 to 1.4 mm in diameter, depending on the size of the parent fish and also on the local race. Incubation time is about 40 days at 3°C (38 F), 15 days at 7°C (45 F), 11 days at 10°C (50 F), they die at temperatures above 19°C (68 F).
The larvae are 5 to 6 mm long at hatching, with a small yolk sac that is absorbed by the time a length of 10 mm is reached. Only the eyes are well pigmented (a camera works only with a black housing) the rest of the body is as transparent as possible, and virtually invisible under water and natural luminance conditions.
The dorsal fin is formed at 15 to 17 mm, the anal fin at about 30 mm - the ventral fins are visible and the tail becomes well forked at 30 to 35 mm - at about 40 mm the little fish begins to look like a herring.
Larvae diagnostics: The larvae of the herring family are very slender and can easily be distinguished from all other young fish of their distribution range of similar form by the location of the vent, which is so far back that it lies close to the base of the tail. But it requires critical examination to distinguish several clupeoids one from another in their early stages, especially herring from sprats.
At the age of one year they are about 100 mm long, first spawning at 3 years.
Schooling
Atlantic herring are world famous for their huge schools, often numbering in the hundreds of thousands or even millions. One recorded enormous school covered 4 km² in area and reportedly had more than 4 billion fish.

Feeding


Herring is a pelagic feeder - their prey consists of copepods, amphipods, larval snails, diatoms (only herring larvae below 20 mm), peridinians, molluscan larvae, fish eggs, euphausids, mysids, small fishes, herring larvae, menhaden larvae, pteropods, annelids, tintinnids (only herring larvae below 45 mm), Haplosphaera, Calanus, Pseudocalanus, Acartia, Hyperia, Centropages, Temora, Meganyctiphanes norvegica.
Young herring capture copepods predominantly individually ("particulate feeding" or "raptorial feeding") (Kils 1992), a feeding method also used by adult herring on large prey items like euphausids.
If prey concentrations reach very high levels, as in microlayers, at fronts or directly below the surface, herring ram forwards with wide open mouth and far expanded opercula over several feet, then closing and cleaning the gill rakers for a few milliseconds ("sift feeding" or "filter feeding").