From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Size of this preview: 640 × 397 pixels
Size of this preview: 640 × 397 pixels Full resolution (1,136 × 704 pixels, file size: 75 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
 |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. The description on its description page there is shown below.Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
|
This image was (or all images in this article or category were) uploaded in the JPEG format.
However, it contains information that could be stored more efficiently or more accurately in the PNG format or SVG format. If possible, please upload a PNG or SVG version of this image without compression artifacts, derived from a non-JPEG source or with existing artifacts removed. |
|
Deutsch | English | Español | Français | 日本語 | Português | Русский | +/- |
 |
This graph image should be recreated using vector graphics as an SVG file. This has several advantages; see Commons:Media for cleanup for more information. If an SVG form of this image is already available, please upload it. After uploading an SVG, replace this template with {{ vector version available|new image name.svg}}. |
العربية | Български | Català | Česky | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Français | Galego | 한국어 | Italiano | Magyar | Lietuvių | Nederlands | 日本語 | Polski | Português | Română | Русский | Suomi | Svenska | Türkçe | Українська | 中文(繁體) | 中文(简体) | +/- |
Summary
| Description |
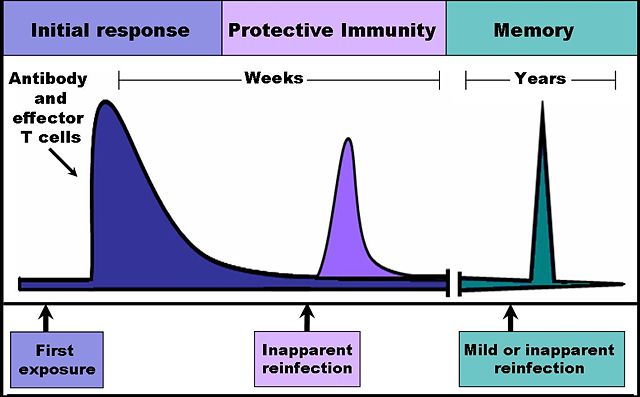
The time course of an immune response. Immune reactants, such as antibodies and effector T-cells, work to eliminate an infection, and their levels and activity rapidly increase following an encounter with an infectious agent, whether that agent is a pathogen or a vaccine. For several weeks these reactants remain in the serum and lymphatic tissues and provide protective immunity against reinfection by the same agent. During an early reinfection, few outward symptoms of illness are present, but the levels of immune reactants increase and are detectable in the blood and/or lymph. Following clearance of the infection, antibody level and effector T-cell activity gradually declines. Because immunological memory has developed, reinfection at later time points leads to a rapid increase in antibody production and effector T cell activity. These later infections can be mild or even inapparent. |
| Source |
User created but based on . |
| Date |
January 29, 2007 |
| Author |
DO11.10 |
Permission
( Reusing this image) |
see below
|
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses:
 |
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation license, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled " GNU Free Documentation license".
Aragonés | العربية | Asturianu | Беларуская (тарашкевіца) | Български | বাংলা | ইমার ঠার/বিষ্ণুপ্রিয়া মণিপুরী | Brezhoneg | Bosanski | Català | Cebuano | Česky | Dansk | Deutsch | Ελληνικά | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | Euskara | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Gaeilge | Galego | עברית | Hrvatski | Magyar | Bahasa Indonesia | Ido | Íslenska | Italiano | 日本語 | ქართული | ភាសាខ្មែរ | 한국어 | Kurdî / كوردی | Latina | Lëtzebuergesch | Lietuvių | Bahasa Melayu | Nnapulitano | Nederlands | Norsk (nynorsk) | Norsk (bokmål) | Occitan | Polski | Português | Română | Русский | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | Shqip | Српски / Srpski | Svenska | తెలుగు | ไทย | Tagalog | Türkçe | Українська | اردو | Tiếng Việt | Volapük | Yorùbá | 中文(简体) | 中文(繁體) | +/- |
You may select the license of your choice.
|
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
|
|
Date/Time |
Dimensions |
User |
Comment |
| current |
02:27, 30 January 2007 |
1,136×704 (75 KB) |
DO11.10 |
|
|
|
01:37, 30 January 2007 |
1,136×704 (75 KB) |
DO11.10 |
|
|
|
01:29, 30 January 2007 |
1,136×702 (72 KB) |
DO11.10 |
|
File links
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):