Pearl
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Everyday life
A pearl is a hard, roundish object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk. Just like the shell of mollusks, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate in minute crystalline form, which has been deposited in concentric layers. The ideal pearl is perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes of pearls ( baroque pearls) occur.
The finest quality pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries, and the word pearl has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, and admirable.
Almost any shelled mollusk can, by natural processes, produce some kind of "pearl" when an irritating microscopic object becomes trapped within the mollusk's mantle folds, but virtually none of these "pearls" are valued as gemstones.
True iridescent pearls, the most desirable pearls, are produced by two groups of molluscan bivalves or clams. One family lives in the sea: the pearl oysters. The other, very different group of bivalves live in freshwater, and these are the river mussels; for example, see the freshwater pearl mussel.
Saltwater pearls can grow in several species of marine pearl oysters in the family Pteriidae. Freshwater pearls grow within certain (but by no means all) species of freshwater mussels in the order Unionida, the families Unionidae and Margaritiferidae. These various species of bivalves are able to make true pearls because they have a thick iridescent inner shell layer which is composed of " mother of pearl" or nacre. The mantle tissue of a living bivalve can create a pearl in the same manner that it creates the pearly inner layer of the shell.
Fine gem-quality saltwater and freshwater pearls can and do sometimes occur completely naturally, but this is rare. Many hundreds of pearl oysters or pearl mussels have to be gathered and opened, and thus killed, in order to find even one pearl, and for many centuries that was the only way pearls were obtained. This was the main reason why pearls fetched such extraordinary prices in the past. In modern times however, almost all the pearls for sale were formed with a good deal of expert intervention from human pearl farmers.
A true pearl is made from layers of nacre, by the same living process as is used in the secretion of the mother of pearl which lines the shell. A "natural pearl" is one that formed without any human intervention at all, in the wild, and is very rare. A "cultured pearl", on the other hand, is one that has been formed on a pearl farm. The great majority of pearls on the market are cultured pearls.
Imitation or fake pearls are also widely sold in inexpensive jewelry, but the quality of the iridescence is usually very poor, and generally speaking, fake pearls are usually quite easy to distinguish from the real thing.
Pearls have been harvested, or more recently cultivated, primarily for use in jewelry, but in the past they were also stitched onto lavish clothing, as worn, for example, by royalty. Pearls have also been crushed and used in cosmetics, medicines, or in paint formulations.
Pearl is considered to be the birthstone for June.
Physical properties
The unique luster of pearls depends upon the reflection, refraction, and diffraction of light from the translucent layers. The thinner and more numerous the layers in the pearl, the finer the luster. The iridescence that pearls display is caused by the overlapping of successive layers, which breaks up light falling on the surface.
Pearls are often white or cream, but the color can vary quite a lot according to the natural colour of the nacre in the various species of mollusk used. Thus pearls can also be black, or various pastel shades. In addition, pearls (especially freshwater pearls) can be dyed yellow, green, blue, brown, pink, purple, or black.
Freshwater and saltwater pearls
Freshwater and saltwater pearls may sometimes look quite similar, but they come from very different sources.
Freshwater pearls form in various species of freshwater mussels, family Unionidae, which live in lakes, rivers, ponds and other bodies of fresh water. These freshwater pearl mussels occur not only in hotter climates, but also in colder more temperate areas such as Scotland: see the freshwater pearl mussel. However, most freshwater cultured pearls sold today come from China.
Saltwater pearls grow within pearl oysters, family Pteriidae, which live in tropical oceans. Saltwater pearl oysters are usually cultivated in protected lagoons. The three main types of saltwater pearls are Akoya, South Sea and Tahitian.
Creation of a pearl
The difference between natural and cultured pearls focuses on whether the pearl was created spontaneously by nature — without human intervention — or with human aid. Pearls are formed inside the shell of certain bivalve mollusks: as a response to an irritant inside its shell, the mollusk creates a pearl to seal off the irritation.
The mantle of the mollusk deposits layers of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in the form of the minerals aragonite or calcite (both crystalline forms of calcium carbonate) held together by an organic horn-like compound called conchiolin. This combination of calcium carbonate and conchiolin is called nacre, or as most know it, mother-of-pearl. The commonly held belief that a grain of sand acts as the irritant is in fact rarely the case. Typical stimuli include organic material, parasites, or even damage that displaces mantle tissue to another part of the animal's body. These small particles or organisms enter the animal when the shell valves are open for feeding or respiration. In cultured pearls, the irritant is typically a cut piece of the mantle epithelium, together with processed shell beads, the combination of which the animal accepts into its body.
Natural pearls
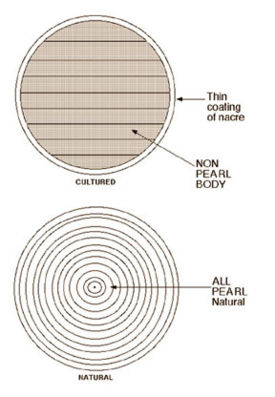
Natural pearls are nearly 100% nacre. It is thought that natural pearls form under a set of accidental conditions when a microscopic intruder or parasite enters a bivalve mollusk, and settles inside the shell. The mollusk, being irritated by the intruder, secretes the calcium carbonate substance called nacre to cover the irritant. This secretion process is repeated many times, thus producing a pearl. Natural pearls come in many shapes, with round ones being comparatively rare.
Cultured pearls
Cultured pearls (nucleated and non-nucleated or tissue nucleated cultured pearls) and imitation pearls can be distinguished from natural pearls by X-ray examination. Nucleated cultured pearls are often 'pre-formed' as they tend to follow the shape of the implanted shell bead nucleus. Once the pre-formed beads are inserted into the oyster, it secretes a few layers of nacre around the outside surface of the implant before it is removed after six months or more. When a nucleated cultured pearl is X-rayed it will reveal a different structure to that of a natural pearl. It exhibits a solid center with no concentric growth rings, compared to a solid centre with growth rings.
Gemological identification
A well equipped gem testing laboratory is able to distinguish natural pearls from cultured pearls by using a gemological x-ray in order to examine the centre of a pearl. With an x-ray it is possible to see the growth rings of the pearl, where the layers of calcium carbonate are separated by thin layers of conchiolin. The differentiation of a natural pearls from or tissue-nucleated cultured pearls can be very difficult without the use of this x-ray technique.
Natural and cultured pearls can be distinguished from imitation pearls using a microscope. Another method of testing for imitations is to rub the pearl against the surface of a front tooth. Imitation pearls are completely smooth, but natural and cultured pearls are composed of nacre platelets, which feel slightly gritty.
Value of a natural pearl
Quality natural pearls are very rare jewels. The actual value of a natural pearl is determined in the same way as it would be for other "precious" gems. The valuation factors include size, shape, quality of surface, orientation, and luster.
Single natural pearls are often sold as a collector's item, or set as centerpieces in unique jewelry. Very few matched strands of natural pearls exist, and those that do often sell for hundreds of thousands of dollars. Yachtsman and financier Cartier purchased the landmark Cartier store on Fifth Avenue in New York for $100 cash and a double strand of matched natural pearls valued at $1 million.
Keshi pearls, although they often occur by chance, are not considered natural pearls. They are a byproduct of the culturing process, and hence do not happen without human intervention. These pearls are quite small: typically a few millimeters in size. Keshi pearls are produced by many different types of marine mollusks and freshwater mussels in China. Today many "keshi" pearls are actually intentional, with post-harvest shells returned to the water to regenerate a pearl in the existing pearl sac.
Origin of a natural pearl
Previously natural pearls were found in many parts of the world. Present day natural pearling is confined mostly to seas off Bahrain. Australia also has one of the world's last remaining fleets of pearl diving ships. Australian pearl divers dive for south sea pearl oysters to be used in the cultured south sea pearl industry. The catch of pearl oysters is similar to the numbers of oysters taken during the natural pearl days. Hence significant numbers of natural pearls are still found in the Australian Indian Ocean waters from wild oysters. X-Ray examination is required to positively verify natural pearls found today.
Different types of cultured pearls

Black pearls, frequently referred to as Black Tahitian Pearls, are highly valued because of their rarity; the culturing process for them dictates a smaller volume output and can never be mass produced. This is due to bad health and/or non-survival of the process, rejection of the nucleus (the small object such as a tiny fish, grain of sand or crab that slips naturally inside an oyster's shell or inserted by a human), and their sensitivity to changing climatic and ocean conditions. Before the days of cultured pearls, black pearls were rare and highly valued for the simple reason that white pearl oysters rarely produced natural black pearls, and black pearl oysters rarely produced any natural pearls at all. Since pearl culture technology, the black pearl oyster found in Tahiti and many other Pacific Island area has been extensively used for producing cultured pearls. The rarity of the black cultured pearl is now a "comparative" issue. The black cultured pearl is rare when compared to Chinese freshwater cultured pearls, and Japanese and Chinese Akoya cultured pearls, and is more valuable than these pearls. However, it is more abundant than the south sea pearl, which is more valuable than the black cultured pearl. This is simply due to the fact that the black pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera is far more abundant than the elusive, rare, and larger south sea pearl oyster - Pinctada maxima, which cannot be found in lagoons, but which must be dived for in a rare number of deep ocean habitats. Black cultured pearls from the black pearl oyster — Pinctada margaritifera — are NOT south sea pearls, although they are often mistakenly described as black south sea pearls. In the absence of an official definition for the pearl from the black oyster, these pearls are usually referred to as "black Tahitian pearls". The correct definition of a south sea pearl — as described by CIBJO and the GIA — is a pearl produced by the Pinctada maxima pearl oyster. South sea pearls are the colour of their host Pinctada maxima oyster — and can be white, silver, pink, gold, cream, and any combination of these basic colors, including overtones of the various colors of the rainbow displayed in the pearl nacre of the oyster shell itself.
Other "pearls"
Biologically speaking, under the right set of circumstances, almost any shelled mollusk can produce some kind of "pearl," however, most of these molluscan "pearls" have no luster or iridescence. In fact the great majority of mollusk species produce pearls which are not attractive to look at, and are sometimes not even very durable, such that they usually have no value at all, except perhaps to a scientist, or as a curiosity. These objects would be referred to as "calcareous concretions" by a gemologist, even though a malacologist would still consider them to be pearls.
One unusual example of calcareous concretions which nonetheless can sometimes have value, are the "pearls" which are found very rarely growing between the mantle and the shell of the queen conch or pink conch, Strombus gigas, a large sea snail or marine gastropod from the Caribbean Sea. These "pearls", which are pink in colour, are a by-product of the conch fishing industry, and the best of them show some chatoyance.
Somewhat similar gastropod "pearls", this time more orange in hue, are (again very rarely) found in the horse conch Pleuroploca gigantea.
Largest example of a "pearl" from another mollusk species
The largest "pearl" known, was found in the Philippines in 1934. It is a naturally-occurring, non-nacreous, calcareous concretion from a giant clam. Because it did not grow in a pearl oyster it is not pearly, instead it has a porcellaneous surface, in other words it is glossy like a china plate. Gemologically speaking, it is not a pearl. Other "pearls" from giant clams are known to science, but this is a particularly large one.
The object weighs 14 lb (6.4 kg) and was supposedly first discovered by an anonymous Filipino Muslim diver off the island of Palawan in 1934. According to the legend as it is currently told, a Palawan chieftain gave the pearl to Wilbur Dowell Cobb in 1936 as a gift for having saved the life of his son. The pearl had been named the "Pearl of Allah" by the Muslim tribal chief, because it resembled a turbaned head. Another even more elaborate legend says that this object is actually the Pearl of Lao-Tzu, a cultured mabe pearl created with a carved amulet and then supposedly progressively grafted into several giant clams, before supposedly being lost due to a shipwreck in 1745. This legend has been discredited, however because this "pearl" is indeed the product of a giant clam, Tridacna gigas, which cannot be grafted. The "pearl" is also a whole pearl, not a mabe pearl, and whole pearl culturing technology is only 100 years old.
The history of pearl hunting and pearl farming
Pearl hunting
For thousands of years, most seawater pearls were retrieved by divers working in the Indian Ocean, in areas like the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, and in the Gulf of Mannar (by the ancient Tamils).
Starting in the Han Dynasty (206 BC - 220 AD), the Chinese hunted extensively for seawater pearls in the South China Sea.
When Spanish conquistadors arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they discovered that around the islands of Cubagua and Margarita, some 200 km north of the Venezuelan coast, was an extensive bed of pearls. One of them, the Peregrina, was offered to the Spanish queens. This pearl later became very famous when Richard Burton purchased it for his wife Elizabeth Taylor. Margarita pearls are extremely difficult to find today and are known for their unique yellowish colour. The most famous Margarita necklace that any one can see today is the one that then Venezuelan President Romulo Betancourt gave to Jacqueline Kennedy when she and her husband, President John F. Kennedy paid an official visit to Venezuela.
Before the beginning of the 20th Century, pearl hunting was the most common way of harvesting pearls. Divers manually pulled oysters from ocean floors and river bottoms and checked them individually for pearls. Not all natural oysters produce pearls. In a haul of three tons, only three or four oysters will produce perfect pearls.
The development of pearl farming
However, almost all pearls used for jewelry are cultured by planting a core or nucleus into pearl oysters. The pearls are usually harvested after one year for Akoya, and 2-4 years for Tahitian and South Sea, and 2-7 years for freshwater. This mariculture process was first developed by Tatsuhei Mise and Tokichi Nishikawa in Japan.
The nucleus is generally a polished bead made from freshwater mussel shell. Along with a small piece of mantle tissue from another mollusk to serve as a catalyst for the pearl sac, it is surgically implanted into the gonad (reproductive organ) of a saltwater mollusk. In freshwater perliculture, only the piece of tissue is used in most cases, and is inserted into the fleshy mantle of the host mussel. South Sea and Tahitian pearl oysters, also known as Pinctada maxima and Pinctada margaritifera, which survive the subsequent surgery to remove the finished pearl are often implanted with a new, larger nucleus as part of the same procedure and then returned to the water for another 2-3 years of growth.
Despite the common misperception, Mikimoto did not patent the process of pearl culture. The accepted process of pearl culture was developed by a team of scientists at Tokyo University between 1907 and 1916. The team was headed by Tokichi Nishikawa and Tatsuhei Mise. Nishikawa was granted the patent in 1916, and married the daughter of Mikimoto. Mikimoto was able to use Nishikawa's technology. After the patent was granted in 1916, the technology was immediately commercially applied to akoya pearl oysters in Japan in 1916. Mise's brother was the first to produce a commercial crop of pearls in the akoya oyster. Mitsubishi's Baron Iwasaki immediately applied the technology to the south sea pearl oyster in 1917 in the Philippines, and later in Buton, and Palau. Mitsubishi was the first to produce a cultured south sea pearl - although it was not until 1928 that the first small commercial crop of pearls was successfully produced.
The original Japanese cultured pearls, known as akoya pearls, are produced by a species of small pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata martensii, which is no bigger than 6 to 7 mm in size, hence akoya pearls larger than 10 mm in diameter are extremely rare and highly prized. Today a hybrid mollusk is used in both Japan and China in the production of akoya pearls. It is a cross between the original Japanese species, and the Chinese species Pinctada chemnitzii.
Recent pearl production
China has recently overtaken Japan in akoya pearl production. Japan has all but ceased its production of akoya pearls smaller than 8mm. Japan maintains its status as a pearl processing centre, however, and imports the majority of Chinese akoya pearls. These pearls are then processed (often simply matched and sorted), relabeled as product of Japan, and exported.
In the past couple of decades, cultured pearls have been produced using larger oysters in the south Pacific and Indian Ocean. The largest pearl oyster is the Pinctada maxima, which is roughly the size of a dinner plate. South Sea pearls are characterized by their large size and silvery colour. Sizes up to 14 mm in diameter are not uncommon. Australia is one of the most important sources of South Sea pearls.
Mitsubishi commenced pearl culture with the south sea pearl oyster in 1916, as soon as the technology patent was commercialized. By 1931 this project was showing signs of success, but was upset by the death of Tatsuhei. Although the project was recommenced after Tatsuhei's death, the project was discontinued at the beginning of WWII before significant productions of pearls were achieved.
After WWII, new south sea pearl projects were commenced in the early 1950s in Burma and Kuri Bay and Port Essington in Australia. Japanese companies were involved in all projects using technicians from the original Mitsubishi south sea pre-war projects. Despite often being described as black south sea pearls, Tahitian pearls are not in fact south sea pearls. The correct definition of a south sea pearl is a "pearl produced by the Pinctada maxima pearl oyster."
Japanese freshwater pearl farming
In 1914, pearl farmers began culturing freshwater pearls using the pearl mussels native to Lake Biwa. This lake, the largest and most ancient in Japan, lies near the city of Kyoto. The extensive and successful use of the Biwa Pearl Mussel is reflected in the name Biwa pearls, a phrase which was at one time nearly synonymous with freshwater pearls in general. Since the time of peak production in 1971, when Biwa pearl farmers produced six tons of cultured pearls, pollution and overharvesting have caused the virtual extinction of this animal. Japanese pearl farmers recently cultured a hybrid pearl mussel — a cross between Biwa Pearl Mussels and a closely related species from China, "Hyriopsis cumingi, in lake Kasumigaura. This industry closed in 2006 due to lake pollution.
Japanese pearl producers also invested in producing cultured pearls with freshwater mussels in the region of Shanghai, China. China has since become the world's largest producer of freshwater pearls, producing more than 1,500 metric tons per year. Japan has all but ceased production in the last decade.
Led by pearl pioneer John Latendresse and his wife Chessy, the United States began farming freshwater cultured pearls in the mid 1960's. National Geographic Magazine introduced the American cultured pearl as a commercial product in their August 1985 issue. The Tennessee pearl farm has emerged as a tourist destination in recent years, but commercial production of freshwater pearls has ceased.
Pearls in jewelry
The value of the pearls in jewelry is determined by a combination of the luster, colour, size, lack of surface flaw and symmetry that are appropriate for the type of pearl under consideration. Among those attributes, luster is the most important differentiator of pearl quality according to jewelers. All factors being equal, however, the larger the pearl the more valuable it is. Large, perfectly round pearls are rare and highly valued. Teardrop-shaped pearls are often used in pendants.
Pearls come in eight basic shapes: round, semi-round, button, drop, pear, oval, baroque, and circled. Perfectly round pearls are the rarest and most valuable shape. Semi-rounds are also used in necklaces or in pieces where the shape of the pearl can be disguised to look like it is a perfectly round pearl. Button pearls are like a slightly flattened round pearl and can also make a necklace, but are more often used in single pendants or earrings where the back half of the pearl is covered, making it look like a larger, round pearl.
Drop and pear shaped pearls are sometimes referred to as teardrop pearls and are most often seen in earrings, pendants, or as a centre pearl in a necklace. Baroque pearls have a different appeal to them than more standard shapes because they are often highly irregular and make unique and interesting shapes. They are also commonly seen in necklaces. Circled pearls are characterized by concentric ridges, or rings, around the body of the pearl.
In general, cultured pearls are less valuable than natural pearls, and imitation pearls are less valuable than cultured pearls. One way that jewelers can determine whether a pearl is cultivated or natural is to have a gem lab perform an x-ray of the pearl. If the x-ray reveals a nucleus, the pearl is likely a bead-nucleated saltwater pearl. If no nucleus is present, but irregular and small dark inner spots indicating a cavity are visible, combined with concentric rings of organic substance, the pearl is likely a cultured freshwater. Cultured freshwater pearls can often be confused for natural pearls which present as homogeneous pictures which continuously darken toward the surface of the pearl. Natural pearls will often show larger cavities where organic matter has dried out and decomposed.
Some imitation pearls are simply made of mother-of-pearl, coral or conch, while others are made from glass and are coated with a solution containing fish scales called essence d'Orient. Although imitation pearls look the part, they do not have the same weight or smoothness as real pearls, and their luster will also dim greatly.
There is also a unique way of naming pearl necklaces. While most other necklaces are simply referred to by their physical measurement, strings of pearls have their own set of names that characterize the pearls based on where they hang when worn around the neck. A collar will sit directly against the throat and not hang down the neck at all; they are often made up of multiple strands of pearls. Pearl chokers nestle just at the base of the neck. The size called a princess comes down to or just below the collarbone. A matinee of pearls falls just above the breasts. An opera will be long enough to reach the breastbone or sternum of the wearer, and longer still, a pearl rope is any length that falls down farther than an opera.
Necklaces can also be classified as uniform, or graduated. In a uniform strand of pearls, all pearls are classified as the same size, but actually fall in a range. A uniform strand of akoya pearls, for example, will measure within 0.5 mm. So a strand will never be 7 mm, but will be 6.5-7 mm. Freshwater pearls, Tahitian pearls, and South Sea pearls all measure to a full millimeter when considered uniform. A graduated strand of pearls most often has at least 3 mm of differentiation from the ends to the centre of the necklace. Popularized in the 1950s by the GIs bringing strands of cultured akoya pearls home from Japan, the graduated style was much more affordable as most pearls in any given strand were small.
Earrings and necklaces can also be classified on the grade of the color of the pearl. While white and more recently black pearls are by far the most popular colors other tinges of colour can be found on pearls. Pink, blue, champagne, green and even purple can be found, but to form a complete string of same size and shade pearls can take years. Some colors like purple can only be found in certain types of clams, while other clams can produce a variety of colors if given the right environment.