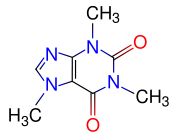
Caffeine
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Chemical compounds; Drink
| Caffeine | |
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| IUPAC name | 1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione |
| Other names | 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, trimethylxanthine, theine, methyltheobromine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | [58-08-2] |
| RTECS number | EV6475000 |
| SMILES | C[n]1cnc2N(C)C(=O)N(C)C(=O)c12 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Odorless, white needles or powder |
| Density | 1.2 g·cm−3, solid |
| Melting point |
237 °C (non-equilibrium, superheated) |
| Boiling point |
178 °C ( sublimes) |
| Solubility in water | 22 mg·mL−1 (25 °C) 180 mg·mL−1 (80 °C) 670 mg·mL−1 (100 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| Main hazards | May be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin. |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | N/A |
| LD50 | 192 mg/kg (rat) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references |
|
Caffeine is a bitter white crystalline xanthine alkaloid compound that acts as a psychoactive stimulant drug and a mild diuretic in humans. Caffeine was discovered by a German chemist, Friedrich Ferdinand Runge, in 1819. He coined the term "kaffein," a chemical compound in coffee, which in English became caffeine. Caffeine is also called guaranine when found in guarana, mateine when found in mate, and theine when found in tea; all of these names are synonyms for the same chemical compound.
Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the beans, leaves, and fruit of over 60 plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants. It is most commonly consumed by humans in infusions extracted from the beans of the coffee plant and the leaves of the tea bush, as well as from various foods and drinks containing products derived from the kola nut or from cacao. Other sources include yerba mate, guarana berries, and the Yaupon Holly.
In humans, caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant, having the effect of temporarily warding off drowsiness and restoring alertness. Beverages containing caffeine, such as coffee, tea, soft drinks and energy drinks enjoy great popularity; caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive substance, but unlike most other psychoactive substances, it is legal and unregulated in nearly all jurisdictions. In North America, 90% of adults consume caffeine daily. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration lists caffeine as a "Multiple Purpose Generally Recognized as Safe Food Substance". Recent research, however, suggests that regular caffeine use during pregnancy may increase the risk of miscarriage.
Occurrence
Caffeine is a plant alkaloid, found in many plant species, where it acts as a natural pesticide, with high caffeine levels being reported in seedlings that are still developing foliages, but are lacking mechanical protection; caffeine paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding upon the plant. High caffeine levels have also been found in the surrounding soil of coffee bean seedlings. It is therefore understood that caffeine has a natural function in both a natural pesticide and as an inhibitor of seed germination of other nearby coffee seedlings thus giving it a better chance of survival.
The most commonly used caffeine-containing plants are coffee, tea, and to a lesser extent cocoa. Other, less commonly used, sources of caffeine include the yerba mate and guarana plants, which are sometimes used in the preparation of teas and energy drinks. Two of caffeine's alternative names, mateine and guaranine, are derived from the names of these plants. Some yerba mate enthusiasts assert that mateine is a stereoisomer of caffeine, which would make it a different substance altogether. However, caffeine is an achiral molecule, and therefore has no enantiomers; nor does it have other stereoisomers. Many natural sources of caffeine also contain widely varying mixtures of other xanthine alkaloids, including the cardiac stimulants theophylline and theobromine and other substances such as polyphenols which can form insoluble complexes with caffeine.
The world's primary source of caffeine is the coffee bean (the seed of the coffee plant), from which coffee is brewed. Caffeine content in coffee varies widely depending on the type of coffee bean and the method of preparation used; even beans within a given bush can show variations in concentration. In general, one serving of coffee ranges from 40 milligrams, for a single shot (30 milliliters) of arabica-variety espresso, to about 100 milligrams for a cup (120 milliliters) of drip coffee. Generally, dark-roast coffee has less caffeine than lighter roasts because the roasting process reduces the bean's caffeine content. Arabica coffee normally contains less caffeine than the robusta variety. Coffee also contains trace amounts of theophylline, but no theobromine.
Tea is another common source of caffeine. Tea usually contains about half as much caffeine per serving as coffee, depending on the strength of the brew. Certain types of tea, such as black and oolong, contain somewhat more caffeine than most other teas. Tea contains small amounts of theobromine and slightly higher levels of theophylline than coffee. Preparation has a significant impact on tea, and colour is a very poor indicator of caffeine content. Teas like the pale Japanese green tea gyokuro, for example, contain far more caffeine than much darker teas like lapsang souchong, which has very little.
Caffeine is also a common ingredient of soft drinks such as cola, originally prepared from kola nuts. Soft drinks typically contain about 10 to 50 milligrams of caffeine per serving. By contrast, energy drinks such as Red Bull contain as much as 80 milligrams of caffeine per serving. The caffeine in these drinks either originates from the ingredients used or is an additive derived from the product of decaffeination or from chemical synthesis. Guarana, a prime ingredient of energy drinks, contains large amounts of caffeine with small amounts of theobromine and theophylline in a naturally occurring slow-release excipient.
Chocolate derived from cocoa contains a small amount of caffeine. The weak stimulant effect of chocolate may be due to a combination of theobromine and theophylline as well as caffeine. Chocolate contains too little of these compounds for a reasonable serving to create effects in humans that are on par with coffee. A typical 28-gram serving of a milk chocolate bar has about as much caffeine as a cup of decaffeinated coffee.
In recent years various manufacturers have begun putting caffeine into shower products such as shampoo and soap, claiming that caffeine can be absorbed through the skin. However, the effectiveness of such products has not been proven, and they are likely to have little stimulatory effect on the central nervous system because caffeine is not readily absorbed through the skin.
History
Humans have consumed caffeine since the Stone Age. Early peoples found that chewing the seeds, bark, or leaves of certain plants had the effects of easing fatigue, stimulating awareness, and elevating mood. Only much later was it found that the effect of caffeine was increased by steeping such plants in hot water. Many cultures have legends that attribute the discovery of such plants to people living many thousands of years ago.
According to one popular Chinese legend, the Emperor of China Shennong, reputed to have reigned in about 3,000 BCE, accidentally discovered that when some leaves fell into boiling water, a fragrant and restorative drink resulted. Shennong is also mentioned in Lu Yu's Cha Jing, a famous early work on the subject of tea. The history of coffee has been recorded as far back as the ninth century. During that time, coffee beans were available only in their native habitat, Ethiopia. A popular legend traces its discovery to a goatherder named Kaldi, who apparently observed goats that became elated and sleepless at night after browsing on coffee shrubs and, upon trying the berries that the goats had been eating, experienced the same vitality. The earliest literary mention of coffee may be a reference to Bunchum in the works of the 9th century Persian physician al-Razi. In 1587, Malaye Jaziri compiled a work tracing the history and legal controversies of coffee, entitled "Undat al safwa fi hill al-qahwa". In this work, Jaziri recorded that one Sheikh, Jamal-al-Din al-Dhabhani, mufti of Aden, was the first to adopt the use of coffee in 1454, and that in the 15th century the Sufis of Yemen routinely used coffee to stay awake during prayers.
Towards the close of the 16th century, the use of coffee was recorded by a European resident in Egypt, and about this time it came into general use in the Near East. The appreciation of coffee as a beverage in Europe, where it was first known as "Arabian wine," dates from the 17th century. During this time " coffee houses" were established, the first being opened in Constantinople and Venice. In Britain, the first coffee houses were opened in London in 1652, at St Michael's Alley, Cornhill. They soon became popular throughout Western Europe, and played a significant role in social relations in the 17th and 18th centuries.
The kola nut, like the coffee berry and tea leaf, appears to have ancient origins. It is chewed in many West African cultures, individually or in a social setting, to restore vitality and ease hunger pangs. In 1911, kola became the focus of one of the earliest documented health scares when the US government seized 40 barrels and 20 kegs of Coca-Cola syrup in Chattanooga, Tennessee, alleging that the caffeine in its drink was "injurious to health". On March 13, 1911, the government initiated The United States v. Forty Barrels and Twenty Kegs of Coca-Cola, hoping to force Coca-Cola to remove caffeine from its formula by making claims, such as that the excessive use of Coca-Cola at one girls' school led to "wild nocturnal freaks, violations of college rules and female proprieties, and even immoralities." Although the judge ruled in favour of Coca-Cola, two bills were introduced to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1912 to amend the Pure Food and Drug Act, adding caffeine to the list of "habit-forming" and "deleterious" substances which must be listed on a product's label.
The earliest evidence of cocoa use comes from residue found in an ancient Mayan pot dated to 600 BCE. In the New World, chocolate was consumed in a bitter and spicy drink called xocoatl, often seasoned with vanilla, chile pepper, and achiote. Xocoatl was believed to fight fatigue, a belief that is probably attributable to the theobromine and caffeine content. Chocolate was an important luxury good throughout pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, and cocoa beans were often used as currency.
Chocolate was introduced to Europe by the Spaniards and became a popular beverage by 1700. They also introduced the cacao tree into the West Indies and the Philippines. It was used in alchemical processes, where it was known as Black Bean.
In 1819, the German chemist Friedrich Ferdinand Runge isolated relatively pure caffeine for the first time. According to Runge, he did this at the behest of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. In 1927, Oudry isolated "theine" from tea, but it was later proved by Mulder and Jobat that theine was the same as caffeine. The structure of caffeine was elucidated near the end of the 19th century by Hermann Emil Fischer, who was also the first to achieve its total synthesis. This was part of the work for which Fischer was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1902.
Today, global consumption of caffeine has been estimated at 120,000 tons per annum, making it the world's most popular psychoactive substance. This number equates to one serving of a caffeine beverage for every person, per day. In North America, 90% of adults consume some amount of caffeine daily.
Pharmacology
Caffeine is a central nervous system and metabolic stimulant, and is used both recreationally and medically to reduce physical fatigue and restore mental alertness when unusual weakness or drowsiness occurs. Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system first at the higher levels, resulting in increased alertness and wakefulness, faster and clearer flow of thought, increased focus, and better general body coordination, and later at the spinal cord level at higher doses. Once inside the body, it has a complex chemistry, and acts through several mechanisms as described below.
Metabolism
Caffeine is completely absorbed by the stomach and small intestine within 45 minutes of ingestion. After ingestion it is distributed throughout all tissues of the body and is eliminated by first-order kinetics.
The half-life of caffeine—the time required for the body to eliminate one-half of the total amount of caffeine consumed at a given time—varies widely among individuals according to such factors as age, liver function, pregnancy, some concurrent medications, and the level of enzymes in the liver needed for caffeine metabolism. In healthy adults, caffeine's half-life is approximately 3–4 hours. In women taking oral contraceptives this is increased to 5–10 hours, and in pregnant women the half-life is roughly 9–11 hours. Caffeine can accumulate in individuals with severe liver disease when its half-life can increase to 96 hours. In infants and young children, the half-life may be longer than in adults; half-life in a newborn baby may be as long as 30 hours. Other factors such as smoking can shorten caffeine's half-life.
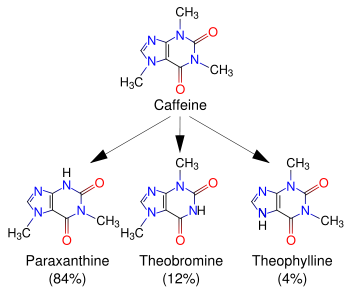
Caffeine is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 oxidase enzyme system (specifically, the 1A2 isozyme) into three metabolic dimethylxanthines, which each have their own effects on the body:
- Paraxanthine (84%): Has the effect of increasing lipolysis, leading to elevated glycerol and free fatty acid levels in the blood plasma.
- Theobromine (12%): Dilates blood vessels and increases urine volume. Theobromine is also the principal alkaloid in cocoa, and therefore chocolate.
- Theophylline (4%): Relaxes smooth muscles of the bronchi, and is used to treat asthma. The therapeutic dose of theophylline, however, is many times greater than the levels attained from caffeine metabolism.
Each of these metabolites is further metabolized and then excreted in the urine.
Mechanism of action
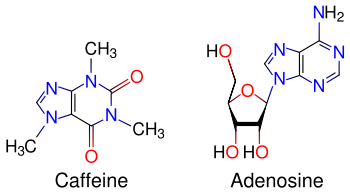
Caffeine acts through multiple mechanisms involving both action on receptors and channels on the cell membrane, as well as intracellular action on calcium and cAMP pathways. By virtue of its purine structure it can act on some of the same targets as adenosine related nucleosides and nucleotides, like the cell surface P1 GPCRs for adenosine, as well as the intracellular Ryanodine receptor (RyR) which is the physiological target of cADPR ( cyclic ADP-ribose), and cAMP-phosphodiesterase (cAMP-PDE). Although the action is agonistic in some cases, it is antagonistic in others. Physiologically, however, caffeine action is unlikely due to increased RyR opening, as it requires plasma concentration above lethal dosage. The action is most likely through adenosine receptors.
Like alcohol, nicotine, and antidepressants, caffeine readily crosses the blood brain barrier. Once in the brain, the principal mode of action of caffeine is as an antagonist of adenosine receptors found in the brain. The caffeine molecule is structurally similar to adenosine, and binds to adenosine receptors on the surface of cells without activating them (an "antagonist" mechanism of action). Therefore, caffeine acts as a competitive inhibitor. The reduction in adenosine activity results in increased activity of the neurotransmitter dopamine, largely accounting for the stimulatory effects of caffeine. Caffeine can also increase levels of epinephrine/adrenaline, possibly via a different mechanism. Acute usage of caffeine also increases levels of serotonin, causing positive changes in mood.
Caffeine is also a known competitive inhibitor of the enzyme cAMP-phosphodiesterase (cAMP-PDE), which converts cyclic AMP (cAMP) in cells to its noncyclic form, allowing cAMP to build up in cells. Cyclic AMP participates in activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA) to begin the phosphorylation of specific enzymes used in glucose synthesis. By blocking its removal caffeine intensifies and prolongs the effects of epinephrine and epinephrine-like drugs such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, or methylphenidate. Increased concentrations of cAMP in parietal cells causes an increased activation of protein kinase A (PKA) which in turn increases activation of H+/K+ ATPase, resulting finally in increased gastric acid secretion by the cell.
Caffeine (and theophylline) can freely diffuse into cells and causes intracellular calcium release (independent of extracellular calcium) from the calcium stores in the endoplasmic reticulum(ER). This release is only partially blocked by Ryanodine receptor blockade with ryanodine, dantrolene, ruthenium red, and procaine (thus may involve ryanodine receptor and probably some additional calcium channels), but completely abolished after calcium depletion of ER by SERCA inhibitors like Thapsigargin (TG) or cyclopiazonic acid (CPA). The action of caffeine on the ryanodine receptor may depend on both cytosolic and the luminal ER concentrations of Ca2+. At low millimolar concentration of caffeine, the RyR channel open probability (Po) is significantly increased mostly due to a shortening of the lifetime of the closed state. At concentrations >5 mM, caffeine opens RyRs even at picomolar cytosolic Ca2+ and dramatically increases the open time of the channel so that the calcium release is stronger than even an action potential can generate. This mode of action of caffeine is probably due to mimicking the action of the physiologic metabolite of NAD called cADPR ( cyclic ADP ribose) which has a similar potentiating action on Ryanodine receptors.
Caffeine may also directly inhibit delayed rectifier and A-type K+ currents and activate plasmalemmal Ca2+ influx in certain vertebrate and invertebrate neurons.
The metabolites of caffeine contribute to caffeine's effects. Theobromine is a vasodilator that increases the amount of oxygen and nutrient flow to the brain and muscles. Theophylline, the second of the three primary metabolites, acts as a smooth muscle relaxant that chiefly affects bronchioles and acts as a chronotrope and inotrope that increases heart rate and efficiency. The third metabolic derivative, paraxanthine, is responsible for an increase in the lipolysis process, which releases glycerol and fatty acids into the blood to be used as a source of fuel by the muscles.

Effects when taken in moderation
The precise amount of caffeine necessary to produce effects varies from person to person depending on body size and degree of tolerance to caffeine. It takes less than an hour for caffeine to begin affecting the body and a mild dose wears off in three to four hours. Consumption of caffeine does not eliminate the need for sleep: it only temporarily reduces the sensation of being tired.
With these effects, caffeine is an ergogenic: increasing the capacity for mental or physical labor. A study conducted in 1979 showed a 7% increase in distance cycled over a period of two hours in subjects who consumed caffeine compared to control tests. Other studies attained much more dramatic results; one particular study of trained runners showed a 44% increase in "race-pace" endurance, as well as a 51% increase in cycling endurance, after a dosage of 9 milligrams of caffeine per kilogram of body weight. The extensive boost shown in the runners is not an isolated case; additional studies have reported similar effects. Another study found 5.5 milligrams of caffeine per kilogram of body mass resulted in subjects cycling 29% longer during high intensity circuits.
Breathing problems in premature infants, apnea of prematurity, are sometimes treated with citrated caffeine, which is available only by prescription in many countries. A reduction in bronchopulmonary dysplasia has been exhibited in premature infants treated with caffeine citrate therapy regimens. The only short term risk associated with this treatment is a temporary reduction in weight gain during the therapy. Longer term studies (18 to 21 months) have shown lasting benefits of treatment of premature infants with caffeine.
While relatively safe for humans, caffeine is considerably more toxic to some other animals such as dogs, horses and parrots due to a much poorer ability to metabolize this compound. Caffeine has a much more significant effect on spiders, for example, than most other drugs do.
Caffeine relaxes the internal anal sphincter muscles, causing a laxative effect and thus should be avoided by those with incontinence.
Tolerance and withdrawal
| Product | Serving size | Caffeine per serving ( mg) | Caffeine per litre ( mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine tablet (regular strength) | 1 tablet | 100 | — |
| Caffeine tablet (extra strength) | 1 tablet | 200 | — |
| Excedrin tablet | 1 tablet | 65 | — |
| Chocolate, Dark ( Hershey's Special Dark) | 1 bar (43 g; 1.5 oz) | 31 | — |
| Chocolate, Milk (Hershey Bar) | 1 bar (43 g; 1.5 oz) | 10 | — |
| Coffee, brewed | 240 mL (8 U.S. fl oz) | 135* | 563* |
| Coffee, decaffeinated | 240 mL (8 U.S. fl oz) | 5* | 21* |
| Coffee, espresso | 57 mL (2 U.S. fl oz) | 100* | 1750* |
| Tea, leaf or bag | 240 mL (8 U.S. fl oz) | 50* | 208* |
| Tea, green | 240 mL (8 U.S. fl oz) | 30* | 63* |
| Soft drink, Coca-Cola Classic | 355 mL (12 U.S. fl oz) | 34 | 96 |
| Soft drink, Mountain Dew | 355 mL (12 U.S. fl oz) | 54.5 | 154 |
| Soft drink, Jolt Cola | 694 mL (23.5 U.S. fl oz) | 150 | 216 |
| Red Bull | 250 mL (8.2 U.S. fl oz) | 80 | 320 |
Because caffeine is primarily an antagonist of the central nervous system's receptors for the neurotransmitter adenosine, the bodies of individuals who regularly consume caffeine adapt to the continual presence of the drug by substantially increasing the number of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system. This increase in the number of the adenosine receptors makes the body much more sensitive to adenosine, with two primary consequences. First, the stimulatory effects of caffeine are substantially reduced, a phenomenon known as a tolerance adaptation. Second, because these adaptive responses to caffeine make individuals much more sensitive to adenosine, a reduction in caffeine intake will effectively increase the normal physiological effects of adenosine, resulting in unwelcome withdrawal symptoms in tolerant users.
Other research questions the idea that up-regulation of adenosine receptors is responsible for tolerance to the locomotor stimulant effects of caffeine, noting, among other things, that this tolerance is insurmountable by higher doses of caffeine (it should be surmountable if tolerance was due to an increase in receptors), and that the increase in adenosine receptor number is modest and doesn't explain the large tolerance which develops to caffeine.
Caffeine tolerance develops very quickly, especially among heavy coffee and energy drink consumers. Complete tolerance to sleep disruption effects of caffeine develops after consuming 400 mg of caffeine 3 times a day for 7 days. Complete tolerance to subjective effects of caffeine was observed to develop after consuming 300 mg 3 times per day for 18 days, and possibly even earlier. Partial tolerance to caffeine has been observed in all other areas, studies with mice indicate that after a long period of caffeine exposure the learning benefits of caffeine observed earlier cannot be found to any significant level. Considering that 80% to 90% of American adults consume caffeine daily, and their mean daily caffeine intake exceeds 200 mg/day, it can be surmised that a large fraction of the U.S. adult population is completely tolerant to most of the effects of caffeine.
Because adenosine, in part, serves to regulate blood pressure by causing vasodilation, the increased effects of adenosine due to caffeine withdrawal cause the blood vessels of the head to dilate, leading to an excess of blood in the head and causing a headache and nausea. Reduced catecholamine activity may cause feelings of fatigue and drowsiness. A reduction in serotonin levels when caffeine use is stopped can cause anxiety, irritability, inability to concentrate and diminished motivation to initiate or to complete daily tasks; in extreme cases it may cause mild depression. Together, these effects have come to be known as a "crash".
Withdrawal symptoms—possibly including headache, irritability, an inability to concentrate, and stomach aches—may appear within 12 to 24 hours after discontinuation of caffeine intake, peak at roughly 48 hours, and usually last from one to five days, representing the time required for the number of adenosine receptors in the brain to revert to "normal" levels, uninfluenced by caffeine consumption. Analgesics, such as aspirin, can relieve the pain symptoms, as can a small dose of caffeine. Most effective is a combination of both an analgesic and a small amount of caffeine.
This is not the only case where caffeine increases the effectiveness of a drug. Caffeine makes pain relievers 40% more effective in relieving headaches and helps the body absorb headache medications more quickly, bringing faster relief. For this reason, many over-the-counter headache drugs include caffeine in their formula. It is also used with ergotamine in the treatment of migraine and cluster headaches as well as to overcome the drowsiness caused by antihistamines.
Overuse
In large amounts, and especially over extended periods of time, caffeine can lead to a condition known as caffeinism. Caffeinism usually combines caffeine dependency with a wide range of unpleasant physical and mental conditions including nervousness, irritability, anxiety, tremulousness, muscle twitching ( hyperreflexia), insomnia, headaches, respiratory alkalosis and heart palpitations. Furthermore, because caffeine increases the production of stomach acid, high usage over time can lead to peptic ulcers, erosive esophagitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, since both "regular" and decaffeinated coffees have been shown to stimulate the gastric mucosa and increase stomach acid secretion, caffeine is probably not the sole component of coffee responsible.
There are four caffeine-induced psychiatric disorders recognized by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition: caffeine intoxication, caffeine-induced anxiety disorder, caffeine-induced sleep disorder, and caffeine-related disorder not otherwise specified (NOS).
Caffeine intoxication
An acute overdose of caffeine, usually in excess of 250 milligrams, can result in a state of central nervous system over-stimulation called caffeine intoxication. Some people seeking caffeine intoxication resort to insufflation (snorting) of caffeine powder, usually finely crushed caffeine tablets. This induces a faster and more intense reaction. The symptoms of caffeine intoxication are not unlike overdoses of other stimulants. It may include restlessness, nervousness, excitement, insomnia,flushing of the face, increased urination, gastrointestinal disturbance, muscle twitching, a rambling flow of thought and speech, irritability, irregular or rapid heart beat, and psychomotor agitation. In cases of much larger overdoses mania, depression, lapses in judgment, disorientation, loss of social inhibition, delusions, hallucinations, psychosis, rhabdomyolysis, and death may occur.
In cases of extreme overdose, death can result. The median lethal dose ( LD50) of caffeine is 192 milligrams per kilogram in rats. The LD50 of caffeine in humans is dependent on weight and individual sensitivity and estimated to be about 150 to 200 milligrams per kilogram of body mass, roughly 80 to 100 cups of coffee for an average adult taken within a limited timeframe that is dependent on half-life. Though achieving lethal dose with caffeine would be exceptionally difficult with regular coffee, there have been reported deaths from overdosing on caffeine pills, with serious symptoms of overdose requiring hospitalization occurring from as little as 2 grams of caffeine. Death typically occurs due to ventricular fibrillation brought about by effects of caffeine on the cardiovascular system.
Treatment of severe caffeine intoxication is generally supportive, providing treatment of the immediate symptoms, but if the patient has very high serum levels of caffeine then peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or hemofiltration may be required.
Anxiety and sleep disorders
Long-term overuse of caffeine can elicit a number of psychiatric disturbances. Two such disorders recognized by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) are caffeine-induced sleep disorder and caffeine-induced anxiety disorder.
In the case of caffeine-induced sleep disorder, an individual regularly ingests high doses of caffeine sufficient to induce a significant disturbance in his or her sleep, sufficiently severe to warrant clinical attention. A study in the British Journal of Addiction concluded that caffeinism, although infrequently diagnosed, may afflict as many as one person in ten of the population.
Parkinson's disease
Several large studies have shown that caffeine intake is associated with a reduced risk of developing Parkinson's disease (PD) in men, but studies in women have been inconclusive. The mechanism by which caffeine affects PD remains a mystery. In animal models, researchers have shown that caffeine can prevent the loss of dopamine-producing nerve cells seen in Parkinson's Disease, but researchers still do not know how this occurs.
Effects on memory and learning
An array of studies found that caffeine could have nootropic effects, inducing certain changes in memory and learning. However, it is still not definitely clear whether the effect is negative or positive.
In one study, caffeine was added to rat neurons in vitro. The dendritic spines (a part of the brain cell used in forming connections between neurons) taken from the hippocampus (a part of the brain associated with memory), grew by 33% and new spines formed. After an hour or two, however, these cells returned to their original shape.
Another study showed that subjects—after receiving 100 milligrams of caffeine—had increased activity in brain regions located in the frontal lobe, where a part of the working memory network is located, and the anterior cingulum, a part of the brain that controls attention. The caffeinated subjects also performed better on the memory tasks.
However, a different study showed that caffeine could impair short term memory and increase the likelihood of the tip of the tongue phenomenon. The study allowed the researchers to suggest that caffeine could aid short-term memory when the information to be recalled is related to the current train of thought, but also to hypothesize that caffeine hinders short-term memory when the train of thought is unrelated. In essence, focused thought coupled with caffeine consumption increases mental performance.
Effects on the heart
Caffeine increases the levels of cAMP in the heart cells, mimicking the effects of epinephrine. cAMP diffuses through the cell and acts as a "secondary messenger," activating protein kinase A (PKA; cAMP-dependent protein kinase). According to one study, caffeine, in the form of coffee, significantly reduces the risk of heart disease in epidemiological studies. However, the protective effect was found only in participants who were not severely hypertensive (i.e. patients that are not suffering from a very high blood pressure). Furthermore, no significant protective effect was found in participants aged less than 65 years or in cerebrovascular disease mortality for those aged equal or more than 65 years.
Effects on children
It is commonly believed that caffeine consumption causes stunted growth in children, but this is not supported by scientific research. However, just as with adults, there is legitimate reason to limit the amount consumed by children.
Caffeine intake during pregnancy
The Food Standards Agency has recommended that pregnant women should limit their caffeine intake to less than 300 mg of caffeine a day – the equivalent of four cups of coffee a day. A higher intake may be associated with miscarriage.
Dr De-Kun Li of Kaiser Permanente Division of Research, which appears in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, concludes that an intake of 200 milligrams or more per day, representing two or more cups, "significantly increases the risk of miscarriage". However, an epidemiologic study published in early January 2008 found no observable increase in risk on miscarriage from caffeine
Production
Being readily available as a byproduct of decaffeination of tea and coffee, caffeine is not usually manufactured. If desired, it may be synthesized from dimethyl urea and malonic acid.
Decaffeination
Pure caffeine is a white powder, and can be extracted from a variety of natural sources. Caffeine extraction is an important industrial process and can be performed using a number of different solvents. Benzene, chloroform, trichloroethylene and dichloromethane have all been used over the years but for reasons of safety, environmental impact, cost and flavor, they have been superseded by the following main methods:
Water extraction
Coffee beans are soaked in water. The water, which contains not only caffeine but also many other compounds which contribute to the flavor of coffee, is then passed through activated charcoal, which removes the caffeine. The water can then be put back with the beans and evaporated dry, leaving decaffeinated coffee with a good flavor. Coffee manufacturers recover the caffeine and resell it for use in soft drinks and over-the-counter caffeine tablets.
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction
Supercritical carbon dioxide is an excellent nonpolar solvent for caffeine (as well as many other organic compounds), and is safer than the organic solvents that are used for caffeine extraction. The extraction process is simple: CO2 is forced through the green coffee beans at temperatures above 31.1 °C and pressures above 73 atm. Under these conditions, CO2 is in a " supercritical" state: it has gaslike properties which allow it to penetrate deep into the beans but also liquid-like properties which dissolve 97–99% of the caffeine. The caffeine-laden CO2 is then sprayed with high pressure water to remove the caffeine. The caffeine can then be isolated by charcoal adsorption (as above) or by distillation, recrystallization, or reverse osmosis.
Extraction by nonhazardous organic solvents
Organic solvents such as ethyl acetate present much less health and environmental hazard than previously used chlorinated and aromatic solvents. The hydrolysis products of ethyl acetate are ethanol and acetic acid, both nonhazardous in small quantities. Another method is to use triglyceride oils obtained from spent coffee grounds.
Stereochemistry
The nitrogen atoms are all essentially planar. Even though some are often drawn with three single bonds, the lone pairs on these atoms are involved in resonance with adjacent double-bonded carbon atoms, and thus adopt an sp2 orbital hybridisation.