| Millennium: |
1st millennium BC |
| Centuries: |
2nd century BC · 1st century BC · 1st century |
| Decades: |
90s BC 80s BC 70s BC 60s BC 50s BC
40s BC 30s BC 20s BC 10s BC 0s BC |
| Categories: |
Births – Deaths
Establishments – Disestablishments |
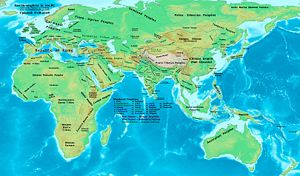
Eastern Hemisphere at the beginning of the 1st century BC.
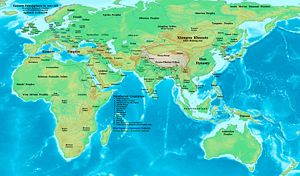
Eastern Hemisphere at the end of the 1st century BC.
The 1st century BC started the first day of 100 BC and ended the last day of 1 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. An alternative name for this century is the last century BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a minus sign, so '2 BC' is equal to 'year -1'.
In the course of the century all the remaining independent lands surrounding the Mediterranean were steadily brought under Roman control, being ruled either directly under governors or through puppet kings appointed by Rome. The Roman state itself was plunged into civil war several times, finally resulting in the marginalization of its 500 year old republic, and the embodiment of total state power in a single man - the emperor. The internal turbulence which plagued Rome at this time can be seen as the last death throes of the Roman Republic, as it finally gave way to the autocratic ambitions of powerful men like Julius Caesar, Mark Antony and Octavian. Octavian's ascension to total power as the emperor Augustus is considered to mark the point in history where the Roman Republic ends and the Roman Empire begins. Some scholars refer to this event as the Roman Revolution. It is generally concluded that the birth of Jesus, the central figure of Christianity took place at the close of this century.
Events
- 92 BC Lucullus invades Armenia, setting off the centuries long Roman vs Persian Wars.
- 81 BC Sulla is appointed dictator of the Roman state, and brings about major reforms.
- 73 BC A slave rebellion lead by the escaped gladiator Spartacus leads to the Third Servile War.
- 63 BC Pompey captures Jerusalem, and establishes Roman annexation of Judea as a client kingdom. King Judah Aristobulus II removed from power, while his brother John Hyrcanus II becomes king under Roman suzerainty.
- 57 BC Silla is founded in southeastern Korea (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi, a 12th century AD historical document).
- 53 BC The Parthians defeat the Romans under Crassus in the Battle of Carrhae
- 49 BC January 10: Julius Caesar crossed the Rubicon river, precipitating war with Rome
- 44 BC Julius Caesar murdered
- 37 BC Goguryeo is founded in southern Manchuria (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi)
- 31 BC Roman Civil War: Battle of Actium - Off the western coast of Greece, forces of Octavian defeat troops under Mark Antony and Cleopatra.
- 27 BC The Roman Senate votes Octavian the title of Augustus. Augustus eventually assumes all authority formerly held by the Roman senate becoming the first emperor. The Roman state is henceforth known as the Roman Empire, and the period from 27 BC to AD 305 as the Principate.
- 18 BC Baekje is founded in midwestern Korea (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi)
- c. 6 to 4 BC Birth of Jesus of Nazareth (see Chronology of Jesus' birth and death and Anno Domini for further details)
Significant persons

Cicero Denouncing Catiline by Cesare Maccari.One of several political conflicts in the Roman Republic during this century

An ancient stone tablet depicting Cleopatra VII and Ptolemy XV Philopator Philometor Caesar, Alexandria, Egypt. These two rulers were the last Pharaohs
- Burebista, greatest king of Dacia
- Catiline, attempted to overthrow Roman Republic
- Caesar Augustus, Roman emperor
- Cicero, Roman politician and writer
- Cleopatra VII of Egypt, Egyptian ruler
- Herod the Great
- Hillel the Elder, Jewish rabbi
- Horace, Roman poet
- Jesus of Nazareth, central figure of Christianity
- Jing Fang, Chinese mathematician and music theorist
- Julius Caesar, Roman politician
- Livy, Roman historian
- Lucretius, Roman philosopher
- Marcus Antonius, Roman politician
- Marcus Junius Brutus, Caesar's adopted son, supposedly killed him
- Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Roman statesman and general
- Marcus Vitruvius Pollio Roman writer, architect and engineer
- Sextus Pompeius, Roman general
- Ptolemy XIII of Egypt, drowned in Nile
- Ovid, Roman poet
- Virgil, Roman poet
- Spartacus, gladiator
- Sima Qian, Chinese historian, father of Chinese historiography
- Tigranes the Great, king of Armenia
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- Sunspots, first recorded by Chinese
- The Antikythera mechanism is made
- The first dome was built by the Romans
- Glass blowing is invented in Roman Syria
- The Chinese Ji Jiu Pian dictionary published in 40 BC during the Han Dynasty is the earliest known reference to the hydraulic-powered trip hammer device.
Decades and years
|
Decades and years |
|
|
1st century BC 3rd century BC← 2nd century BC← ↔ →1st century→2nd century
| 100s BC |
109 BC |
108 BC |
107 BC |
106 BC |
105 BC |
104 BC |
103 BC |
102 BC |
101 BC |
100 BC |
| 90s BC |
99 BC |
98 BC |
97 BC |
96 BC |
95 BC |
94 BC |
93 BC |
92 BC |
91 BC |
90 BC |
| 80s BC |
89 BC |
88 BC |
87 BC |
86 BC |
85 BC |
84 BC |
83 BC |
82 BC |
81 BC |
80 BC |
| 70s BC |
79 BC |
78 BC |
77 BC |
76 BC |
75 BC |
74 BC |
73 BC |
72 BC |
71 BC |
70 BC |
| 60s BC |
69 BC |
68 BC |
67 BC |
66 BC |
65 BC |
64 BC |
63 BC |
62 BC |
61 BC |
60 BC |
| 50s BC |
59 BC |
58 BC |
57 BC |
56 BC |
55 BC |
54 BC |
53 BC |
52 BC |
51 BC |
50 BC |
| 40s BC |
49 BC |
48 BC |
47 BC |
46 BC |
45 BC |
44 BC |
43 BC |
42 BC |
41 BC |
40 BC |
| 30s BC |
39 BC |
38 BC |
37 BC |
36 BC |
35 BC |
34 BC |
33 BC |
32 BC |
31 BC |
30 BC |
| 20s BC |
29 BC |
28 BC |
27 BC |
26 BC |
25 BC |
24 BC |
23 BC |
22 BC |
21 BC |
20 BC |
| 10s BC |
19 BC |
18 BC |
17 BC |
16 BC |
15 BC |
14 BC |
13 BC |
12 BC |
11 BC |
10 BC |
| 0s BC |
9 BC |
8 BC |
7 BC |
6 BC |
5 BC |
4 BC |
3 BC |
2 BC |
1 BC |
|
| 0s |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
|
|
Centuries and millennia |
|
|
| Millennium |
Century |
| BC |
| 4th |
40th |
39th |
38th |
37th |
36th |
35th |
34th |
33rd |
32nd |
31st |
| 3rd |
30th |
29th |
28th |
27th |
26th |
25th |
24th |
23rd |
22nd |
21st |
| 2nd |
20th |
19th |
18th |
17th |
16th |
15th |
14th |
13th |
12th |
11th |
| 1st |
10th |
9th |
8th |
7th |
6th |
5th |
4th |
3rd |
2nd |
1st |
| AD |
| 1st |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
6th |
7th |
8th |
9th |
10th |
| 2nd |
11th |
12th |
13th |
14th |
15th |
16th |
17th |
18th |
19th |
20th |
| 3rd |
21st |
22nd |
23rd |
24th |
25th |
26th |
27th |
28th |
29th |
30th |
| 4th |
31st |
|
|



