Portal:Asia
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Countries; Geography of Asia; Portals

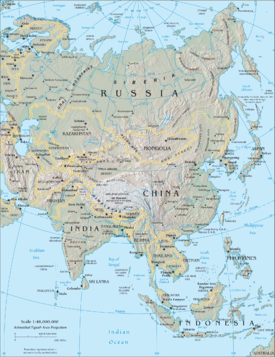
Asia is the largest continent in the world. It has a land mass at around 49,694,700 km² and covers 8.6% of the Earth's total surface area, or 29.4% of its land area. It is traditionally defined as part of the landmass of Africa- Eurasia lying east of the Suez Canal, east of the Ural Mountains, and south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black Seas.
Asia is considered one of the most populous regions in the world, containing around 60% of the world's human population. Of these only 2% live in the northern and interior half ( Siberia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang, Tibet, Qinghai, western Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan). The wealth of Asia differs widely between, and within, states. This is due to its vast size, meaning a huge range of different cultures, environments, historical ties and government systems. The largest economies in Asia in terms of nominal GDP are Japan, People's Republic of China and South Korea, the smallest East Timor. In terms of Purchasing Power Parity however, the People's Republic of China has the largest economy in Asia and the second largest in the world, followed by Japan and India as the world's third and fourth largest economies respectively. Asia is also known for its rich history and culture. Asian art, music, and cuisine, as well as literature, are important parts of Asian culture. Eastern philosophy and religion also plays a major role, with Sikhism, Hinduism, Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, Islam, and Christianity all playing major roles. One of the most complex parts of Asian culture is the relationship between traditional cultures and the Western world.
The People's Republic of China ( simplified Chinese: 中 华 人 民 共 和 国; traditional Chinese: 中 華 人 民 共 和 國; pinyin: Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó listen ), commonly known as China, is the largest country in East Asia and among the largest countries in the world. With a population of over 1.3 billion, roughly a fifth of the earth's total population, it is the most populous country in the world. Its capital is Beijing.
The Communist Party of China (CPC) has led the PRC under a single-party system since the state's establishment in 1949. The PRC is involved in a long-running dispute over the political status of Taiwan. The CPC's rival during the Chinese Civil War, the Kuomintang (KMT), retreated to Taiwan and surrounding islands after its civil war defeat in 1949, claiming legitimacy over China and Mongolia while it was the ruling power of the Republic of China (Taiwan). The CPC regards the KMT's claims as illegitimate. The term " Mainland China" is often used to denote the areas under PRC rule, but sometimes excludes its two Special Administrative Regions: Hong Kong and Macau.
Afghanistan · Armenia · Azerbaijan · Bahrain · Bangladesh · Bhutan · British Indian Ocean Territory (United Kingdom) · Brunei · Cambodia · People's Republic of China (mainland China) · Taiwan (Republic of China) · Christmas Island (Australia) · Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Australia) · Georgia · Hong Kong (PR China) · India · Indonesia · Iran · Cyprus · Iraq · Israel · Japan · Jordan · Kazakhstan · Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) · Republic of Korea (South Korea) · Kuwait · Kyrgyzstan · Laos · Lebanon · Macau (PR China) · Malaysia · Maldives · Mongolia · Myanmar (Burma) · Nepal · Oman · Pakistan · Palestine · Philippines · Qatar · Russia · Saudi Arabia · Singapore · Sri Lanka · Syria · Tajikistan · Thailand · Timor-Leste (East Timor) · Turkey · Turkmenistan · United Arab Emirates · Uzbekistan · Vietnam · Yemen
|