Drum kit
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Musical Instruments
| The drum kit |
|
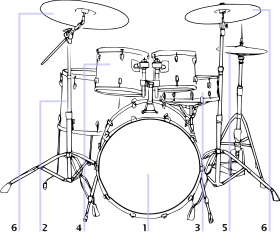
1 Bass drum | 2 Floor tom | 3 Snare 4 Toms | 5 Hi-hat | 6 Crash cymbal and Ride cymbal |
| Other components |
|
China cymbal | Splash cymbal | Sizzle cymbal |
A drum kit (or drum set or trap set) is a collection of drums, cymbals and sometimes other percussion instruments, such as a cowbell, wood block, chimes or tambourines, arranged for convenient playing by a single drummer.
The individual instruments of a drum kit are struck by a variety of implements held in the hand, including sticks, brushes, and mallets. Two notable exceptions include the bass drum, played by a foot-operated pedal, and the hi hat cymbals, which use a foot pedal in addition to the normal striking motion. Although other instruments can be used on a pedal, it is not common, as the feet are usually occupied by these two. Percussion notation is often used by drummers to signify which drum kit components are to be played.
Differing music styles implement the components of a drum kit in different manners. For example, in most forms of rock music, the bass drum and snare drum are the primary instruments used to create a drum beat. In jazz, however, the ride cymbal and hi hats (or brushed snare drum and hi hats) usually fill this role.
The exact collection of drum kit components depends on factors like musical style, personal preference, financial resources, and transportation options of the drummer. Cymbal, hi-hat, and tom-tom stands, as well as bass drum pedals and drummer thrones, are often referred to as " hardware."
History and development
Drum kits first developed when drummers were encouraged to play as many percussion instruments as possible due to budget and space considerations in theaters. Up until then drums and cymbals were played separately in an orchestral fashion. Initially drummers played the bass and snare drums by hand, then in the 1890s they started experimenting with footpedals to play the bass drum. William F. Ludwig made the bass drum pedal system workable in 1909, paving the way for the modern drum kit.
By World War I drum kits were characterized by very large marching bass drums and many percussion items suspended on and around it, and they became a central part of jazz music. Hi-hat stands appeared around 1926. Metal consoles were developed to hold Chinese tom-toms, with swing out stands for snare drums and cymbals. On top of the console was a "contraptions" (shortened to "trap") tray used to hold whistles, klaxons, and cowbells, thus drum kits were dubbed "trap kits."
By the 1930s Gene Krupa streamlined trap kits down to a basic four piece drum set standard: bass, snare, tom-tom, and floor tom. He also used rim-mounted cymbal holders. In time legs were fitted to larger floor toms, and "consolettes" were devised to hold smaller tom-toms on the bass drum. In the 1940s Louie Bellson pioneered use of two bass drums, or the double bass drum kit. By the 1950s big bands were becoming uneconomical and jazz more obscure, thus rock and roll became the leading music genre. In 1964 drumming became more popular when Ringo Starr of The Beatles played his Ludwig kit on American television.
By the 1980s drummers like Bill Bruford and Neil Peart were adding more drums and cymbals to their kits and using electronic drums. Double bass pedals were developed to play on one bass drum, eliminating the need for a second bass drum. In the 1990s and 2000s, some drummers in popular music and indie music have reverted back to the Gene Krupa style of smaller drum kits.