Betelgeuse incident
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Air & Sea transport
The Betelgeuse incident, also known as the Betelgeuse or Whiddy Island disaster, occurred on 8 January 1979, at around 1 a.m., when the oil tanker Betelgeuse exploded in Ireland at the offshore jetty of the Whiddy Island Oil Terminal due to the failure of the ship's structure during an operation to discharge its cargo of oil. The tanker was owned by Total S.A. and the oil terminal was owned and operated by Gulf Oil.
The explosion and resulting fire claimed the lives of 50 people (42 French nationals, 7 Irish nationals and 1 United Kingdom national). Only 27 bodies were recovered. A further fatality occurred during the salvage operation with the loss of a Dutch diver.
Background
During the 1960s, developments in the pattern of oil transportation indicated that it would soon become most economic to move oil between the Middle East and Europe using Ultra Large Crude Carrier vessels. These vessels were so large that they would not be able to enter most of the older ports on the Atlantic Ocean, North Sea and English Channel coasts.
Accordingly, it was judged appropriate to build a new oil terminal in Europe capable of handling the largest vessels that were planned. The intention was that oil coming from the Middle East would be off-loaded at this terminal and then stored for transshipment to European refineries using smaller vessels. The closure of the Suez Canal in 1967 as a result of the Six-Day War reinforced the economic viability of this scheme. Oil shipments had to come round the Cape of Good Hope, thus avoiding the vessel size constraints previously imposed by the canal.
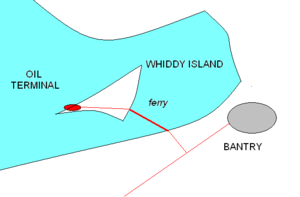
In 1966, the Gulf Oil Corporation identified Whiddy Island in Bantry Bay, Ireland, as being the most suitable site for the new terminal. Whiddy Island offered a long, sheltered deep-water anchorage. Furthermore, it was well away from any major population centres and shipping lanes. Construction started in 1967 and the terminal was completed in 1969.
The onshore facility included a 'tank farm' consisting of two tanks for ballast, two for bunker fuel oil, one for diesel oil and twelve crude oil storage tanks, each capable of holding 81,280 tonnes, bringing the total capacity to approximately 1.3 million tonnes of oil. The offshore facility was comprised of an island type berth (known colloquially as the 'jetty') 488 metres (1,600 ft) in length, approximately 396 metres (1,300 ft) from the shore. The jetty was commonly described as "a massive concrete structure" and access to it was only possible by boat. It was claimed that the jetty was capable of accommodating vessels of up to 500,000 metric tons of deadweight (DWT), although no such vessels existed at that time.
The construction and operation of the terminal transformed the economy of the Bantry area. In 1968, the tanker Universe Ireland went into service for Gulf. At 312,000 DWT this was the largest ship in the world. It was intended to use this vessel mainly to move oil between Kuwait and Whiddy Island. It was the first of six such tankers planned for use by the company.
The terminal was very successful for the first five years of operation, but then events began to move against it. The Suez Canal reopened and the economics of ULCCs began to appear less satisfactory than had originally been anticipated. Shipping goods in the form of infrequent but very large loads involves engaging more idle capital in the form of stock than the alternatives. Also, the process of transshipment is costly. The whole economic basis of the Whiddy terminal was incompatible with the ' just-in-time' approach to industrial management which was being widely adopted at the time. That apart, the late 1970s saw a levelling-off in demand for oil as the result of both economic recession and a rise in the price of oil. All these circumstances caused a fall in the utilisation of the terminal to a level below that which had been planned for. Thus, by the late 1970s, the local Gulf operating company (Gulf Oil Terminals (Ireland) Ltd) was struggling to maintain the viability of the terminal. The company had been forced to undertake a number of cost saving measures.
The incident
On 24 November 1978, the Betelgeuse left Ras Tanura in the Persian Gulf bound for Leixoes, Portugal with a full cargo of crude oil. Built in 1968 by Chantiers de l'Atlantique in Saint-Nazaire, France, the 121,432 DWT vessel was registered by Total S.A. at Le Havre, France.
Originally the Betelgeuse was to call at Sines, Portugal, to lighten ship, but poor weather conditions prevented the vessel from entering the harbour. Plans were further frustrated at Leixoes, where a ship had grounded across the entrance to the harbour, preventing the Betelgeuse from berthing there to discharge her cargo. The Betelgeuse was then instructed to sail to Whiddy Island, Ireland.
The Betelgeuse first put in at Vigo, Spain to change some of her crew, and then sailed for Whiddy Island on 30 December 1978. During the passage the vessel encountered heavy weather in the Bay of Biscay and after reporting a leakage of oil was instructed to head towards Brest, France at reduced speed. However, the origin of the leak was discovered and stopped. The vessel proceeded on its original planned course, arriving in Bantry Bay on 4 January 1979.
By 8 p.m. on 6 January 1979, the Betelgeuse had completed berthing at the offshore jetty. At 11:30 p.m. the same day, the vessel commenced discharging its 114,000 tonnes of mixed Arabian crude oil, which was expected to take about 36 hours. A number of the crew went ashore while this was in progress and the wife of one of the officers joined her husband on the vessel.
At about 1 a.m. (evidence on the precise time conflicts) on Monday, 8 January, a rumbling or cracking noise was heard from the vessel, followed shortly by a huge explosion within its hull. The force of the explosion was seen to blow men from the jetty into the sea. Local residents reported seeing the Betelgeuse engulfed in a ball of fire a few moments later. A series of further explosions followed, breaking the vessel in half. Much of the oil cargo still on board ignited and this generated temperatures estimated to exceed 1,000 °C. The concrete unloading jetty crumbled and firefighters, arriving on the scene from several neighbouring towns, were unable to get near the vessel. The firefighters concentrated their efforts on preventing the fire from spreading to the tanks of the storage farm and on containing the oil spillage. Local families living on the island fled for their lives.
After a few hours the Betelgeuse sank at her moorings in 30 metres of water, which largely extinguished the main body of the fire. In spite of this, rescue workers were not able to approach the wreck (some of which was still above water) for two weeks due to clouds of toxic and inflammable gas surrounding it. After two weeks, it was possible to start recovering bodies from the wreck and pumping off the remains of the oil cargo that was still on board.
The aftermath
What became known variously as 'the Betelgeuse incident', 'the Betelgeuse disaster' or 'the Whiddy Island disaster' was the worst maritime disaster in Irish history. (Gulf and Total executives commonly referred to 'the Betelgeuse incident'). Military and civilian personnel were mobilised from all over Ireland to deal with it. The incident was the subject of agonised debate in the Dáil. One TD noted that there had been earlier incidents at the Whiddy Island terminal and questioned whether Gulf's status as a major employer had made the authorities reluctant to enforce a rigorous inspection regime.
The Irish government appointed a Tribunal to investigate the incident, presided over by Justice Declan Costello. This Tribunal took a year to hear evidence and prepare a 480 page report. The report indicated three main factors that had contributed to the incident. These were:
- The poor condition of the Betelgeuse for which its operator, Total S.A., was to blame. Immediately before the incident, the vessel's hull and tanks were cracked, corroded and leaking. The 11 year old vessel had been worked hard and was at the end of its service life.
- Incorrect unloading sequences and ballasting which resulted in the buoyancy of the hull becoming uneven and the hull therefore strained. Lack of crew training or knowing malpractice were possible explanations. Total was held largely to blame for this. However, given that all the personnel involved in the unloading had died in the explosion, it was difficult to be certain as to what had happened.
- Inadequate and poorly maintained fire fighting and rescue systems both on the vessel and on the jetty. Gulf and Total were held jointly to blame for this. A combination of human failings and financial constraints were the immediate causes.
It was determined that a faulty unloading operation had unbalanced the vessel, causing it to break its back and thereby rupturing several empty ballast tanks. Vapour from the ruptured tanks had escaped into the vessel and exploded in a fireball. However, the Costello Tribunal's findings were never accepted by Total.
”Total recalls its view that the tanks exploded as the result of a fire which it believes started out on the jetty. The company can but contest the report’s conclusions which assume that the ballasting operations were carried out in a most unlikely way by a highly qualified crew.” - The Times, July 26 1980 . "Gulf and Total accused." (Total rejoinder to the Costello Tribunal report)
Total drew attention to the unexplained absence from his post of the Gulf employee whose duty it was to supervise the unloading from the on-shore control room. The individual concerned had left the control room some time before the trouble started (see below) and his absence may have contributed to a lack of urgency in responding to events. Exactly what happened that night has never been established beyond doubt.
All the crew on board the ship at the time of the incident (41 in total) are believed to have died, although not all the bodies were found. In addition, one visitor to the ship (an officer's wife) and eight terminal workers were killed. Initial efforts to contain the fire were hampered by a lack of organisation and poorly maintained fire fighting equipment at the terminal. The Bantry fire brigade spent some time waiting at the town pier for a launch to take them onto the island. The terminal's own fire engine would not start. Firefighters had to break into the terminal's main depot in order to access equipment (much of which did not work) and materials.
There was some controversy over the exact timing of events and the response of the terminal management to the disaster as it unfolded. Some local residents claimed that there was anything up to 5 minutes between the audible structural failure of the vessel and the time at which the initial explosion happened. If this were so, the opportunity to attempt an evacuation had been missed. But the terminal management insisted that the explosion had almost immediately followed the structural failure.
”The Tribunal singles out one man who might have raised the alarm and saved the lives of those who perished : Mr John Connolly who was not in his post as despatcher in the control room of the terminal. To suppress that fact Gulf personnel and the Bantry telephone operator entered into a conspiracy. False entries were made in logs, false accounts were given of the disaster and efforts were made to avoid giving statements to the police.”- The Times, July 26 1980 . "Gulf and Total accused."
No escape from the jetty or the vessel was possible in the absence of rescue boats, given that there was no fixed link from the jetty to the shore. However, all concerned praised the initiative and courage of the firefighters and rescue workers.
A Dutch salvage firm, L Smit & Co, raised the Betelgeuse in four sections. The first section (the bow) was towed out to open water, 100 miles (160 km) offshore, and scuttled. This measure attracted protests from the fishing community, so two further sections were sealed up and towed to breaking yards in Spain for disposal. A fourth section was broken up locally. During the salvage operation, the life of a diver was lost. The last section was not removed until July 1980. Local fishing grounds were badly contaminated and a clean-up was not finally complete until 1983.
The costs of salvage, clean-up and compensation are believed to have totalled around US$120 million. That included compensation paid by Total to Gulf. Most of the relevant costs were paid by insurance companies and all the various claims and counter-claims were eventually settled out of court. Gulf never reopened the terminal and a feasibility study in 1985 showed that it no longer had any potential use in international oil trade. In 1986, Gulf surrendered its lease on the site to the Irish government. The government used the terminal (after carrying out a limited refurbishment) to hold its strategic oil reserve, with loading and unloading carried out via a buoy. The terminal's main jetty was not rebuilt.
A number of memorial services have been held to commemorate anniversaries of the incident. The most recent of these was on the 25th anniversary in January 2004. Relatives of the victims joined with local residents in a special service held at St Finbarr’s Church in Bantry. A memorial sculpture, incorporating the ship's bell which was recovered from the wreck, has been erected in the hillside graveyard overlooking the harbour. The bodies of two unidentified casualties from the incident are interred nearby.