From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Size of this preview: 640 × 440 pixels
Size of this preview: 640 × 440 pixels Full resolution (1,164 × 800 pixels, file size: 79 KB, MIME type: image/png)
 |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. The description on its description page there is shown below.Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
| Description |
|
| Source |
This media is lacking source information.
Please edit this file's description and provide a source.
العربية | Česky | Deutsch | English | Español | Français | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Nederlands | Polski | Português | Русский | 中文 | 中文(简体) | 中文(繁體) | +/-
|
| Date |
|
| Author |
This media is lacking author information.
العربية | Česky | Deutsch | English | Español | Suomi | Français | עברית | 日本語 | 한국어 | Lietuvių | Nederlands | Polski | Русский | 中文(简体) | 中文(繁體) | +/-
|
Permission
( Reusing this image) |
see below
|
|
|
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby release it into the public domain. This applies worldwide.
In case this is not legally possible:
I grant anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law.
Afrikaans | Alemannisch | Aragonés | العربية | Asturianu | Български | Català | Cebuano | Česky | Cymraeg | Dansk | Deutsch | Eʋegbe | Ελληνικά | English | Español | Esperanto | Euskara | Estremeñu | فارسی | Français | Galego | 한국어 | हिन्दी | Hrvatski | Ido | Bahasa Indonesia | Íslenska | Italiano | עברית | Kurdî / كوردی | Latina | Lietuvių | Latviešu | Magyar | Македонски | Bahasa Melayu | Nederlands | Norsk (bokmål) | Norsk (nynorsk) | 日本語 | Polski | Português | Ripoarisch | Română | Русский | Shqip | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | Српски / Srpski | Suomi | Svenska | ไทย | Tagalog | Türkçe | Українська | Tiếng Việt | Walon | 中文(简体) | 中文(繁體) | zh-yue-hant | +/- |
Source code
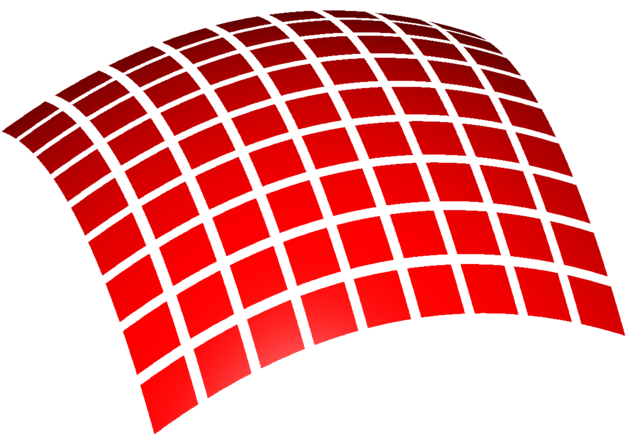
% An illustration of the surface integral.
% It shows how a surface is split into surface elements.
function main ()
% the function giving the surface and its gradient
f=inline('10-(x.^2+y.^2)/15', 'x', 'y');
BoxSize=5; % surface dimensions are 2*BoxSize x 2*BoxSize
M = 10; % M x M = the number of surface elements into which to split the surface
N=100; % N x N = number of points in each surface element
spacing = 0.1; % spacing between surface elements
H=2*BoxSize/(M-1); % size of each surface element
gridsize=H/N; % distance between points on a surface element
figure(1); clf; hold on; axis equal; axis off;
for i=1:(M-1)
for j=1:(M-1)
Lx = -BoxSize + (i-1)*H+spacing; Ux = -BoxSize + (i )*H-spacing;
Ly = -BoxSize + (j-1)*H+spacing; Uy = -BoxSize + (j )*H-spacing;
% calc the surface element
XX=Lx:gridsize:Ux;
YY=Ly:gridsize:Uy;
[X, Y]=meshgrid(XX, YY);
Z=f(X, Y);
% plot the surface element
surf(X, Y, Z, 'FaceColor','red', 'EdgeColor','none', ...
'AmbientStrength', 0.3, 'SpecularStrength', 1, 'DiffuseStrength', 0.8);
end
end
view (-18, 40); % viewing angle
camlight headlight; lighting phong; % make nice lightning
% save to file
print('-dpng', '-r200', 'Surface_integral_illustration.png');
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
|
|
Date/Time |
Dimensions |
User |
Comment |
| current |
03:43, 22 April 2007 |
1,164×800 (79 KB) |
Oleg Alexandrov |
|
|
|
03:42, 22 April 2007 |
2,400×1,800 (104 KB) |
Oleg Alexandrov |
|
|
|
03:33, 22 April 2007 |
800×536 (47 KB) |
Oleg Alexandrov |
|
File links
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):

