2nd century
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General history
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 1st century · 2nd century · 3rd century |
| Decades: | 100s 110s 120s 130s 140s 150s 160s 170s 180s 190s |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
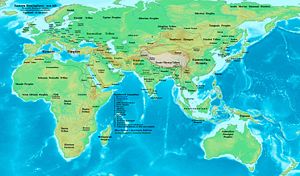
The 2nd century is the period from 101 to 200 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period
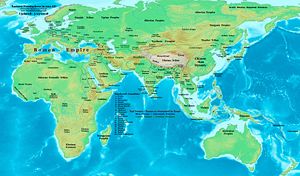
Early in the century, the Roman Empire attained its greatest expansion under the emperor Trajan, but after his death became primarily defensive for the rest of its history. Much prosperity took place throughout the empire at this time, ruled as it were by the Five Good Emperors, a succession of just and able rulers. This period also saw the removal of the Jews from Jerusalem during the reign of Hadrian after Bar Kokhba's revolt. The last quarter of the century saw the end of the period of peace and prosperity known as the Pax Romana at the death of the emperor Marcus Aurelius, last of the " Five Good Emperors", and the accession of his ineffective and deranged son Commodus.
Although the Han Dynasty of China was firmly cemented into power and extended its imperial influence into Central Asia during the first half of the century, by the second half there was widespread corruption and open rebellion. This set in motion its ultimate decline, until it was overthrown in 220.
Events
- 96–180: Five Good Emperors of Rome: Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, Marcus Aurelius
- The kingdom of Aksum emerges
- 122–132: Hadrian's Wall across Britain
- 132–135: Bar Kokhba's revolt against Rome
- 144: Marcion, rejected by Church of Rome, founds Marcionism
- 167–175: First Marcomanni War
- 178–180: Second Marcomanni War (depicted in the movie Gladiator)
- 184–205: the Yellow Turban Rebellion of the Han Dynasty in China begins
Significant persons
- Rabbi Akiva Head of all the Jewish Sages
- Rabbi Yehuda haNasi Prince of the Jewish people
- Commodus, Roman Emperor, claimed to be Hercules reincarnated
- Galen, medical writer
- Irenaeus, second bishop of Lyon
- Juvenal Roman satirical poet
- Montanus, Christian heretic
- Nagarjuna, founder of Madhyamaka Buddhism
- Pliny the Younger
- Plutarch, Greek historian
- Ptolemy, Greek astronomer, astrologer and geographer
- Septimius Severus, Roman Emperor
- Suetonius, Roman historian
- Valentinius, most famous Christian Gnostic
- Zhang Daoling, Chinese Taoist hermit
- Zhang Heng, Chinese statesman, poet, inventor, astronomer, geographer, and engineer
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- Cai Lun of China invents paper (c. 105)
- Ptolemy compiles a catalogue of all stars visible to the naked eye. He also compiles three of the most influential books in western history:
-
- the Almagest which becomes the basis for western and Middle Eastern astronomy until the time of Copernicus and Kepler;
- the astrological treatise, Tetrabiblos;
- and the Geographia
- 125: Zhang Heng of China invents the world's first water-powered armillary sphere
- 132: Zhang Heng of China invents first seismometer to detect the cardinal direction of earthquakes
Decades and years
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||