Telecommunication
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Engineering

Telecommunication is the assisted transmission of signals over a distance for the purpose of communication. In earlier times, this may have involved the use of smoke signals, drums, semaphore, flags, or heliograph. In modern times, telecommunication typically involves the use of electronic transmitters such as the telephone, television, radio or computer. Early inventors in the field of telecommunication include Alexander Graham Bell, Guglielmo Marconi and John Logie Baird. Telecommunication is an important part of the world economy and the telecommunication industry's revenue has been placed at just under 3 percent of the gross world product.
Key concepts
| Etymology |
| The word telecommunication was adapted from the French word télécommunication. It is a compound of the Greek prefix tele- (τηλε-), meaning 'far off', and the Latin communicare, meaning 'to share'. The French word télécommunication was coined in 1904 by French engineer and novelist Édouard Estaunié. |
Basic elements
A telecommunication system consists of three basic elements:
- a transmitter that takes information and converts it to a signal;
- a transmission medium that carries the signal; and,
- a receiver that receives the signal and converts it back into usable information.
For example, in a radio broadcast the broadcast tower is the transmitter, free space is the transmission medium and the radio is the receiver. Often telecommunication systems are two-way with a single device acting as both a transmitter and receiver or transceiver. For example, a mobile phone is a transceiver.
Telecommunication over a phone line is called point-to-point communication because it is between one transmitter and one receiver. Telecommunication through radio broadcasts is called broadcast communication because it is between one powerful transmitter and numerous receivers.
Analog or digital
Signals can be either analog or digital. In an analog signal, the signal is varied continuously with respect to the information. In a digital signal, the information is encoded as a set of discrete values (for example ones and zeros). During transmission the information contained in analog signals will be degraded by noise. Conversely, unless the noise exceeds a certain threshold, the information contained in digital signals will remain intact. This noise resistance represents a key advantage of digital signals over analog signals.
Networks
A collection of transmitters, receivers or transceivers that communicate with each other is known as a network. Digital networks may consist of one or more routers that route information to the correct user. An analogue network may consist of one or more switches that establish a connection between two or more users. For both types of network, repeaters may be necessary to amplify or recreate the signal when it is being transmitted over long distances. This is to combat attenuation that can render the signal indistinguishable from noise.
Channels
A channel is a division in a transmission medium so that it can be used to send multiple streams of information. For example, a radio station may broadcast at 96.1 MHz while another radio station may broadcast at 94.5 MHz. In this case, the medium has been divided by frequency and each channel has received a separate frequency to broadcast on. Alternatively, one could allocate each channel a recurring segment of time over which to broadcast — this is known as time-division multiplexing and is sometimes used in digital communication.
Modulation
The shaping of a signal to convey information is known as modulation. Modulation can be used to represent a digital message as an analogue waveform. This is known as keying and several keying techniques exist (these include phase-shift keying, frequency-shift keying and amplitude-shift keying). Bluetooth, for example, uses phase-shift keying to exchange information between devices.
Modulation can also be used to transmit the information of analogue signals at higher frequencies. This is helpful because low-frequency analogue signals cannot be effectively transmitted over free space. Hence the information from a low-frequency analogue signal must be superimposed on a higher-frequency signal (known as a carrier wave) before transmission. There are several different modulation schemes available to achieve this (two of the most basic being amplitude modulation and frequency modulation). An example of this process is a DJ's voice being superimposed on a 96 MHz carrier wave using frequency modulation (the voice would then be received on a radio as the channel “96 FM”).
Society and telecommunication
Telecommunication is an important part of modern society. In 2006, estimates placed the telecommunication industry's revenue at $1.2 trillion or just under 3% of the gross world product (official exchange rate).
On the microeconomic scale, companies have used telecommunication to help build global empires. This is self-evident in the case of online retailer Amazon.com but, according to academic Edward Lenert, even the conventional retailer Wal-Mart has benefited from better telecommunication infrastructure compared to its competitors. In cities throughout the world, home owners use their telephones to organize many home services ranging from pizza deliveries to electricians. Even relatively poor communities have been noted to use telecommunication to their advantage. In Bangladesh's Narshingdi district, isolated villagers use cell phones to speak directly to wholesalers and arrange a better price for their goods. In Cote d'Ivoire, coffee growers share mobile phones to follow hourly variations in coffee prices and sell at the best price.
On the macroeconomic scale, Lars-Hendrik Röller and Leonard Waverman suggested a causal link between good telecommunication infrastructure and economic growth. Few dispute the existence of a correlation although some argue it is wrong to view the relationship as causal.
Due to the economic benefits of good telecommunication infrastructure, there is increasing worry about the digital divide. This is because the world's population does not have equal access to telecommunication systems. A 2003 survey by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) revealed that roughly one-third of countries have less than 1 mobile subscription for every 20 people and one-third of countries have less than 1 fixed line subscription for every 20 people. In terms of Internet access, roughly half of all countries have less than 1 in 20 people with Internet access. From this information, as well as educational data, the ITU was able to compile an index that measures the overall ability of citizens to access and use information and communication technologies. Using this measure, countries such as Sweden, Denmark and Iceland received the highest ranking while African countries such as Niger, Burkina Faso and Mali received the lowest.
History
Early telecommunications
Early forms of telecommunication include smoke signals and drums. Drums were used by natives in Africa, New Guinea and South America whereas smoke signals were used by natives in North America and China. Contrary to what one might think, these systems were often used to do more than merely announce the presence of a camp.
In the Middle Ages, chains of beacons were commonly used on hilltops as a means of relaying a signal. Beacon chains suffered the drawback that they could only pass a single bit of information, so the meaning of the message such as "The enemy has been sighted" had to be agreed upon in advance. One notable instance of their use was during the Spanish Armada, when a beacon chain relayed a signal from Plymouth to London.
In 1792, Claude Chappe, a French engineer, built the first fixed visual telegraphy system (or semaphore line) between Lille and Paris. However semaphore suffered from the need for skilled operators and expensive towers at intervals of ten to thirty kilometres (six to nineteen miles). As a result of competition from the electrical telegraph, the last commercial line was abandoned in 1880.
Telegraph and telephone
The first commercial electrical telegraph was constructed by Sir Charles Wheatstone and Sir William Fothergill Cooke and opened on 9 April 1839. Both Wheatstone and Cooke viewed their device as "an improvement to the [existing] electromagnetic telegraph" not as a new device.
Samuel Morse independently developed a version of the electrical telegraph that he unsuccessfully demonstrated on 2 September 1837. His code was an important advance over Wheatstone's signaling method. The first transatlantic telegraph cable was successfully completed on 27 July 1866, allowing transatlantic telecommunication for the first time.
The conventional telephone was invented independently by Alexander Bell and Elisha Gray in 1876. Antonio Meucci invented the first device that allowed the electrical transmission of voice over a line in 1849. However Meucci's device was of little practical value because it relied upon the electrophonic effect and thus required users to place the receiver in their mouth to “hear” what was being said. The first commercial telephone services were set-up in 1878 and 1879 on both sides of the Atlantic in the cities of New Haven and London.
Radio and television
In 1832, James Lindsay gave a classroom demonstration of wireless telegraphy to his students. By 1854, he was able to demonstrate a transmission across the Firth of Tay from Dundee, Scotland to Woodhaven, a distance of two miles, using water as the transmission medium. In December 1901, Guglielmo Marconi established wireless communication between St. John's, Newfoundland (Canada) and Poldhu, Cornwall (England), earning him the 1909 Nobel Prize in physics (which he shared with Karl Braun). However small-scale radio communication had already been demonstrated in 1893 by Nikola Tesla in a presentation to the National Electric Light Association.
On March 25, 1925, John Logie Baird was able to demonstrate the transmission of moving pictures at the London department store Selfridges. Baird's device relied upon the Nipkow disk and thus became known as the mechanical television. It formed the basis of experimental broadcasts done by the British Broadcasting Corporation beginning September 30, 1929. However, for most of the twentieth century televisions depended upon the cathode ray tube invented by Karl Braun. The first version of such a television to show promise was produced by Philo Farnsworth and demonstrated to his family on September 7, 1927.
Computer networks and the Internet
On September 11, 1940, George Stibitz was able to transmit problems using teletype to his Complex Number Calculator in New York and receive the computed results back at Dartmouth College in New Hampshire. This configuration of a centralized computer or mainframe with remote dumb terminals remained popular throughout the 1950s. However, it was not until the 1960s that researchers started to investigate packet switching — a technology that would allow chunks of data to be sent to different computers without first passing through a centralized mainframe. A four-node network emerged on December 5, 1969; this network would become ARPANET, which by 1981 would consist of 213 nodes.
ARPANET's development centred around the Request for Comment process and on April 7, 1969, RFC 1 was published. This process is important because ARPANET would eventually merge with other networks to form the Internet and many of the protocols the Internet relies upon today were specified through the Request for Comment process. In September 1981, RFC 791 introduced the Internet Protocol v4 (IPv4) and RFC 793 introduced the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) — thus creating the TCP/IP protocol that much of the Internet relies upon today.
However, not all important developments were made through the Request for Comment process. Two popular link protocols for local area networks (LANs) also appeared in the 1970s. A patent for the token ring protocol was filed by Olof Soderblom on October 29, 1974 and a paper on the Ethernet protocol was published by Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs in the July 1976 issue of Communications of the ACM.
Modern operation
Telephone

In an analogue telephone network, the caller is connected to the person he wants to talk to by switches at various telephone exchanges. The switches form an electrical connection between the two users and the setting of these switches is determined electronically when the caller dials the number. Once the connection is made, the caller's voice is transformed to an electrical signal using a small microphone in the caller's handset. This electrical signal is then sent through the network to the user at the other end where it transformed back into sound by a small speaker in that person's handset. There is a separate electrical connection that works in reverse, allowing the users to converse.
The fixed-line telephones in most residential homes are analogue — that is, the speaker's voice directly determines the signal's voltage. Although short-distance calls may be handled from end-to-end as analogue signals, increasingly telephone service providers are transparently converting the signals to digital for transmission before converting them back to analogue for reception. The advantage of this is that digitized voice data can travel side-by-side with data from the Internet and can be perfectly reproduced in long distance communication (as opposed to analogue signals that are inevitably impacted by noise).
Mobile phones have had a significant impact on telephone networks. Mobile phone subscriptions now outnumber fixed-line subscriptions in many markets. Sales of mobile phones in 2005 totalled 816.6 million with that figure being almost equally shared amongst the markets of Asia/Pacific (204 m), Western Europe (164 m), CEMEA (Central Europe, the Middle East and Africa) (153.5 m), North America (148 m) and Latin America (102 m). In terms of new subscriptions over the five years from 1999, Africa has outpaced other markets with 58.2% growth. Increasingly these phones are being serviced by systems where the voice content is transmitted digitally such as GSM or W-CDMA with many markets choosing to depreciate analogue systems such as AMPS.
There have also been dramatic changes in telephone communication behind the scenes. Starting with the operation of TAT-8 in 1988, the 1990s saw the widespread adoption of systems based on optic fibres. The benefit of communicating with optic fibres is that they offer a drastic increase in data capacity. TAT-8 itself was able to carry 10 times as many telephone calls as the last copper cable laid at that time and today's optic fibre cables are able to carry 25 times as many telephone calls as TAT-8. This increase in data capacity is due to several factors: First, optic fibres are physically much smaller than competing technologies. Second, they do not suffer from crosstalk which means several hundred of them can be easily bundled together in a single cable. Lastly, improvements in multiplexing have led to an exponential growth in the data capacity of a single fibre.
Assisting communication across many modern optic fibre networks is a protocol known as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The ATM protocol allows for the side-by-side data transmission mentioned in the second paragraph. It is suitable for public telephone networks because it establishes a pathway for data through the network and associates a traffic contract with that pathway. The traffic contract is essentially an agreement between the client and the network about how the network is to handle the data; if the network cannot meet the conditions of the traffic contract it does not accept the connection. This is important because telephone calls can negotiate a contract so as to guarantee themselves a constant bit rate, something that will ensure a caller's voice is not delayed in parts or cut-off completely. There are competitors to ATM, such as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), that perform a similar task and are expected to supplant ATM in the future.
Radio and television
In a broadcast system, a central high-powered broadcast tower transmits a high-frequency electromagnetic wave to numerous low-powered receivers. The high-frequency wave sent by the tower is modulated with a signal containing visual or audio information. The antenna of the receiver is then tuned so as to pick up the high-frequency wave and a demodulator is used to retrieve the signal containing the visual or audio information. The broadcast signal can be either analogue (signal is varied continuously with respect to the information) or digital (information is encoded as a set of discrete values).
The broadcast media industry is at a critical turning point in its development, with many countries moving from analogue to digital broadcasts. This move is made possible by the production of cheaper, faster and more capable integrated circuits. The chief advantage of digital broadcasts is that they prevent a number of complaints with traditional analogue broadcasts. For television, this includes the elimination of problems such as snowy pictures, ghosting and other distortion. These occur because of the nature of analogue transmission, which means that perturbations due to noise will be evident in the final output. Digital transmission overcomes this problem because digital signals are reduced to discrete values upon reception and hence small perturbations do not affect the final output. In a simplified example, if a binary message 1011 was transmitted with signal amplitudes [1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0] and received with signal amplitudes [0.9 0.2 1.1 0.9] it would still decode to the binary message 1011 — a perfect reproduction of what was sent. From this example, a problem with digital transmissions can also be seen in that if the noise is great enough it can significantly alter the decoded message. Using forward error correction a receiver can correct a handful of bit errors in the resulting message but too much noise will lead to incomprehensible output and hence a breakdown of the transmission.
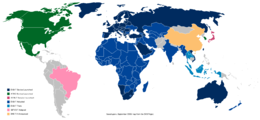
In digital television broadcasting, there are three competing standards that are likely to be adopted worldwide. These are the ATSC, DVB and ISDB standards; the adoption of these standards thus far is presented in the captioned map. All three standards use MPEG-2 for video compression. ATSC uses Dolby Digital AC-3 for audio compression, ISDB uses Advanced Audio Coding (MPEG-2 Part 7) and DVB has no standard for audio compression but typically uses MPEG-1 Part 3 Layer 2. The choice of modulation also varies between the schemes. In digital audio broadcasting, standards are much more unified with practically all countries choosing to adopt the Digital Audio Broadcasting standard (also known as the Eureka 147 standard). The exception being the United States which has chosen to adopt HD Radio. HD Radio, unlike Eureka 147, is based upon a transmission method known as in-band on-channel transmission that allows digital information to "piggyback" on normal AM or FM analogue transmissions.
However, despite the pending switch to digital, analogue receivers still remain widespread. Analogue television is still transmitted in practically all countries. The United States had hoped to end analogue broadcasts on December 31, 2006; however, this was recently pushed back to February 17, 2009. For analogue television, there are three standards in use (see a map on adoption here). These are known as PAL, NTSC and SECAM. For analogue radio, the switch to digital is made more difficult by the fact that analogue receivers are a fraction of the cost of digital receivers. The choice of modulation for analogue radio is typically between amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM). To achieve stereo playback, an amplitude modulated subcarrier is used for stereo FM.
The Internet
The Internet is a worldwide network of computers and computer networks that can communicate with each other using the Internet Protocol. Any computer on the Internet has a unique IP address that can be used by other computers to route information to it. Hence, any computer on the Internet can send a message to any other computer using its IP address. These messages carry with them the originating computer's IP address allowing for two-way communication. In this way, the Internet can be seen as an exchange of messages between computers.
An estimated 16.9% of the world population has access to the Internet with the highest access rates (measured as a percentage of the population) in North America (69.7%), Oceania/Australia (53.5%) and Europe (38.9%). In terms of broadband access, England (89%), Iceland (26.7%), South Korea (25.4%) and the Netherlands (25.3%) lead the world.
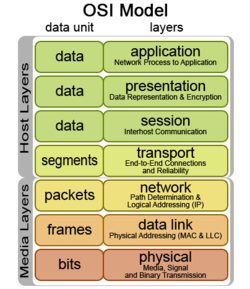
The Internet works in part because of protocols that govern how the computers and routers communicate with each other. The nature of computer network communication lends itself to a layered approach where individual protocols in the protocol stack run more-or-less independently of other protocols. This allows lower-level protocols to be customized for the network situation while not changing the way higher-level protocols operate. A practical example of why this is important is because it allows an Internet browser to run the same code regardless of whether the computer it is running on is connected to the Internet through an Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection. Protocols are often talked about in terms of their place in the OSI reference model (pictured on the right), which emerged in 1983 as the first step in an unsuccessful attempt to build a universally adopted networking protocol suite.
For the Internet, the physical medium and data link protocol can vary several times as packets traverse the globe. This is because the Internet places no constraints on what physical medium or data link protocol is used. This leads to the adoption of media and protocols that best suit the local network situation. In practice, most intercontinental communication will use the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) protocol (or a modern equivalent) on top of optic fibre. This is because for most intercontinental communication the Internet shares the same infrastructure as the public switched telephone network.
At the network layer, things become standardized with the Internet Protocol (IP) being adopted for logical addressing. For the world wide web, these “IP addresses” are derived from the human readable form using the Domain Name System (e.g. 72.14.207.99 is derived from www.google.com). At the moment, the most widely used version of the Internet Protocol is version four but a move to version six is imminent.
At the transport layer, most communication adopts either the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP is used when it is essential every message sent is received by the other computer where as UDP is used when it is merely desirable. With TCP, packets are retransmitted if they are lost and placed in order before they are presented to higher layers. With UDP, packets are not ordered or retransmitted if lost. Both TCP and UDP packets carry port numbers with them to specify what application or process the packet should be handled by. Because certain application-level protocols use certain ports, network administrators can restrict Internet access by blocking the traffic destined for a particular port.
Above the transport layer, there are certain protocols that are sometimes used and loosely fit in the session and presentation layers, most notably the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. These protocols ensure that the data transferred between two parties remains completely confidential and one or the other is in use when a padlock appears at the bottom of your web browser. Finally, at the application layer, are many of the protocols Internet users would be familiar with such as HTTP (web browsing), POP3 (e-mail), FTP (file transfer), IRC (Internet chat), BitTorrent (file sharing) and OSCAR (instant messaging).
Local area networks
Despite the growth of the Internet, the characteristics of local area networks (computer networks that run at most a few kilometres) remain distinct. This is because networks on this scale do not require all the features associated with larger networks and are often more cost-effective and efficient without them.
In the mid-1980s, several protocol suites emerged to fill the gap between the data link and applications layer of the OSI reference model. These were Appletalk, IPX and NetBIOS with the dominant protocol suite during the early 1990s being IPX due to its popularity with MS-DOS users. TCP/IP existed at this point but was typically only used by large government and research facilities. As the Internet grew in popularity and a larger percentage of traffic became Internet-related, local area networks gradually moved towards TCP/IP and today networks mostly dedicated to TCP/IP traffic are common. The move to TCP/IP was helped by technologies such as DHCP that allowed TCP/IP clients to discover their own network address — a functionality that came standard with the AppleTalk/IPX/NetBIOS protocol suites.
It is at the data link layer though that most modern local area networks diverge from the Internet. Whereas Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) are typical data link protocols for larger networks, Ethernet and Token Ring are typical data link protocols for local area networks. These protocols differ from the former protocols in that they are simpler (e.g. they omit features such as Quality of Service guarantees) and offer collision prevention. Both of these differences allow for more economic set-ups.
Despite the modest popularity of Token Ring in the 80's and 90's, virtually all local area networks now use wired or wireless Ethernet. At the physical layer, most wired Ethernet implementations use copper twisted-pair cables (including the common 10BASE-T networks). However, some early implementations used coaxial cables and some recent implementations (especially high-speed ones) use optic fibres. Optic fibres are also likely to feature prominently in the forthcoming 10-gigabit Ethernet implementations. Where optic fibre is used, the distinction must be made between multi-mode fibre and single-mode fibre. Multi-mode fibre can be thought of as thicker optical fibre that is cheaper to manufacture but that suffers from less usable bandwidth and greater attenuation (i.e. poor long-distance performance).