Toluene
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Chemical compounds
| Toluene | |
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Other names | phenylmethane toluol methylbenzene |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | [108-88-3] |
| RTECS number | XS5250000 |
| SMILES | Cc1ccccc1 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C7H8 (C6H5CH3) |
| Molar mass | 92.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear colorless, liquid |
| Density | 0.8669 g/mL, liquid |
| Melting point |
−93 °C |
| Boiling point |
110.6 °C |
| Solubility in water | 0.053 g/100 mL (20-25°C) |
| Viscosity | 0.590 c P at 20°C |
| Structure | |
| Dipole moment | 0.36 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| MSDS | ScienceLab.com |
| Main hazards | highly flammable |
| NFPA 704 | |
| R-phrases | R11, R38, R48/20, R63, R65, R67 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S36/37, S29, S46, S62 |
| Flash point | 4 °C/ 39.2 °F |
| Related compounds | |
| Related aromatic hydrocarbon | benzene xylene naphthalene |
| Related compounds | methylcyclohexane |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references |
|
Toluene, also known as methylbenzene or phenylmethane, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners, redolent of the sweet smell of the related compound benzene. It is an aromatic hydrocarbon that is widely used as an industrial feedstock and as a solvent. Like other solvents, toluene is also used as an inhalant drug for its intoxicating properties.
History
The name toluene was derived from the older name toluol that refers to tolu balsam, an aromatic extract from the tropical Colombian tree Myroxylon balsamum, from which it was first isolated. It was originally named by Jöns Jakob Berzelius.
Chemical properties
Toluene reacts as a normal aromatic hydrocarbon towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. The methyl group makes it around 25 times more reactive than benzene in such reactions. It undergoes smooth sulfonation to give p-toluenesulfonic acid, and chlorination by Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3 to give ortho and para isomers of chlorotoluene. It undergoes nitration to give ortho and para nitrotoluene isomers, but if heated it can give dinitrotoluene and ultimately the explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT).
With other reagents the methyl side chain in toluene may react, undergoing oxidation. Reaction with potassium permanganate leads to benzoic acid, whereas reaction with chromyl chloride leads to benzaldehyde ( Étard reaction). Halogenation can be performed under free radical conditions. For example, N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) heated with toluene in the presence of AIBN leads to benzyl bromide.
Catalytic hydrogenation of toluene to methylcyclohexane requires a high pressure of hydrogen to go to completion, because of the stability of the aromatic system. pka is approximately 45.
Preparation
Toluene occurs naturally at low levels in crude oil and is usually produced in the processes of making gasoline via a catalytic reformer, in an ethylene cracker or making coke from coal. Final separation (either via distillation or solvent extraction) takes place in a BTX plant.
Uses
Toluene is a common solvent, able to dissolve: paints, paint thinners, many chemical reactants, rubber, printing ink, adhesives (glues), lacquers, leather tanners, and disinfectants. It can also be used as a fullerene indicator, and is a raw material for toluene diisocyanate (used in the manufacture of polyurethane foam) and TNT. Industrial uses of toluene include dealkylation to benzene and disproportionation to a mixture of benzene and xylene. When oxidized it yields benzaldehyde and benzoic acid, two important intermediates in chemistry. It is also used as a carbon source for making Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. Toluene can be used to break open red blood cells in order to extract hemoglobin in biochemistry experiments.
Toluene can be used as an octane booster in gasoline fuels used in internal combustion engines. Toluene at 84% by volume, fueled all the turbo Formula 1 teams in the 1980s.
Toxicology and metabolism
Inhalation of toluene fumes can be intoxicating, but in larger doses nausea-inducing. Toluene may enter the human system not only through vapour inhalation from the liquid evaporation, but also following soil contamination events, where human contact with soil, ingestion of contaminated groundwater or soil vapour off-gassing can occur.
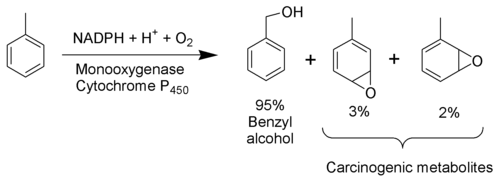
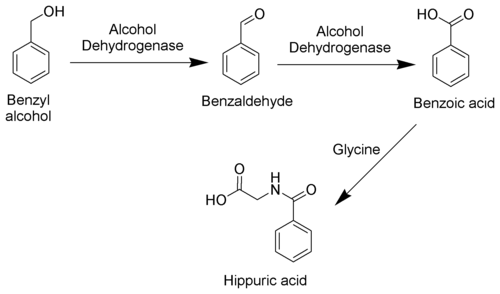
The toxicity of toluene can be explained mostly by its metabolism. As toluene has very low water solubility, it cannot exit the body via the normal routes (urine, feces, or sweat). It must be metabolized in order to be excreted. The methyl group of toluene is more easily oxidized by cytochrome P450 than the benzene ring. Therefore, in the metabolism of toluene, 95% is oxidized to become benzyl alcohol. The toxic metabolites are created by the remaining 5% that are oxidized to benzaldehyde and cresols. Most of the reactive products are detoxified by conjugation to glutathione but the remainder may severely damage cells.
Toluene is mainly excreted as benzoic acid and hippuric acid, both formed by further metabolic oxidation of benzyl alcohol.