Squash (sport)
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Sports
Squash is a racquet sport that was formerly called squash racquets, a reference to the "squashable" soft ball used in the game (compared with the harder ball used in its parent game Racquets (or rackets; see below)). The game is played by two players (or four players for doubles) with "standard" rackets in a four-walled court with a small, hollow rubber ball. Squash is characterized as a "high-impact" exercise that can place strain on the joints, notably the knees.
Squash is recognized by CIO and remains in contention for incorporation in a future Olympic program.
History
The game of squash was developed based on other pre-existing racquet sports, especially racquets and fives, a set of sports played predominantly by boarders at British independent schools. Squash itself was developed at one of these schools, London's Harrow School, in the early 19th century, when the boys noted that puncturing a racquets' ball caused it to squash when hitting the wall, allowing a greater variety of shots. By the end of the century it had spread to Britain's other private schools as well as Oxford and Cambridge universities. In 1908 a squash sub-committee of the Tennis and Rackets Association was formed to regulate the sport, followed in 1928 by the British Squash Rackets Association.
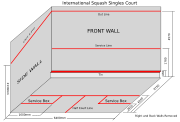
Court
The court size was codified in the 1920s at 975 cm (32 feet) and 640 cm (21 feet) wide. The front wall has a "front wall line" 457 cm (15 feet) above the floor, connected by a raking "front" line meeting the "out" line on the back wall at 213 cm (7 feet) above the floor. The front wall also has a "service line" whose top is 183 cm (6 feet) above the floor with the "board" (the equivalent of a net) 48 cm (18.9 inches) high. The floor is marked with a transverse "half-court" line and further divided into two rear "quarter courts" and two "service boxes", as shown in the diagram above.
The traditional "American" court for the U.S. game, (now referred to as " hardball squash") is a similar size, but narrower at 18 feet 6 inches (564 cm). The floor and wall markings differ slightly from the "International" court and the tin is lower, at 15 inches (38 cm) high. However, hardball squash was replaced by softball in America as the standard version of squash and has since almost completely died out.
A "Converted Court" is the result of converting racquetball courts to squash. Racquetball courts are 20 feet (610 cm) wide and 40 feet (1220 cm) in length, so it is relatively easy to install a back wall, producing a squash court of 20 feet (610 cm) wide by 32 feet (975 cm) long.
Playing equipment
Standard rackets are governed by the rules of the game. Traditionally they were made of laminated timber (typically Ash), with a small strung area using natural gut strings. After a rule change in the mid-1980s, they are now almost always made of composite materials or metals (graphite, kevlar, titanium, boron) with synthetic strings. Modern rackets have maximum dimensions of 686 mm (27.0 in.) long and 215 mm (8.5 in.) wide, with a maximum strung area of 500 square centimetres (approx. 90 sq. in.), the permitted maximum weight is 255 grams (approx. 9 oz.), but most weigh between 110 and 200 grams (4-7 oz.).
Squash balls are 39.5 mm and 40.5 mm in diametre, and weigh between 23 and 25grams. They are made with two pieces of rubber compound, glued together to form a hollow sphere and buffed to a matte finish. Different balls are provided for varying temperature and atmospheric conditions and standards of play: more experienced players use slow balls that are smaller and have less bounce than those used by less experienced players (slower balls tend to die in court corners, rather than standing up to allow easier shots). Depending on its specific rubber composition, a squash ball may have the property that it bounces more at higher temperatures. Players tend to warm up balls by bouncing them on the ground prior to play. As a rally progresses, play is complicated as the ball usually becomes hotter and faster.
Small coloured dots on the ball indicate its dynamic level (bounciness), and thus the standard of play for which it is suited. The recognised speed colours indicating the degree of dynamism are:
- Double Yellow - Extra super slow (very low bounce)
- Yellow - Super slow (low bounce)
- Green or White - slow (average bounce)
- Red - Medium (high bounce)
- Blue - Fast (very high bounce)
Balls are manufactured to these standards by Prince, Dunlop, Pointfore, Wilson, and others. The "double-yellow dot ball", introduced in 2000, is currently the competition standard, replacing the earlier "yellow-dot" that was long considered the competition standard. There is also a high-altitude "orange dot" ball, used in places such as Mexico City, Calgary, Denver, and Johannesburg. In North America, the Dunlop "green dot" ball is often used at high altitude, as well.
Other balls available are:
- Dunlop "Max Blue" (aimed at beginners), which is 12% larger and has 40% longer "hang time" than a "double-yellow dot ball" and has "instant bounce"
- Dunlop "Max Progress" (red) (for players wishing to improve their technique), which is 6% larger with a 20% longer hang-time than a "double-yellow dot ball" and has instant bounce
Given the game's vigorousness, players must wear comfortable sports clothing and robust indoor (non-marking) sports shoes. In competition, men usually wear shorts and a t-shirt or a polo shirt. Women normally wear a skirt and a t-shirt or a tank top, or a sports dress. Towelling wrist and head bands may also be required in humid climates. Polycarbonate lens goggles are recommended, as players might be struck with a fast-swinging racket or the ball, that typically reaches speeds exceeding 200 km/h (125 mph). In the 2004 Canary Wharf Squash Classic, John White was recorded driving balls at speeds over 270 km/h (170 mph). Many squash venues mandate the use of eye protection and some association rules require that all juniors and doubles players must wear eye protection.
Play and scoring
The players usually spin a racket to decide who commences serving at the start of the match, and this player starts the first rally by electing to serve from either the left or right service box. For a legal serve, one of the server's feet must be in that box and, after being struck by the racket, the ball must strike the front wall above the service line and below the out line and land in the opposite quarter court, unless volleyed by the receiver.
The players then take turns hitting the ball against the front wall (referred to as "rallying"). The ball may be volleyed (hit whilst still in the air) or hit after its first bounce and before the second. To be considered good, the ball must reach the front wall below the "out" line and above the "board" or "tin" before touching the floor. A ball landing on either the out line or the line above the tin, contrary to tennis, is considered to be out. The ball may also be struck against any of the other three walls before reaching the front wall. Shots that are first played off the side or back walls are referred to as "boasts" or "angles".
The rally continues until a player is unable to return his or her opponent's shot or makes a mistake or a "let" or "stroke" is awarded by the referee for interference (see below).
A point is scored only by the server (when the receiver is unable to return the ball to the front wall before it has bounced twice). When the receiver wins the rally, they are awarded only the right to serve. They may choose to serve from either service box.
Games are usually played to 9 points (alternatively, the receiver may opt to call "set two" and play to 10 when the score first reaches 8-8). Competition matches are usually played to "best-of-five" (i.e., the player to win the most out of 5 games).
Alternatively, in the point-a-rally scoring system, points are scored by the winner of each rally, whether or not he or she served. Traditionally, PARS scoring was up to 15 points (or the receiver calls 15 or 17 when the game reaches 14-14). However, in 2004, the PARS scoring was reduced to 11 for the professional game (if the game reaches 10-10, a player must win by two clear points). PARS is now used on the men's Professional Tour, and the tin height has been lowered by two inches for the men's professional tournaments (these changes have been made in a hope to shorten the length of the rallies and therefore the match). The women's Professional Tour, however, still uses the original "up to 9 English scoring" and the original tin height.
In the International game, club, doubles and recreational matches are usually played using the traditional British scoring system. Scoring systems and rules can be adapted subtly to accommodate shorter game time or multiple players. The British scoring is generally used for USSRA (United States Squash Racquets Association) matches.
Strategy and tactics
The strategy of the game is to hit the ball straight up the side walls to the back corners referred to as a "rail," straight drive, wall, or "length", then move to the centre of the court near the "T" to be well placed to retrieve the opponent's return. Attacking with soft or "short" shots to the front corners (referred to as "drop shots") causes the opponent to cover more of the court and may result in an outright winner. "Angle" shots are used for deception and again to cause the opponent to cover more of the court.
A key strategy in squash is known as "dominating the T" (the intersection of the red lines near the centre of the court where the player is in the best position to retrieve the opponent's next shot). Skilled players will return a shot, and then move back toward the T before playing the next shot. From this position, the player can quickly access any part of the court to retrieve the opponent's next shot with a minimum of movement.
Rallies between experienced players may involve 30 or more shots and therefore a very high premium is placed on fitness, both aerobic and anaerobic. As players become more skilled and, in particular, better able to retrieve shots, points often become a war of attrition. At higher levels of the game, the fitter player has a major advantage.
Almost all players will fall into the following categories of style of play:
- "Retriever"- Usually a very fit player, plays patiently, can retrieve most shots hit by an opponent, but doesn't have a particularly strong attacking game.
- "Shooter" or "attacking player"- May be a patient player as well, but is more comfortable trying to hit winning shots or going for "nicks". Generally has very good shot accuracy and deception skills.
- "Power Player"- Tries to overpower their opponent by hitting the ball with extreme pace. Not known for their fitness, or patience.
- "All-Around Player"- Is comfortable playing all different styles and places, comfortable in all areas of the court.
- "Attritional Attacking"- Most professional players fit into this category, with the likes of David Palmer and James Willstrop; where they are prepared to rally down the wall, however as soon as the player leaves a loose ball inches from the side wall, they are ready to kill the ball into the nicks.
Ability to change the direction of ball at the last instant is also important to off-balance the opponent. Expert players can anticipate the opponent's shot a few tenths of a second before the average player, giving them a chance to react sooner. Such skill is usually acquired by a lot of practice and game experience.
Interference and obstruction
Interference and obstruction are an inevitable aspect of this sport, since two players are confined within a shared space. Generally, the rules entitle players to reasonable access to the ball, a reasonable swing and an unobstructed shot to any part of the front wall. When interference occurs, a player may appeal for a "let" and the referee (or the players themselves if there is no official) then interprets the extent of the interference. The referee may elect to allow a let and the players then replay the point, or award a "stroke" (either a point or the right to serve) to the appealing player, depending on the degree of interference and whether the player interfered with was likely to have hit a winning shot had the interference not occurred.
When it is deemed that there has been little or no interference, the rules provide that no let is to be allowed, in the interests of continuity of play and the discouraging of spurious appeals for lets. Because of the subjectivity in interpreting the nature and magnitude of interference, the awarding (or withholding) of lets and strokes is often controversial.
When a player's shot hits his or her opponent prior to hitting the front wall, interference has occurred. If the ball was travelling towards the side wall when it hit the opponent, it is usually a let. However, it is a stroke to the player who hit the ball if the ball was travelling straight to the front wall when the ball hit the opponent.
Cultural, social, and health aspects
There are several variations of squash played across the world. In the U.S. hardball singles and doubles are played with a much harder ball and different size courts (as noted above). Whilst hardball singles has lost much of its popularity in North America (in favour of the International version), the hardball doubles game is still active. There is also a doubles version of squash played with the standard ball, sometimes on a wider court, and a more tennis-like variation known as squash tennis.
The relatively small court and low-bouncing ball makes scoring points harder than in its American cousin, racquetball, as the ball may be played to all four corners of the court. Since every ball must strike the front wall above the tin (unlike racquetball), the ball cannot be easily "killed". As a result, rallies tend to be longer than in racquetball.
Most squash players prefer partners who are compatible physically, mentally, and technically, as a small difference in ability may result in one player overwhelmingly dominating the match. Currently there is no international standard method (other than for professional players) for evaluating skill levels for players.
Squash provides an excellent cardiovascular workout. In one hour of squash, a player may expend approximately 700 to 1000 kilocalories (3,000 to 4,000 kJ) which is significantly more than most other sports. and over 70% more than either general tennis or racquetball. The sport also provides a good upper and lower body workout by utilising both the legs to run around the court and the arms and torso to swing the racquet. In 2003, Forbes rated squash as the number one healthiest sport to play. However, some studies have implicated squash as a cause of possible fatal cardiac arrhythmia and argued that squash is an inappropriate form of exercise for older men with heart disease.
Squash now has a universal appeal, and there are courts in 148 countries in the world.
Players and records
The (British) Squash Rackets Association conducted its first British Open championship for men in December 1930, using a "challenge" system. Charles Read was designated champion in 1930, but was beaten in home and away matches by Don Butcher, who was then recorded as the champion for 1931. The championship continues to this day, but has been conducted with a "knockout" format since 1947.
Since its inception, the men's British Open has been dominated by relatively few players: F.D. Amr Bey (Egypt) in the 1930s; Mahmoud Karim (Egypt) 1940s; brothers Hashim Khan and Azam Khan (Pakistan) 1950s and 1960s; Jonah Barrington (Great Britain and Ireland) and Geoff Hunt (Australia) 1960s and 1970s; Jahangir Khan (Pakistan) 1980s; and Jansher Khan (Pakistan) 1990s.
The women's championship started in 1921, and has similarly been dominated by relatively few players: Joyce Cave and Nancy Cave (England) in the 1920s; Margot Lumb (England) 1930s; Janet Morgan (England) 1950s; Heather McKay (Australia) 1960s and 1970s; Vicki Cardwell (Australia) and Susan Devoy (New Zealand) 1980s; Michelle Martin (Australia) 1990s; and Sarah Fitz-Gerald (Australia) 1990s and 2000s.
Heather McKay, with her lengthy and absolute dominance of the game (she remained undefeated for 18 years during the 1960s and 1970s), is undoubtedly the greatest woman player of all time. Amongst the men, most modern commentators consider Jahangir Khan (1980s) or (the distantly related) Jansher Khan (1990s) to be the greatest male players. Other worthy contenders are Jonah Barrington, Geoff Hunt, and Hashim Khan.
Because of its traditions, the British Open has been considered by many to be more prestigious than the World Open, which began in the mid-1970s. However, some have shown concern about the ability of the former to sustain its prominence, citing its failure in 2005 to attract top players, probably due in part to the disparity in prize money. In 2005 the combined men's and women's prize money for the British Open came to $71,000, compared with the 2005 World Open's prize money, estimated to be about $270,000.
Hashim Khan was the first of a line of great Pakistani squash champions, including Jahangir Khan and Jansher Khan. Jahangir, now president of the World Squash Federation, won the British Open ten times and the World Open six times. Jansher took over his mantle in the late 1980s and went on to win eight World Open and six British Open titles.
Former world number one Peter Nicol has stated that he believes squash has a "very realistic chance" of being added to the list of Olympic sports for the 2016 games..
The current #1 rank is held by Amr Shabana of Egypt in the men's competition . and Nicol David of Malaysia in the women's competition.
Wider acceptance
Squash players and associations have lobbied for many years for the sport to be accepted into the Olympic Games, with no success to date. Few would argue with its worthiness by traditional measures, since it is played throughout the world and is similar to tennis in terms of athletic skills and fitness requirements, but the principal limitation has always been the difficulty in observing the sport as a spectator, either in person or on television. The ball travels so quickly that television audiences are hard-pressed to follow the action, even though some tournaments have attempted to remedy the problem by utilizing a specially coated ball for increased visibility. To maximize the viewing audience at tournaments, promoters often utilize an all-glass court that is designed to permit spectators to be seated around all four walls but is specially tinted so as not to distract the players. Because of these viewership restrictions, professional squash players earn vastly less than their counterparts in the tennis world.