Fibreglass
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Engineering
Fibreglass (also called fibreglass and glass fibre) is material made from extremely fine fibers of glass. It is used as a reinforcing agent for many polymer products; the resulting composite material, properly known as fibre-reinforced polymer (FRP) or glass-reinforced plastic (GRP), is called "fibreglass" in popular usage.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of fibreglass was only made possible with the advent of finer machine-tooling. In 1893, Edward Drummond Libbey exhibited a dress at the World's Columbian Exposition incorporating glass fibers with the diameter and texture of silk fibers. What is commonly known as "fibreglass" today, however, was invented in 1938 by Russell Games Slayter of Owens-Corning as a material to be used as insulation. It is marketed under the trade name Fiberglas, which has become a genericized trademark.
Formation
Glass fibre is formed when thin strands of silica-based or other formulation glass is extruded into many fibers with small diameters suitable for textile processing. Glass, even as a fibre, has little crystalline structure (see amorphous solid). The properties of the structure of glass in its softened stage are very much like its properties when spun into fibre. One definition of glass is "an inorganic substance in a condition which is continuous with, and analogous to the liquid state of that substance, but which, as a result of a reversible change in viscosity during cooling, has attained so high a degree of viscosity as to be for all practical purposes rigid."
The technique of heating and drawing glass into fine fibers has been known for millennia; however, the use of these fibers for textile applications is more recent. The first commercial production of fibreglass was in 1936. In 1938, Owens-Illinois Glass Company and Corning Glass Works joined to form the Owens-Corning Fiberglas Corporation. Until this time all fibreglass had been manufactured as staple. When the two companies joined together to produce and promote fibreglass, they introduced continuous filament glass fibers. Owens-Corning is still the major fibreglass producer in the market today.
Chemistry
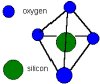
The basis of textile grade glass fibers is silica, SiO2. In its pure form it exists as a polymer, (SiO2)n. It has no true melting point but softens up to 2000°C, where it starts to degrade. At 1713°C, most of the molecules can move about freely. If the glass is then cooled quickly, they will be unable to form an ordered structure. In the polymer it forms SiO4 groups which are configured as a tetrahedron with the silicon atom at the centre, and four oxygen atoms at the corners. These atoms then form a network bonded at the corners by sharing the oxygen atoms.
The vitreous and crystalline states of silica (glass and quartz) have similar energy levels on a molecular basis, also implying that the glassy form is extremely stable. In order to induce crystallization, it must be heated to temperatures above 1200°C for long periods of time.
Although pure silica is a perfectly viable glass and glass fiber, it must be worked with at very high temperatures which is a drawback unless its specific chemical properties are needed. It is usual to introduce impurities into the glass in the form of other materials, to lower its working temperature. These materials also impart various other properties to the glass which may be beneficial in different applications. The first type of glass used for fibre was soda lime glass or A glass. It was not very resistant to alkali. A new type, E-glass was formed that is alkali free (< 2%) and is an alumino-borosilicate glass. This was the first glass formulation used for continuous filament formation. E-glass still makes up most of the fibreglass production in the world. Its particular components may differ slightly in percentage, but must fall within a specific range. The letter E is used because it was originally for electrical applications. S-glass is a high strength formulation for use when tensile strength is the most important property. C-glass was developed to resist attack from chemicals, mostly acids which destroy E-glass. T-glass is a North American variant of C-glass. A-glass is an industry term for cullet glass, often bottles, made into fibre. AR-glass is alkali resistant glass. Most glass fibers have limited solubility in water but it is very dependent on pH. Chloride ions will also attack and dissolve E-glass surfaces. A recent trend in the industry is to reduce or eliminate the boron content in the glass fibers.
Since E-glass does not really melt but soften, the softening point is defined as "the temperature at which a 0.55 – 0.77 mm diameter fibre 235 mm long, elongates under its own weight at 1 mm/min when suspended vertically and heated at the rate of 5°C per minute". The strain point is reached when the glass has a viscosity of 1014.5 poise. The annealing point, which is the temperature where the internal stresses are reduced to an acceptable commercial limit in 15 minutes, is marked by a viscosity of 1013 poise.
Properties
Glass fibers are useful because of their high ratio of surface area to weight. However, the increased surface area makes them much more susceptible to chemical attack.
By trapping air within them, blocks of glass fibre make good thermal insulation, with a thermal conductivity of 0.05 W/m-K.
Glass strengths are usually tested and reported for "virgin" fibers: those which have just been manufactured. The freshest, thinnest fibers are the strongest because the thinner fibers are more ductile. The more the surface is scratched, the less the resulting tenacity. Because glass has an amorphous structure, its properties are the same along the fiber and across the fibre. Humidity is an important factor in the tensile strength. Moisture is easily adsorbed, and can worsen microscopic cracks and surface defects, and lessen tenacity.
In contrast to carbon fibre, glass can undergo more elongation before it breaks. There is a correlation between bending diameter of the filament and the filament diameter. See KH Hillermeier, 1973, Freudenstadt. The viscosity of the molten glass is very important for manufacturing success. During drawing (pulling of the glass to reduce fiber circumference) the viscosity should be relatively low. If it is too high the fiber will break during drawing, however if it is too low the glass will form droplets rather than drawing out into fibre.
Manufacturing processes
Melting
There are two main types of glass fiber manufacture and two main types of glass fiber product. First, fibre is made either from a direct melt process or a marble remelt process. Both start with the raw materials in solid form. The materials are mixed together and melted in a furnace. Then, for the marble process, the molten material is sheared and rolled into marbles which are cooled and packaged. The marbles are taken to the fibre manufacturing facility where they are inserted into a can and remelted. The molten glass is extruded to the bushing to be formed into fibre. In the direct melt process, the molten glass in the furnace goes right to the bushing for formation.
Formation
The bushing plate is the most important part of the machinery. This is a small metal furnace containing nozzles for the fibre to be formed through. It is almost always made of platinum alloyed with rhodium for durability. Platinum is used because the glass melt has a natural affinity for wetting it. When bushings were first used they were 100% platinum and the glass wetted the bushing so easily it ran under the plate after exiting the nozzle and accumulated on the underside. Also, due to its cost and the tendency to wear, the platinum was alloyed with rhodium. In the direct melt process, the bushing serves as a collector for the molten glass. It is heated slightly to keep the glass at the correct temperature for fibre formation. In the marble melt process, the bushing acts more like a furnace as it melts more of the material.
The bushings are what make the capital investment in fibre glass production expensive. The nozzle design is also critical. The number of nozzles ranges from 200 to 4000 in multiples of 200. The important part of the nozzle in continuous filament manufacture is the thickness of its walls in the exit region. It was found that inserting a counterbore here reduced wetting. Today, the nozzles are designed to have a minimum thickness at the exit. The reason for this is that as glass flows through the nozzle it forms a drop which is suspended from the end. As it falls, it leaves a thread attached by the meniscus to the nozzle as long as the viscosity is in the correct range for fibre formation. The smaller the annular ring of the nozzle or the thinner the wall at exit, the faster the drop will form and fall away, and the lower its tendency to wet the vertical part of the nozzle. The surface tension of the glass is what influences the formation of the meniscus. For E-glass it should be around 400 mN per m.
The attenuation (drawing) speed is important in the nozzle design. Although slowing this speed down can make coarser fibre, it is uneconomic to run at speeds for which the nozzles were not designed.
Continuous filament process
In the continuous filament process, after the fibre is drawn, a size is applied. This size helps protect the fiber as it is wound onto a bobbin. The particular size applied relates to end-use. While some sizes are processing aids, others make the fiber have an affinity for a certain resin, if the fibre is to be used in a composite. Size is usually added at 0.5–2.0% by weight. Winding then takes place at around 1000 m per min.
Staple fibre process
In staple fiber production, there are a number of ways to manufacture the fibre. The glass can be blown or blasted with heat or steam after exiting the formation machine. Usually these fibers are made into some sort of mat. The most common process used is the rotary process. Here, the glass enters a rotating spinner, and due to centrifugal force is thrown out horizontally. The air jets push it down vertically and binder is applied. Then the mat is vacuumed to a screen and the binder is cured in the oven.
Laminating Operations
Filament Winding Operation
Fibreglass Sheet Laminating Operation
First, you have to mix resin with catalyst (e.g butanox LA), otherwise it won't go off for days/ weeks. Then you need wet out the mould with the resulting mixture, and put the sheets of fibreglass over it. You then roll them down into to mould using more resin, and make sure it is attached to the mould all over, and there is no air trapped in between the layers. Steel rollers are useful to make sure the resin is between all the layers, and the glass is wet right through, otherwise it doesn't stick. You have to be fast though, or the resin goes off and you have to start again.
Fibreglass Spray Lay-Up Operation
The fibreglass spray lay-up process is similar to the hand lay-up process but the difference comes from the application of the fibre and resin material to the mold. Spray-up is an open-molding composites fabrication process where resin and reinforcements are sprayed onto a mold. The resin and glass may be applied separately or simultaneously "chopped" in a combined stream from a chopper gun. Workers roll out the spray-up to compact the laminate. Wood, foam or other core material may then be added, and a secondary spray-up layer imbeds the core between the laminates. The part is then cured, cooled and removed from the reusable mold.
Fibreglass Hand Lay-Up Operation
Pultrusion Operation
Pultrusion is a manufacturing method used to make strong light weight composite materials, in this case fibreglass. Fibers (the glass material) are pulled from spools through a device that coats them with a resin. They are then typically heat treated and cut to length. Pultrusions can be made in a variety of shapes or cross-sections such as a W or S cross-section. The word pultrusion describes the method of moving the fibers through the machinery. It is pulled through using either a hand over hand method or a continuous roller method. This is opposed to an extrusion which would push the material through dies.
Uses
End uses for regular fibre glass are mats, insulation, reinforcement, sound absorption, heat resistant fabrics, corrosion resistant fabrics and high strength fabrics. Fibre glass is also the main source of material used by the modern automobile industry.
Corrugated fiberglass panels are also widely used for outdoor canopy or greenhouse construction. These are thin, rigid panels with a wavy or zig-zag cross-section, usually a pale green or yellow colour (although they are also available in other colors). They are usually available in widths of 2-4 feet and lengths of 6-16 feet. Overlapping one wave pattern on each edge is often sufficient to prevent most water or wind penetration through the seams.