Portal:Medicine
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Health and medicine; Portals
Medicine is both an area of knowledge (a science), and the application of that knowledge (by the medical profession and other health professionals such as nurses). The various specialized branches of the science of medicine correspond to the equally specialized medical professions dealing with particular organs or diseases. The science of medicine is the knowledge of body systems and diseases, while the profession of medicine refers to the social structure of the group of people formally trained to apply that knowledge to treat disease.
Medicine comprises various specialized sub-branches, such as cardiology, pulmonology, neurology, or other fields such as sports medicine, research or public health.
"Medicine" is also often used amongst medical professionals as shorthand for internal medicine. Veterinary medicine is the practice of health care in animal species other than human beings.
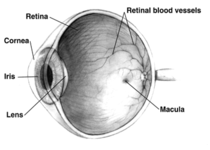
Eyes are organs of vision that detect light. Different kinds of light-sensitive organs are found in a variety of organisms. The simplest eyes do nothing but detect whether the surroundings are light or dark, while more complex eyes can distinguish shapes and colors. The visual fields of some such complex eyes largely overlap, to allow better depth perception ( binocular vision), as in humans; and others are placed so as to minimize the overlap, such as in rabbits and chameleons.
In most vertebrates and some mollusks, the eye works by allowing light to enter it and project onto a light-sensitive panel of cells known as the retina at the rear of the eye, where the light is detected and converted into electrical signals. These are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. Such eyes are typically roughly spherical, filled with a transparent gel-like substance called the vitreous humour, with a focusing lens and often an iris which regulates the intensity of the light that enters the eye. The eyes of cephalopods, fish, amphibians and snakes usually have fixed lens shapes, and focusing vision is achieved by telescoping the lens—similar to how a camera focuses.
(More...)
- ... that mythomania is a condition involving compulsive lying by a person with no obvious motivation?
- ... that a jet injector is a type of medical injecting syringe that uses a high-pressure narrow jet of the injection liquid instead of a hypodermic needle to penetrate the epidermis?
- ... that an iridectomy is the surgical removal of part of the iris, most frequently performed in the treatment of closed-angle glaucoma and iris melanoma?
- "… the best thing for being sad… is to learn something.” - Merlin to Arthur; The Sword in the Stone by T. H. White
- "Health is like money, we never have a true idea of its value until we lose it.” - Josh Billings
- "Be careful about reading health books. You may die of a misprint.” - Mark Twain