Image:Maxwell Dist-Inverse Speed.jpg
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Size of this preview: 411 × 480 pixels
Full resolution (600 × 700 pixels, file size: 151 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
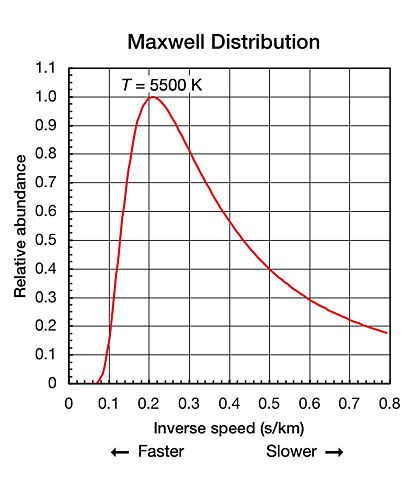
This graph shows the Maxwell distribution of helium atom speeds at 5500 kelvin. The speeds are shown as inverse speed so one can more easily compare this shape to that of a Planck curve. In this graph, the left end of the X-axis represents higher energies and higher speeds. Greg L 03:14, 4 August 2006 (UTC)
Licensing
 |
I, the creator of this work, hereby grant the permission to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. Subject to disclaimers. |
| |
A PNG version of this image is also available, and should be used in place of this image whenever possible. If this is a fair-use image, please ensure the image has been replaced by the PNG version, and mark it for deletion by adding
For more information about the Portable Network Graphics format, see the article on PNG. |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:02, 13 August 2006 | 600×700 (151 KB) | Greg L ( Talk | contribs) | (This graph shows the Maxwell distribution of helium atom speeds at 5500 kelvin. The speeds are shown as ''inverse speed'' so one can more easily compare this shape to most graphs of the Planck curve. Consequently in this graph, the left end of the X-axis) |
| revert | 23:15, 4 August 2006 | 600×662 (150 KB) | Greg L ( Talk | contribs) | (This graph shows the Maxwell distribution of helium atom speeds at 5500 kelvin. The speeds are shown as ''inverse'' speed so one can more easily compare this shape the common way of displaying the Planck curve of black-body radiation. In this graph—as w) |
| revert | 03:14, 4 August 2006 | 600×725 (148 KB) | Greg L ( Talk | contribs) | (This graph shows the Maxwell distribution of helium atom speeds at 5500 kelvin. The speeds are shown as ''inverse'' speed so one can more easily compare the shape of the Planck curve, which has shorter wavelengths (higher energies and associated speeds) ) |
See the setup instructions for more information.
File links
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Orientation | Normal |
|---|---|
| Horizontal resolution | 71 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 71 dpi |
| Software used | Adobe Photoshop 7.0 |
| File change date and time | 17:58, 12 August 2006 |
| Colour space | sRGB |
Categories: Self-published work | Images made obsolete by a PNG version