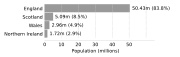United Kingdom
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Europe; European Countries; Geography of Great Britain
|
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: " Dieu et mon droit" (French) "God and my right" |
||||||
| Anthem: " God Save the Queen" |
||||||
|
Location of the United Kingdom (dark green)
– on the European continent (light green & dark grey) |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
London |
|||||
| Official languages | English | |||||
| Recognised regional languages | Welsh, Irish, Ulster Scots, Scots, Scottish Gaelic, Cornish | |||||
| Ethnic groups ( 2001) | 92.1% White, 4.00% South Asian, 2.00% Black, 1.20% Mixed Race, 0.80% East Asian and Other |
|||||
| Demonym | British, Briton | |||||
| Government | Parliamentary system and Constitutional monarchy | |||||
| - | Monarch | Queen Elizabeth II | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Gordon Brown MP | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||
| - | Upper House | House of Lords | ||||
| - | Lower House | House of Commons | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Acts of Union | 1 May 1707 | ||||
| - | Act of Union | 1 January 1801 | ||||
| - | Anglo-Irish Treaty | 12 April 1922 | ||||
| EU accession | 1 January 1973 | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 244,820 km² ( 79th) 94,526 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 1.34 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | mid-2006 estimate | 60,587,300 ( 22nd) | ||||
| - | 2001 census | 58,789,194 | ||||
| - | Density | 246/km² ( 48th) 637/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2006 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | US$2.270 trillion ( 6th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | US$37,328 ( 13th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $2.772 trillion ( 5th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | US$45,845 ( 9th) | ||||
| Gini (2005) | 34 | |||||
| HDI (2005) | ▲ 0.946 (high) ( 16th) | |||||
| Currency | Pound sterling (£) ( GBP) |
|||||
| Time zone | GMT ( UTC+0) | |||||
| - | Summer ( DST) | BST ( UTC+1) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .uk | |||||
| Calling code | +44 | |||||
| Footnotes | ||||||
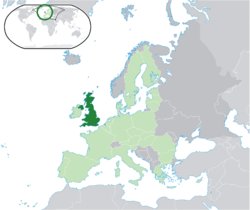
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom, the UK, or Britain, is a sovereign island country located off the northwestern coast of continental Europe. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the northeast part of the island of Ireland and many small islands. Northern Ireland is the only part of the UK with a land border, sharing it with the Republic of Ireland. Apart from this land border, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel and the Irish Sea. The largest island, Great Britain, is linked to France by the Channel Tunnel.
The United Kingdom is a union of four constituent countries: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. The United Kingdom is governed by a parliamentary system with its seat of government in London, the capital, and is a constitutional monarchy with Queen Elizabeth II as the head of state. The Crown Dependencies of the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man, formally possessions of the Crown, are not part of the UK but form a federacy with it. The UK has fourteen overseas territories, all remnants of the British Empire, which at its height encompassed almost a quarter of the world's land surface, making it the largest empire in history. As a result of the empire, British influence can be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies such as Canada, Australia, India, and the United States. Queen Elizabeth II remains the head of the Commonwealth of Nations and head of state of each of the Commonwealth realms.
The UK is a developed country, with the fifth (nominal GDP) or sixth (PPP) largest economy in the world. It was the world's foremost power during the 19th and early 20th century, but the economic cost of two world wars and the decline of its empire in the latter half of the 20th century diminished its leading role in global affairs. The UK nevertheless retains strong economic, cultural, military and political influence and is a nuclear power, with the second or third (depending on method of calculation) highest defence spending in the world. It is a member state of the European Union, holds a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council, and is a member of the G8, NATO, WTO and the Commonwealth of Nations.
History
On May 1st, 1707, the political union of the Kingdom of England (which included the once independent Principality of Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain usually referred to thereafter as the Kingdom of Great Britain. This event was the result of the Treaty of Union that was agreed on 22 July 1706, and then ratified by the Parliaments of England and Scotland each passing an Act of Union in 1707. Almost a century later, the Kingdom of Ireland, which had been brought under English control between 1541 and 1691, joined the united Kingdom of Great Britain with the passing of the Act of Union 1800. Prior to 1707, England and Scotland had existed as separate sovereign and independent states with their own monarchs and political structures from the 9th century, though a personal union was created between the kingdoms after the Scottish King, James VI, became King of England as well in 1603.
In its first century, the United Kingdom played an important role in developing Western ideas of the Parliamentary System as well as making significant contributions to literature, the arts and science. The UK-led Industrial Revolution transformed the country and fuelled the British Empire. During this time, like other Great Powers, the UK was involved in colonial exploitation, including the slave trade, though the passing of the 1807 Slave Trade Act made the UK the first country to prohibit trade in slaves.
After the defeat of Napoleon in the Napoleonic Wars, the UK became the principal naval power of the 19th century. The United Kingdom remained an eminent power into the mid-20th century, and its empire expanded to its maximum size by 1921, gaining the League of Nations mandate over former German and Ottoman colonies after World War I.
Long simmering tensions in Ireland led to the partition of the island in 1920, followed by independence for the Irish Free State in 1922. Six of the nine counties of the province of Ulster remained within the UK, which then changed to the current name in 1927 of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.

After World War I, the world's first large-scale international broadcasting network, the BBC, was created. Britain was one of the major Allied powers in World War II, and wartime leader Winston Churchill and his peacetime successor Clement Atlee helped plan the post-war world as part of the "Big Three". World War II left the United Kingdom financially damaged. Loans taken out during and after World War II from both Canada and the United States were economically costly but, along with post-war Marshall aid, the UK began the road to recovery.
The immediate post-war years saw the establishment of the British Welfare State, including one of the world's first and most comprehensive public health services, while the demands of a recovering economy brought people from all over the Commonwealth to create a multiethnic Britain. Although the new post-war limits of Britain's political role were confirmed by the Suez Crisis of 1956, the international spread of the language meant the continuing impact of its literature and culture, while at the same time from the 1960s its popular culture found influence abroad. Following a period of global economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the 1980s saw the inflow of substantial oil revenues and economic growth. The premiership of Margaret Thatcher marked a significant change of direction from the post-war political and economic consensus; a path that was not reversed by the New Labour government of Tony Blair in 1997.
The United Kingdom was one of the 12 founding members of the European Union at its launch in 1992 with the signing of the Treaty on European Union. Prior to that, it had been a member of the EU's forerunner, the European Economic Community (EEC), from 1973. The attitude of the present Labour government towards further integration with this organisation is mixed, with the Offical Opposition, the Conservative Party, favouring a return of some powers and competencies to the state.
The end of the 20th century saw a major change to the government of the United Kingdom with the creation of a devolved Scottish parliament and Welsh Assembly following popular approval in pre-legislative referenda. This produced the prospect of a legislative path to independence for Scotland when the Scottish National Party won the 2007 election and formed a minority government in Scotland, with a mandate to hold a referendum on independence by 2011.
Government and politics
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy with Queen Elizabeth II, as head of state; the monarch of the UK also serves as head of state of fifteen other Commonwealth countries, putting the UK in a personal union with those other states. The Crown has sovereignty over the Isle of Man and the Bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey. Collectively, these three territories are known as the Crown dependencies, lands owned by the British monarch but not part of the United Kingdom. They are not part of the European Union. However, the Parliament of the United Kingdom has the authority to legislate for the dependencies, and the British government manages their foreign affairs and defence.
The UK has fourteen overseas territories around the world, the last remaining territories of the British Empire. The overseas territories are not considered part of the UK, but in most cases, the local populations have British citizenship and the right of abode in the UK. This has been the case since 2002.
The UK has a parliamentary government based on strong traditions: the Westminster system has been emulated around the world — a legacy of the British Empire.
The UK's constitution governs the legal framework of the country and consists mostly of written sources, including statutes, judge made case law, and international treaties. As there is no technical difference between ordinary statutes and law considered to be "constitutional law," the British Parliament can perform "constitutional reform" simply by passing Acts of Parliament and thus has the power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. However, no Parliament can pass laws that future Parliaments cannot change. The United Kingdom is one of the three countries in the world today that does not have a codified constitution (the other two being New Zealand and Israel).
The position of Prime Minister, the UK's head of government, belongs to the Member of Parliament who can obtain the confidence of a majority in the House of Commons, usually the current leader of the largest political party in that chamber. The Prime Minister and Cabinet are formally appointed by the Monarch to form Her Majesty's Government. However, the Prime Minister chooses the Cabinet, and by convention, HM The Queen respects the Prime Minister's choices. The Cabinet is traditionally drawn from members of the Prime Minister's party in both legislative houses, and mostly from the House of Commons, to which they are responsible. Executive power is exercised by the Prime Minister and Cabinet, all of whom are sworn into Her Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, and become Ministers of the Crown. The Rt Hon Gordon Brown MP, leader of the Labour Party, has been Prime Minister, First Lord of the Treasury and Minister for the Civil Service since 27 June 2007.
The Parliament of the United Kingdom that meets in the Palace of Westminster, is the ultimate legislative authority in the United Kingdom. A devolved parliament in Scotland and devolved assemblies in Northern Ireland, and Wales were established following public approval as expressed in referenda, but these are not sovereign bodies and could be abolished by the UK parliament. The UK parliament is made up of two houses: an elected House of Commons and an appointed House of Lords, and any Bill passed requires the assent of HM The Queen to become law. For elections to the House of Commons, the UK is currently divided into 646 constituencies, with 529 in England, 18 in Northern Ireland, 59 in Scotland and 40 in Wales, though this number will rise to 650 at the next General Election. Each constituency elects one Member of Parliament by simple plurality. General Elections are called by the Monarch when the Prime Minister so advises. Though there is no minimum term for a Parliament, a new election must be called within five years of the previous general election.
For elections to the European Parliament, the UK has 78 MEPs, elected in 12 multi-member constituencies. Questions over sovereignty have been brought forward due to the UK's membership of the European Union.
The UK's three major political parties are the Labour Party, the Conservative Party, and the Liberal Democrats, winning between them 616 out of the 646 seats available in the House of Commons at the 2005 General Election. Most of the remaining seats were won by parties that only contest elections in one part of the UK such as the Scottish National Party (Scotland only), Plaid Cymru (Wales only), and the Democratic Unionist Party, Social Democratic and Labour Party, Ulster Unionist Party, and Sinn Féin (Northern Ireland only, though Sinn Féin also contests elections in Ireland). In accordance with party policy, no elected Sinn Féin Member of Parliament has ever attended the House of Commons to speak in the House on behalf of their constituents as Members of Parliament are required to take an oath of allegiance to the Monarch. However, the current five Sinn Féin MPs have since 2002 made use of the offices and other facilities available at Westminster.
Devolved national administrations
Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each has a devolved, unicameral legislature and its own government or Executive, led by a First Minister. England, despite being the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is ruled and legislated for directly by the UK government and parliament. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question which concerns the fact that MPs from Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales help decide the laws that apply to England alone.
The Scottish Parliament has wide ranging legislative powers over any matter that has not been specifically ' reserved' to the UK parliament, including education, healthcare, Scots law and local government. Following their victory at the 2007 elections, the pro-independence SNP formed a minority government with its leader, Alex Salmond, becoming First Minister of Scotland. The pro-union parties responded to the electoral success of the SNP by creating a Commission to examine the case for devolving additional powers while excluding Scottish independence as an option, though the leader of the Scottish Labour Party, Wendy Alexander, has now indicated that Labour will support calls for independence to be placed before the people in a referendum in the hope that a vote to reject independence would settle the constitutional debate for a generation.Most opinion polls do show minority support for independence though support varies depending on the nature of the question. However, a poll in April 2008 that used the proposed referendum wording found support for independence had reached 41% with just 40% supporting retention of the Union.
The National Assembly for Wales has more limited devolved powers than those devolved to Scotland though following the passing of the Government of Wales Act 2006, the Assembly can now legislate in some areas through Legislative Competency Orders which can be granted on a case by case basis. The current Welsh Assembly Government was formed several weeks after the 2007 elections, following a brief period of minority administration, when Plaid Cymru joined Labour in a coalition government under the continuing leadership of First Minister Rhodri Morgan.
The Northern Ireland Assembly has powers closer to those already devolved to Scotland. The Northern Ireland Executive is currently lead by First Minister Peter Robinson ( Democratic Unionist Party) and deputy First Minister Martin McGuinness ( Sinn Féin).
Local government
Each country of the United Kingdom has its own system of local government, with power over local government in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland being devolved. (City status, being governed by Royal Charter, is conferred separately from local government arrangements.)
England's upper-tier subdivisions are the nine Regions also known as European Union government office regions. A London referendum in 1998 on the question of having a directly elected assembly and directly elected mayor produced a large majority in favour and it was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies. However, a rejection by a referendum in 2004 of a proposed assembly in the North East region stopped this idea in its tracks. Below the region level, London consists of 32 London boroughs and the rest of England has either county councils and district councils or unitary authorities.
Northern Ireland is presently divided into 26 districts for local government purposes though these councils do not carry out the same range of functions as would be the case in the rest of the United Kingdom. However, on 13 March 2008, the Executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils to replace the present system.
Scotland is divided into 32 council areas with wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen and Dundee are separate council areas as also is Highland Council which includes a third of Scotland's area but just over 200,000 people. The power invested in local authorities is administered by elected councillors, of which there are currently 1,222 who are each paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by Single Transferable Vote in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost or Convenor to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales consists of 22 unitary authorities, including the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport which are separate unitary authorities in their own right.
Foreign relations and armed forces


The United Kingdom is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of the G8 and NATO, and a member state of the European Union. The UK has a " Special Relationship" with the United States. Apart from the US and Europe, Britain's close allies include Commonwealth nations, Ireland and other English speaking countries. Britain's global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations and its armed forces, which maintain approximately eighty military installations and other deployments around the globe.
The Army, Navy and Air Force are collectively known as the British Armed Forces (or Her Majesty's Armed Forces) and officially the Armed Forces of the Crown. The commander-in-chief is the monarch, HM Queen Elizabeth II and they are managed by the Ministry of Defence. The armed forces are controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Chief of the Defence Staff.
The United Kingdom fields one of the most technologically advanced and best trained armed forces in the world. According to various sources, including the Ministry of Defence, the UK has the second highest military expenditure in the world, despite only having the 27th largest military in terms of manpower. Total defence spending currently accounts for 2.2% of total national GDP, compared to 4.4% at the end of the Cold War. It is the second largest spender on military science, engineering and technology. The Royal Navy is considered to be the only other blue-water navy along with those of France and the United States. The British Armed Forces are equipped with advanced weapons systems, including the Challenger 2 tank and the Eurofighter Typhoon jet fighter. The Ministry of Defence signed contracts worth £3.2bn to build two new super carrier sized aircraft carriers on 3 July 2008.
The United Kingdom is one of the five recognised countries possessing nuclear weapons, utilising the Vanguard class submarine-based Trident II ballistic missile system.
The British Armed Forces are charged with protecting the United Kingdom and its overseas territories, promoting the United Kingdom's global security interests, and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps, as well as the Five Power Defence Arrangements and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained at Ascension Island, Belize, Brunei, Canada, Diego Garcia, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar, Kenya, and Cyprus.
The British Army had a reported strength of 102,440 in 2005, the Royal Air Force a strength of 49,210 and the 36,320-strong Royal Navy, which includes the Royal Marines, who provide commando units specialising in amphibious warfare.
The United Kingdom Special Forces, provide troops trained for quick, mobile, military responses in counter-terrorism, land, maritime and amphibious operations, often where secrecy or covert tactics are required.
There are reserve forces supporting the regular military. These include the Territorial Army, the Royal Naval Reserve, Royal Marines Reserve and the Royal Auxiliary Air Force. This puts total active and reserve duty military personnel at approximately 429,500, deployed in over eighty countries.
Despite the United Kingdom's military capabilities, recent pragmatic defence policy has a stated assumption that "the most demanding operations" would be undertaken as part of a coalition. Setting aside the intervention in Sierra Leone, operations in Bosnia, Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq may all be taken as precedent. Indeed the last war in which the British military fought alone was the Falklands War of 1982, in which they were victorious.
Law and criminal justice
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system due to it being created by the political union of previously independent countries with Article 19 of the Treaty of Union guaranteeing the continued existence of Scotland's separate legal system. Today the UK has three distinct systems of law: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law. Recent constitutional changes will see a new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom come into being in October 2009 that will take on the appeal functions of the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords. The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, comprising the same members as the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the UK overseas territories, and the British crown dependencies.
England, Wales and Northern Ireland
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law are based on common-law principles. The essence of common-law is that law is made by judges sitting in courts, applying their common sense and knowledge of legal precedent ( stare decisis) to the facts before them. The Courts of England and Wales are headed by the Supreme Court of Judicature of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). The Appellate Committee of the House of Lords (usually just referred to, as "The House of Lords") is presently the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil cases in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the hierarchy.
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995 though, since that peak, there has been an overall fall of 42% in crime from 1995 to 2006/7.Despite the fall in crime rates, the prison population of England and Wales has almost doubled over the same period, to over 80,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 147 per 100,000. Her Majesty's Prison Service, which reports to the Ministry of Justice, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales.
Scotland
Scots law, a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles, applies in Scotland. The chief courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases, and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases. The Appellate Committee of the House of Lords (usually just referred to as "The House of Lords") presently serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law but only if the Court of Session grants leave to appeal or the initial judgement was by a majority decision. Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as Sheriff solemn Court, or with a Sheriff and no jury, known as (Sheriff summary Court). The Sheriff courts provide a local court service with 49 Sheriff courts organised across six Sheriffdoms.
The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts for a criminal trial: " guilty", " not guilty" and " not proven". Both "not guilty" and "not proven" result in an acquittal with no possibility of retrial. The Scottish Prison Service (SPS) manages the prisons in Scotland which contain between them over 7,500 prisoners. The Cabinet Secretary for Justice is responsible for the Scottish Prison Service within the Scottish Government.
Geography
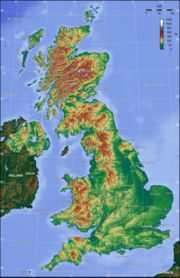
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland comprises the island of Great Britain (most of England, Scotland and Wales) and the northeastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland (Northern Ireland), together with smaller islands. The mainland lies between latitudes 49° and 59° N (the Shetland Islands reach to nearly 61° N), and longitudes 8° W to 2° E. The Royal Greenwich Observatory, near London, is the defining point of the Prime Meridian. The UK lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, and comes within 35 kilometres (22 mi) of the northwest coast of France, from which it is separated by the English Channel. Northern Ireland shares a 360-kilometre (224 mi) land boundary with Ireland. The Channel Tunnel ("Chunnel") now links the UK with France beneath the English Channel. The greatest distance between two points on the UK mainland of Great Britain is 1,350 kilometres (840 mi) between Land's End in Cornwall (near Penzance) and John O'Groats in Caithness (near Thurso), a two day journey by car. When measured directly north-south it is a little over 1,100 kilometres (700 mi) in length and is a fraction under 500 kilometres (300 mi) at its widest. The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 245,000 square kilometres (94,600 sq mi).
The United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. The temperature varies with the seasons but seldom drops below −10 °C (14.0 °F) or rises above 35 °C (95 °F). The prevailing wind is from the southwest, bearing frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean. Eastern parts are most sheltered from this wind and are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters, especially in the west, where winters are wet, especially over high ground. Summers are warmest in the south east of England, being closest to the European mainland, and coolest in the north. Snowfall can occur in winter and early spring, though it rarely settles to great depth away from high ground.
England accounts for just over half of the total area of the UK, covering 130,410 square kilometres (50,350 sq mi). Most of the country consists of lowland terrain, and mountainous terrain north-west of the Tees-Exe line. Mountain chains are found in the north-west (Cumbrian Mountains of the Lake District), north (the upland moors of the Pennines and limestone hills of the Peak District) and south-west (Exmoor and Dartmoor). Lower ranges include the limestone hills of the Isle of Purbeck, Cotswolds and Lincolnshire Wolds, and the chalk downs of the Southern England Chalk Formation. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber Estuary. England's highest mountain is Scafell Pike, which is in the Lake District 978 metres (3,209 ft). England has a number of large towns and cities and, in terms of Larger Urban Zones, has six of the top 50 Zones in the European Union.
Scotland accounts for about a third of the total area of the UK, covering 78,789 square kilometres (30,420 sq mi). The topography of Scotland is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh to Stonehaven. The faultline separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland's mountainous terrain, including the highest peak, Ben Nevis, at 1,344 metres (4,409 ft). Lowland areas, in the southern part of Scotland, are flatter and home to most of the population, especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt. Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland, although Edinburgh is the capital and political centre of the country. Scotland also has nearly eight hundred islands, mainly west and north of the mainland, notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands.
Wales accounts for less than a tenth of the total area of the UK, covering just 20,758 square kilometres (8,010 sq mi). Wales is mostly mountainous though South Wales is less mountainous than North and Mid Wales. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport and surrounding South Wales Valleys. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia, and include Snowdon (Yr Wyddfa in Welsh), which, at 1,085 m (3,560 ft) is the highest peak in Wales. The 14 (or possibly 15) Welsh mountains over 3,000 feet (914 m) high are known collectively as the Welsh 3000s. Wales borders England to the east and the sea in the other three directions: the Bristol Channel to the south, St George's Channel to the west, and the Irish Sea to the north. Wales has over 1,200 km (750 miles) of coastline. There are several islands off the Welsh mainland, the largest being Anglesey (Ynys Môn) in the northwest.
Northern Ireland accounts for just 14,160 square kilometres (5,470 sq mi) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh, at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), the largest body of water in the UK and Ireland. The highest peak is Slieve Donard at 849 metres (2,785 ft) in the province's Mourne Mountains.
Cities and conurbations
The capitals of the individual countries of the UK are: Belfast (Northern Ireland), Cardiff (Wales), Edinburgh (Scotland) and London (England), which is also the capital of the UK as a whole.
| Rank | City | Location | Pop. | Rank | City | Location | Pop. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London | London | 7,172,091 | 11 | Coventry | West Midlands | 303,475 | |||
| 2 | Birmingham | West Midlands | 970,892 | 12 | Kingston upon Hull | Yorkshire and the Humber | 301,416 | |||
| 3 | Glasgow | Scotland | 629,501 | 13 | Bradford | Yorkshire and the Humber | 293,717 | |||
| 4 | Liverpool | North West England | 469,017 | 14 | Cardiff | Wales | 292,150 | |||
| 5 | Leeds | Yorkshire and the Humber | 443,247 | 15 | Belfast | Northern Ireland | 276,459 | |||
| 6 | Sheffield | Yorkshire and the Humber | 439,866 | 16 | Stoke-on-Trent | West Midlands | 259,252 | |||
| 7 | Edinburgh | Scotland | 430,082 | 17 | Wolverhampton | West Midlands | 251,462 | |||
| 8 | Bristol | South West England | 420,556 | 18 | Nottingham | East Midlands | 249,584 | |||
| 9 | Manchester | North West England | 394,269 | 19 | Plymouth | South West England | 243,795 | |||
| 10 | Leicester | East Midlands | 330,574 | 20 | Southampton | South East England | 234,224 | |||
| 2001 Census | ||||||||||
The largest conurbations are as follows:
- Greater London Urban Area - 8.28 million
- West Midlands conurbation - 2.28 million
- Greater Manchester Urban Area - 2.24 million
- West Yorkshire Urban Area - 1.50 million
- Greater Glasgow - 1.17 million
Demography
Population, migration and ethnicity
At the April 2001 UK Census, the total population of the United Kingdom was 58,789,194, the third largest in the European Union (behind Germany and France), the fifth largest in the Commonwealth and the twenty-first largest in the world. By mid-2006, this had been estimated to have increased to 60,587,300. Much of this increase was due to net immigration but was also due to a rising birth rate and increasing life expectancy.
England's population by mid-2006 was estimated to be 50,762,900 making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world with 383 people resident per square kilometre. About a quarter of the UK population lives in England's prosperous south-east and is predominantly urban and suburban, with an estimated 7,517,700 in the capital of London.
The mid-2006 estimates put Scotland's population at 5,116,900, Wales at 2,965,900 and Northern Ireland at 1,741,600 with much lower population densities than England. Compared to England's 383 people resident per square kilometre, the corresponding figures were 142 for Wales, 125 for Northern Ireland and just 65 for Scotland.
In 2006, the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.84 children per woman, below the replacement rate of 2.1 but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63. Within the UK, England and Wales, at 1.86, were both close to the UK average, but Scotland was lower at only 1.67. The UK's TFR was considerably higher during the 1960s 'baby boom', peaking at 2.95 children per woman in 1964.
The present day population of the UK is descended from varied ethnic stocks though mainly: pre-Celtic, Celtic, Roman, Anglo-Saxon, and the Normans. Since 1945, international ties forged by the British Empire have contributed to substantial immigration, especially from Africa, Caribbean and South Asia. Since EU citizens are free to live and work in other EU member states, the accession of new to the EU of new member states from Central and Eastern Europe in 2004 has resulted in rising immigration from these countries. As of 2008, the trend is reversing and many Poles are returning to Poland. As of 2001, 92.1% of the population identified themselves as White, leaving 7.9% of the UK population identifying themselves as mixed race or ethnic minority.
| Ethnic group | Population | % of total* |
|---|---|---|
| White | 54,153,898 | 92.1% |
| Mixed race | 677,117 | 1.2% |
| Indian | 1,053,411 | 1.8% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1.3% |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 0.5% |
| Other Asian (non-Chinese) | 247,644 | 0.4% |
| Black Caribbean | 565,876 | 1.0% |
| Black African | 485,277 | 0.8% |
| Black (others) | 97,585 | 0.2% |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 0.4% |
| Other | 230,615 | 0.4% |
| * Percentage of total UK population | ||
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4% of London's population and 37.4% of Leicester's was estimated to be non-white as of June 2005, whereas less than 5% of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West were from ethnic minorities according to the 2001 census. As of 2007, 22% of primary school children and 17.7% of children at secondary school in England were from ethnic minority families. Britain's immigrant population will almost double in the next two decades to 9.1 million, a report said on January 31, 2008.
In contrast with some other European countries, high foreign-born immigration is contributing to a rising population, accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. The latest official figures (2006) show net immigration to the UK of 191,000 (591,000 immigrants and 400,000 emigrants) up from 185,000 in 2005 (overall, there was a loss of 126,000 Britons and a gain of 316,000 foreign citizens). One in six were from Eastern European countries, with larger numbers coming from New Commonwealth countries. Immigration from the Indian subcontinent, mainly fuelled by family reunion, accounted for two-thirds of net immigration. By contrast, at least 5.5 million British-born people are living abroad. The most popular emigrant destinations were Australia, Spain, France, New Zealand and the U.S.
A study by a city forecaster, however, contends that the above immigration figures are unreliable and that net immigration for 2005 was circa 400,000. Nonetheless, the proportion of foreign-born people in the UK population remains slightly below that of some other European countries.
In 2004, the number of people who became British citizens rose to a record 140,795 - a rise of 12% on the previous year. This number had risen dramatically since 2000. The overwhelming majority of new citizens come from Africa (32%) and Asia (40%), the largest three groups being people from Pakistan, India and Somalia. In 2006, there were 149,035 applications for British citizenship, 32% fewer than in 2005. The number of people granted citizenship during 2006 was 154,095, 5% fewer than in 2005. The largest groups of people granted British citizenship were from India, Pakistan, Somalia and the Philippines. 21.9% of babies born in England and Wales in 2006 were born to mothers who were born outside the UK, (146,956 out of 669,601), according to official statistics released in 2007 that also show the highest birth rates for 26 years. As in the rest of the European Union, however, the birth rate remains below the replacement rate.
When the EU enlarged further east in 2004 and again in 2007, this gave the right for nationals from countries like Poland, Slovakia, Lithuania, and more recently Romania and Bulgaria to live in the UK. Figures published in August 2007 indicated that 682,940 people applied to the Worker Registration Scheme (for nationals of the central and eastern European states that joined the EU in May 2004) between 1 May 2004 and 30 June 2007, of whom 656,395 were accepted. Self-employed workers and people who are not working (including students) are not required to register under the scheme so this figure represents a lower limit on immigration inflow. These figures do not indicate the number of immigrants who have since returned home, but 56% of applicants in the 12 months ending 30 June 2007 reported planning to stay for a maximum of three months, with net migration in 2005 from the new EU states standing at 64,000. Research suggests that a total of around 1 million people had moved from the new EU member states to the UK by April 2008, but that half this number have since returned home or moved on to a third country. One in every four Poles in the UK is planning to remain for life, a survey has revealed.
National Insurance Number data suggests that 2.5 million foreign workers moved to the UK to work (including those moving for short periods), the majority from EU countries, between 2002 and 2007.
The UK government is currently introducing a new points-based immigration system to replace the existing schemes for immigration from outside of the European Economic Area.
Languages
Though the UK does not de jure have an official language, the predominant spoken language is English, a West Germanic language descended from Old English featuring a large number of borrowings from Old Norse, Norman French and Latin. The English language has spread across the world (largely due to the British Empire) and has thus become the business language of the world. Worldwide, it is taught as a second language more than any other.
The other indigenous languages of the UK are Scots (which is closely related to English) and four Celtic languages. The latter fall into two groups: two P-Celtic languages ( Welsh and Cornish); and two Q-Celtic languages ( Irish and Scottish Gaelic). Celtic dialectal influences from Cumbric persisted in Northern England for centuries, most famously in a unique set of numbers used for counting sheep (see Yan Tan Tethera). According to the 2001 census, just above 20% of the population of Wales claim to be able to speak Welsh which represents a slight increase on 1991. In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England. Welsh and Scottish Gaelic are also spoken by small groups around the globe with some Gaelic still spoken in Nova Scotia, Canada, and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina.
Immigrant languages constitute for up to 10% of the UK's population, French is spoken by 2.3% of the country's population, 1.0% of Britons speak Polish reflecting the recent mass migration to the UK. 0.9% of the UK's population speak German and 0.8% Spanish. The majority of other foreign languages spoken in the UK originate from Europe, Asia and Africa. A large percentage of the immigrants to the UK come from Anglophone countries (such as Nigeria, Jamaica, Hong Kong and the Philippines), which is why there is not a great deal of diversity between some of the country's ethnic minority communities.
Religion
While the United Kingdom has a long tradition of Christianity and a link between church and state still remains in England, in practice the UK is a predominantly secular society with only 38% proclaiming a belief in a God. People identify themselves with religion in the UK for both cultural and religious reasons and this is reflected by the disparity between the figures for those proclaiming a belief in a God and those identifying themselves with a particular religion. Christianity has the largest number of adherents followed by Islam, Hinduism, Sikhism and Judaism.
Christianity

Christianity is the major religion with many Christian churches, denominations, and groups. The Tearfund Survey in 2007 revealed 53% identified themselves as Christian. The report compared this to the 2004 British Social Attitudes Survey in which the results were very similar, and to the 2001 UK Census in which 71.6% said that Christianity was their religion, although noting that the latter used "a softer question".
The Church of England, which split from Rome in 1534 (see English Reformation) is, today, the ' established' Church in England and the senior branch of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The British monarch is required to be a member of the Church of England under the Act of Settlement 1701 and is its Supreme Governor. The Archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop of the Church. The direct influence of the Church of England has been on the decline for years, but the church retains a representation in the UK Parliament and the right to draft legislative measures (usually related to religious administration), through the General Synod, that can be passed into law, but not amended by Parliament.
The Church of Scotland (known informally as the Kirk), which broke with Rome in 1560 (see Calvinism and Scottish Reformation) is a Presbyterian church, recognised as the national church of Scotland, and not subject to state control. The British monarch is an ordinary member, and is required to swear an oath to "defend the security" of the Church at the coronation. The Scottish Episcopal Church, which is now part of the Anglican Communion, dates from the final establishment of Presbyterianism in Scotland in 1690, when it split from the Church of Scotland, and is not a 'daughter church' of the Church of England. Further splits in the Church of Scotland, especially in the nineteenth century, led to the creation of various other Presbyterian churches in Scotland, including the Free Church of Scotland.
In the 1920s, the Church in Wales was separated from the Church of England and became ' disestablished'. The Church in Wales remains in the Anglican Communion. Methodism and other independent churches are traditionally strong in Wales.
The Anglican Church of Ireland was disestablished in the nineteenth century. It covers the entire island of Ireland (both Northern Ireland and Ireland). In Northern Ireland the Catholic Church in Ireland is the largest single denomination, although Protestants are in the majority overall. The Presbyterian Church in Ireland is the largest Protestant denomination and is in terms of theology and history closely linked to the Church of Scotland
The Roman Catholic Church is the second largest denomination of Christianity in the UK. After the Protestant Reformation, strict laws were passed against Catholics; these were removed by the Catholic Emancipation laws in 1829. There are separate Catholic hierarchies for England and Wales, Scotland and Ireland.
Other large Christian groups include the Methodists (founded by John Wesley in London) and the Baptists. There are also growing Evangelical and Pentecostal churches, many of which have flourished with immigration from around the Commonwealth and beyond. Pentecostal churches are now third after the Church of England and the Roman Catholic Church in terms of church attendance.
Other religions
Muslims in the United Kingdom are believed to number 1.8 million. Mosques are present in most regions: The biggest groups are of Pakistani, Bangladeshi and Indian origin. More recently, refugees from Somalia, Northern Cyprus, the Balkans and Arab countries have increased Britain's Muslim population. The 2006 controversy over the burqa, brought up in comments by politician Jack Straw, reflects a split between some Britons questioning Muslim integration with British society, and others who believe that wearing the veil is compatible with it, in Britain.
Religions of Indian origin, such as Hinduism, Sikhism, Buddhism and Jainism are followed in Britain. As of the 2001 census, there are about 560,000 Hindus and 340,000 Sikhs. Buddhism is practised by about 150,000 people. It is likely that these figures have increased since 2001. One non-governmental organisation estimates that there are 800,000 Hindus in the UK. Leicester houses one of the world's few Jain temples that are outside of India.
There are approximately 270,000 Jews in Britain, according to the 2001 census.
The United Kingdom has a large and growing atheist and agnostic population with 9.1 million (15% of the UK population) claiming no religion in the 2001 census.
Economy

The UK economy is made up (in descending order of size) of the economies of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The British started the Industrial Revolution, and, like most industrialising countries at the time, initially concentrated on heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining, steel production, and textiles. The empire created an overseas market for British products, allowing the United Kingdom to dominate international trade in the 19th century. However, as other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. The British service sector, however, has grown substantially, and now makes up about 73% of GDP.
The service sector of the United Kingdom is dominated by financial services, especially in banking and insurance. London is the world's largest financial centre with the London Stock Exchange, the London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, and the Lloyd's of London insurance market all based in the City of London. It has the largest concentration of foreign bank branches in the world. In the past decade, a rival financial centre in London has grown in the Docklands area, with HSBC and Barclays Bank relocating their head offices there. Many multinational companies that are not primarily UK-based have chosen to site their European or rest-of-world headquarters in London: an example is the US financial services firm Citigroup. The Scottish capital, Edinburgh, has one of the large financial centres of Europe.
London is a major centre for international business and commerce and is the leader of the three "command centres" for the global economy (along with New York City and Tokyo). In recent years, the UK economy has been managed in accordance with principles of market liberalisation and low taxation and regulation. Based on market exchange rates, the United Kingdom is the fifth largest economy in the world, and the second largest in Europe after Germany.
Tourism is very important to the British economy. With over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world.
The British manufacturing sector, however, has greatly diminished, relative to the economy as a whole, since World War II. It is still a significant part of the economy, but only accounted for one-sixth of national output in 2003. The British motor industry is a significant part of this sector, although it has diminished with the collapse of MG Rover and most of the industry is foreign owned. Civil and defence aircraft production is led by the United Kingdom's largest aerospace firm, BAE Systems, and the continental European firm EADS, the owner of Airbus. Rolls-Royce holds a major share of the global aerospace engines market. The chemical and pharmaceutical industry is strong in the UK, with the world's second and sixth largest pharmaceutical firms (GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca, respectively) being based in the UK.
The creative industries accounted for 7.3% GVA in 2004 and grew at an average of 5% per annum between 1997 and 2004.
The United Kingdom's agriculture sector accounts for only 0.9% of the country's GDP.

The UK has a small coal reserve along with significant natural gas, and oil reserves.
Government involvement throughout the economy is exercised by the Chancellor of the Exchequer (currently Alistair Darling) who heads HM Treasury, but the Prime Minister (currently The Rt Hon Gordon Brown MP), is First Lord of the Treasury; the Chancellor of the Exchequer is the Second Lord of the Treasury. However since 1997, the Bank of England, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has control of interest rates and other monetary policy.
As of 2007, United Kingdom's government debt rose to 43.3% of GDP.
The currency of the UK is the pound sterling, represented by the symbol £. The Bank of England is the central bank, responsible for issuing currency. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover the issue. The UK chose not to join the euro at the currency's launch, and the British Prime Minister, The Rt Hon Gordon Brown MP, has ruled out membership for the foreseeable future, saying that the decision not to join had been right for Britain and for Europe. The government of former Prime Minister Tony Blair had pledged to hold a public referendum for deciding membership should " five economic tests" be met. In 2005, more than half (55%) of the UK were against adopting the currency, while 30% were in favour.
Education
Each country of the United Kingdom has a separate education system, with power over education matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland being devolved.
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day to day administration and funding of state schools being the responsibility of Local Authorities. Qualifications at the secondary school and post-secondary ( further education) level are provided by the Scottish Qualifications Authority and delivered through various schools, colleges and other centres. Scotland first legislated for universal provision of education in 1696. The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4% though it has been rising slowly in recent years.Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges as the fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.
Education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Children, Schools and Families and the Secretary of State for Innovation, Universities and Skills, though the day to day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of Local Education Authorities. Universal state education in England and Wales was introduced for primary level in 1870 and secondary level in 1900. Education is mandatory from ages five to sixteen (15 if born in late July or August). The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, only a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Despite a fall in actual numbers, the proportion of children in England attending private schools has risen to over 7%. Just over half of students at the leading universities of Cambridge and Oxford had attended state schools. State schools which are allowed to select pupils according to intelligence and academic ability can achieve comparable results to the most selective private schools: out of the top ten performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 two were state-run grammar schools. England has some of the top universities in the world with Cambridge, Oxford, and London ranked amongst the top 20 in the 2007 THES - QS World University Rankings.There are fears, however, that a decline in England in the number studying a foreign language will have a negative effect on business, and has led to calls for languages to be given greater priority.
The Northern Ireland Assembly is responsible for education in Northern Ireland though responsibility at a local level is administered by 5 Education and Library Boards covering different geographical areas.
The National Assembly for Wales has responsibility for education in Wales. A significant number of students in Wales are educated either wholly or largely through the medium of Welsh and lessons in the language are compulsory for all until the age of 16. There are plans to increase the provision of Welsh Medium schools as part of the policy of having a fully bi-lingual Wales.
The Programme for International Student Assessment ranked the UK 14th in science which was higher than the OECD average.
Healthcare
Each country of the United Kingdom has a separate public healthcare system, with power over the provision of health services in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland being devolved. Though each provides healthcare that is generally free to patients, being funded from general taxation, considerable differences are now developing between the different systems. A much smaller private medical system also exists. The UK and devolved governments take on both the role of suppliers of public healthcare and assessors of the quality of its delivery. Various regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based (e.g. Royal Colleges). Across the UK, there is a large number of medical schools and dental schools, and a considerable establishment for training nurses and professions allied to medicine.
Though the public health systems are commonly referred to as the NHS across the UK, in fact the National Health Service just covers England. The NHS was set up by the National Health Service Act 1946 and came into effect on July 5th 1948. The Secretary of State for Health is answerable to the UK Parliament for the running of the Department of Health and for the work of the NHS (in England). The NHS is one of the largest cohesive organisations of any type in the world employing over 1.3 million people. Public sector healthcare delivery consists of primary ( General Practice), secondary ( district general hospital) and tertiary ( teaching hospital) levels of service. There is considerable interaction and cross-flow between the various levels. NICE advices on whether drugs or treatments should be provided by the NHS.
Healthcare in Scotland is mainly provided by NHS Scotland, Scotland's public healthcare system. The service was founded by the National Health Service (Scotland) Act 1947 (later repealed by the National Health Service (Scotland) Act 1978) that took effect on July 5th, 1948 to coincide with the launch of the NHS in England and Wales. In 2006, the NHS in Scotland had around 158,000 staff including more than 47,500 nurses, midwives and health visitors and over 3,800 consultants. In addition, there were also more than 12,000 doctors, family practitioners and allied health professionals, including dentists, opticians and community pharmacists, who operate as independent contractors providing a range of services within the NHS in return for fees and allowances. The Cabinet Secretary for Health and Wellbeing responsible to the Scottish Parliament for the work of NHS Scotland.
Healthcare in Wales is mainly provided by NHS Wales. It was originally formed as part of the same NHS structure created by the National Health Service Act 1946 but powers over the NHS in Wales came under the Secretary of State for Wales in 1969. In turn, responsibility for NHS Wales was passed to the Welsh Assembly and Executive under devolution in 1999. NHS Wales provides public healthcare in Wales and employs some 90,000 staff, making it Wales’ biggest employer. The Minister for Health and Social Services is the person within the Welsh Assembly Government who holds cabinet responsibilities for both health and social care in Wales.
Healthcare in Northern Ireland is mainly provided by the Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety.
Transport
The transport systems in the United Kingdom are the responsibility of each individual country. The English transport network is the responsibility of the UK Department for Transport (which also has responsibility for some transport matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland that are not devolved) with the Highways Agency being the executive agency responsible for trunk roads and motorways in England apart from the privately owned and operated M6 Toll . The Department for Transport states that traffic congestion is one of the most serious transport problems and that it could cost England an extra £22 billion in wasted time by 2025 if left unchecked. According to the government-sponsored Eddington report of 2006, congestion is in danger of harming the economy, unless tackled by road pricing and expansion of the transport network.
The Scottish transport network is the responsibility of the Scottish Government's Enterprise, Transport and Lifelong Learning Department with Transport Scotland being the Executive Agency that is accountable to the Cabinet Secretary for Finance and Sustainable Growth for Scotland's trunk roads and rail networks. Scotland's rail network has around 340 railway stations and 3,000 kilometres of track with over 62 million passenger journeys made each year.
Across the UK, there is a radial road network of 46,904 kilometres (29,145 mi) of main roads with a motorway network of 3,497 kilometres (2,173 mi). There are a further 213,750 kilometres (132,818 mi) of paved roads. The rail network of 16,116 km (10,072 miles) in Great Britain and 303 route km (189 route mi) in Northern Ireland carries over 18,000 passenger trains and 1,000 freight trains daily. Urban rail networks are well developed in London and other cities. There was once over 48,000 route km (30,000 route mi) of rail network in the UK, however most of this was reduced over a time period from 1955 to 1975, much of it after a report by a government advisor Richard Beeching in the mid 1960s (known as the Beeching Axe). Plans are now being considered to built new high speed lines by 2025.
Heathrow Airport is the world's busiest international airport and, being an island country, the UK has a considerable number of sea ports.
Sport
Many major sports originated in the United Kingdom, including football, rugby, cricket, tennis and golf.
Football

Like many team sports, football is organised on a separate basis for each of the countries of the United Kingdom and each has its own Football Association, national team and league system, though a few clubs play outside their country's respective systems for a variety of historical and logistical reasons. Football was developed in the UK and is comfortably the most popular sport.
England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland compete as separate countries in international competition and, as a consequence, the UK does not compete as a single team in football events at the Olympic Games. Although there are proposals to have a UK team take part in the 2012 Summer Olympic Games, which are to be held in London, the Scottish, Welsh and Northern Irish football associations have declined to participate, fearing that it would undermine their independent status - a fear confirmed by FIFA president Sepp Blatter. England has been the most successful of the home nations, winning the World Cup in 1966.
The English football league system includes hundreds of inter-linked leagues, consisting of thousands of divisions. The FA Premier League is at the top, followed by The Football League and then the Football Conference, where the structure starts to become regional and includes the Northern Premier League, the Southern League, the Isthmian League and more besides. The Premiership is the most-watched football league in the world and is particularly popular in Asia; in the People's Republic of China, matches attract television audiences between 100 million and 360 million, more than any other foreign sport. England is home to world-renowned football clubs such as Liverpool, Manchester United, Chelsea, and Arsenal. English teams have been successful in European Competitions including some who have become European Cup/UEFA Champions League winners: Liverpool (five times), Manchester United (three times), Nottingham Forest (twice) and Aston Villa. More clubs from England have won the European Cup than any other country (four compared to three from Italy, Germany and the Netherlands). Moreover, England ranks second in the all time list of European club trophies won with 35, one behind Italy's 36. The European Cup competition itself was brought about due to the success of another English club, Wolverhampton Wanderers, against top European sides in the 1950s. The 90,000 capacity Wembley Stadium is the principal sporting stadium of England.
The Scottish football league system is much smaller, with just two national leagues: the Scottish Premier League (SPL) and the Scottish Football League which has three divisions. There are, however, other regional leagues that are not connected to the national system, most notably the Highland Football League. One English club, Berwick Rangers, plays in the Scottish system. Scotland is home to world-renowned football clubs such as Rangers and Celtic. Scottish teams that have been successful in European Competitions include Celtic (European Cup in 1967), Rangers (European Cup Winners Cup 1972) and Aberdeen (European Cup Winners Cup and European Super Cup in 1983).
The Welsh football league system includes the Welsh Premier League and regional leagues. Welsh Premiership club The New Saints play their home matches on the English side of the border in Oswestry. The Welsh clubs of Cardiff City, Colwyn Bay, Merthyr Tydfil, Newport County, Swansea City and Wrexham play in the English system. Cardiff's 76,250 seater Millennium Stadium is the principal sporting stadium of Wales.
The Northern Irish football league system includes the Irish Football League. One Northern Irish club, Derry City, plays their football outside of the UK in the Republic of Ireland football league system.
Other sports
Both forms of rugby are national sports. Rugby league originates from and is generally played in the Northern England, while rugby union is played throughout the UK. Though supposedly originating from the actions of William Webb Ellis at the School at Rugby, it is now considered the national sport of Wales. In rugby league the UK has been represented by a single 'Great Britain' team but this will change for the 2008 Rugby League World Cup in which Scotland, England and Ireland will compete as separate nations. This bring it into line with rugby union in which England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland (which consists of players from Ireland and Northern Ireland) already compete in international competition. However, every four years a British and Irish Lions team tours Australia, New Zealand or South Africa, composed of players selected from all the Home nations.
There is no UK-wide cricket team. The game was invented in England and the England Cricket Team, technically the England and Wales team, is the only national team in the UK with Test status. Irish and Scottish players have played for England because neither Scotland nor Ireland have Test status and only play in One Day Internationals. As of 2006, teams representing Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) compete at the One-Day International level. England and Wales has a professional league championship in which County teams compete.
Snooker is also one of Great Britain's sporting exports. A high-skill game similar to billiards, the world championships are held annually in Sheffield. The sport continues to expand worldwide, with huge growth in China.
The game of tennis first originated from the City of Birmingham between 1859 and 1865. The Wimbledon Championships are international tennis events held in Wimbledon in south London every summer and are regarded as the most prestigious event of the global tennis calendar.
Thoroughbred racing is popular throughout the UK. It originated under Charles II of England as the "Sport of Kings" and is a royal pastime to this day. World-famous horse races include the Grand National, the Epsom Derby and Royal Ascot. The town of Newmarket is considered the centre of English racing, largely due to the famous Newmarket Racecourse.
The UK has proved successful in the international sporting arena in rowing. It is widely considered that the sport's most successful rower is Steven Redgrave who won five gold medals and one bronze medal at five consecutive Olympic Games as well as numerous wins at the World Rowing Championships and Henley Royal Regatta.
Golf is one of the most popular participation sports played in the UK, with St Andrews in Scotland being the sport's home course.
Shinty (or camanachd) (A sport derived from the same root as the Irish hurling and similar to bandy) is popular in the Scottish Highlands, sometimes attracting crowds numbering thousands in the most sparsely populated region of the UK.
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK and drivers from Britain have won more world titles than any other country. The country hosts legs of the F1 and World Rally Championship and has its own Touring Car Racing championship, the British Touring Car Championship (BTCC). The British Grand Prix takes place at Silverstone each July.
Dancesport or competitive Ballroom dancing has its origins in the UK when popular dancing at the time was codified by British dance schools from the 1920s onwards. For example, the Slow Waltz is still known as the English Waltz which is now as distinct from its original roots as its name, the Viennese Waltz. The UK remains a major centre for the sport and Ballroom dancing in general with the Empress Ballroom at the Winter Gardens in Blackpool being a popular venue for major competitions.
Culture
The origins of the UK as a political union of formerly independent countries has resulted in the preservation of distinctive cultures in each of the home nations.
For details, see articles on: Culture of England, Culture of Scotland, Culture of Wales, Culture of Northern Ireland.
Cinema
The United Kingdom has been influential in the development of cinema, with the Ealing Studios claiming to be the oldest studios in the world. Despite a history of important and successful productions, the industry is characterised by an ongoing debate about its identity, and the influences of American and European cinema. The BFI Top 100 British films is a poll conducted by the British Film Institute which ranks what they consider to be the 100 greatest British films of all time.
Literature

'British literature' refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands as well as to literature from England, Wales and Scotland prior to the formation of the United Kingdom.
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time. Among the earliest English writers are Geoffrey of Monmouth (12th century), Geoffrey Chaucer (14th century), and Thomas Malory (15th century). In the 18th century, Samuel Richardson is often credited with inventing the modern novel. In the 19th century, there followed further innovation by Jane Austen, the Brontë sisters, the social campaigner Charles Dickens, the naturalist Thomas Hardy, the visionary poet William Blake and romantic poet William Wordsworth. Twentieth century writers include the science fiction novelist H. G. Wells, the controversial D. H. Lawrence, the modernist Virginia Woolf, the prophetic novelist George Orwell and the poet John Betjeman. Most recently, the children's fantasy Harry Potter series by J. K. Rowling has recalled the popularity of J.R.R. Tolkien.
Scotland's contribution includes the detective writer Arthur Conan Doyle, romantic literature by Sir Walter Scott, the epic adventures of Robert Louis Stevenson and the celebrated poet Robert Burns. More recently, the modernist and nationalist Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance. A more grim outlook is found in Ian Rankin's stories and the psychological horror-comedy of Iain Banks. Scotland's capital, Edinburgh, is UNESCO's first worldwide city of literature.
In the early medieval period, Welsh writers composed the Mabinogion. In modern times, the poets R.S. Thomas and Dylan Thomas have brought Welsh culture to an international audience.
Authors from other nationalities, particularly from Ireland, or from Commonwealth countries, have lived and worked in the UK. Significant examples through the centuries include Jonathan Swift, Oscar Wilde, Bram Stoker, George Bernard Shaw, Joseph Conrad, T. S. Eliot and Ezra Pound, and more recently British authors born abroad such as Kazuo Ishiguro and Sir Salman Rushdie.
In theatre, Shakespeare's contemporaries Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson added depth. More recently Alan Ayckbourn, Harold Pinter, Michael Frayn, Tom Stoppard and David Edgar have combined elements of surrealism, realism and radicalism.
Music
Classical music: Notable composers from the United Kingdom have included William Byrd, Henry Purcell, Sir Edward Elgar, Sir Arthur Sullivan (most famous for working with librettist Sir W. S. Gilbert), Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, pioneer of modern British opera. London remains one of the major classical music capitals of the world.
Popular music: Prominent among the UK contributors to the development of rock music in the 1960s and 1970s were The Beatles, Pink Floyd, Eric Clapton, The Rolling Stones, Led Zeppelin, The Who, Queen, and Black Sabbath. Heavy metal, hard rock, punk rock and New Wave were among the variations that followed. In the early 1980s, UK bands from the New Romantic scene such as Duran Duran, Depeche Mode, Spandau Ballet, Soft Cell and Ultravox were prominent. In the 1990s, Britpop bands and electronica music attained international success. More recent pop acts, including The Smiths, Oasis, Amy Winehouse, Coldplay, and the Spice Girls, have ensured the continuation of the UK's massive contribution to popular music.
Philosophy
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of "British Empiricism", a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid. The most famous philosophers of this tradition are John Locke, George Berkeley and David Hume. Britain is notable for a theory of moral philosophy, Utilitarianism, first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill, in his short work Utilitarianism. Other eminent philosophers from the UK and the countries that preceded it include William of Ockham, Thomas Hobbes, Bertrand Russell, Adam Smith and Alfred Ayer. Foreign born philosophers who settled in the UK include Isaiah Berlin, Karl Marx, Karl Popper, and Ludwig Wittgenstein.
Science, engineering and innovation
The modern scientific method was promoted by the English philosopher Francis Bacon in the early seventeenth century, and subsequent advances credited to British scientists and engineers include:
- The laws of motion and illumination of gravity, by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century
- The unification of electromagnetism, by James Clerk Maxwell
- The discovery of hydrogen, by Henry Cavendish
- The steam locomotive, by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian
- The telephone, by Alexander Graham Bell
- Evolution by natural selection, by Charles Darwin
- The Turing machine, by Alan Turing, the basis of modern computers
- The structure of DNA, by Francis Crick and others
- The development of the World Wide Web, largely attributed to Tim Berners-Lee
Notable civil engineering projects, whose pioneers included Isambard Kingdom Brunel, contributed to the world's first national railway transport system. Other advances pioneered in the UK include the marine chronometer, television, the jet engine, the modern bicycle, electric lighting, the electric motor, the screw propeller, the internal combustion engine, military radar, the electronic computer, vaccination and antibiotics.
Scientific journals produced in the UK include Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet. In 2006, it was reported that the UK provided 9% of the world's scientific research papers and a 12% share of citations.
Visual art
The Royal Academy is located in London. Other major schools of art include the Slade School of Art; the six-school University of the Arts, London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; the Glasgow School of Art, and Goldsmiths, University of London. This commercial venture is one of Britain's foremost visual arts organisations. Major British artists include Sir Joshua Reynolds, Thomas Gainsborough, John Constable, William Blake, J. M. W. Turner, William Morris, L.S. Lowry, Francis Bacon, Lucian Freud, David Hockney, Gilbert and George, Richard Hamilton, Peter Blake, Howard Hodgkin, Antony Gormley, and Anish Kapoor. During the late 1980s and 1990s, the Saatchi Gallery in London brought to public attention a group of multigenre artists who would become known as the Young British Artists. Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracy Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood, and the Chapman Brothers are among the better known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
Symbols
- The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag commonly known as the "Union Jack". It was created by the superimposition of the flags of England ( St George's Cross) and Scotland ( Saint Andrew's Cross), with the Saint Patrick's cross, to represent Ireland, being added to this in 1801. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. However, the possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out.
- The national anthem of the United Kingdom is " God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is female. The anthem's name, however, remains "God Save the King".

- Britannia is a personification of the United Kingdom, originating from the Roman occupation of southern and central Great Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag. Sometimes she is depicted as riding the back of a lion. At and since the height of the British Empire, Britannia has often associated with maritime dominance, as in the patriotic song Rule Britannia.
- The lion symbol is depicted behind Britannia on the 50 pence piece and one is shown crowned on the back of the 10 pence piece. It is also used as a symbol on the non-ceremonial flag of the British Army.
- The bulldog is sometimes used as a symbol of Great Britain, and has been associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of Nazi Germany.
National symbols within the United Kingdom
- A number of 'national anthems' are used for the individual countries of the UK with varying degrees of popular acceptance, the most popular being Flower of Scotland, Hen Wlad Fy Nhadau in Wales, Londonderry Air in Northern Ireland and Jerusalem in England.
- Lions have been used as heraldic devices, including in the royal arms of the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Kingdom of Gwynedd in Wales. The lion is featured on the emblem of the England national football team, giving rise to the popular football anthem Three Lions, and the England national cricket team. The "three lions" on the English coat of arms were originally two leopards. An extra leopard was added by Richard the Lionheart and with the help of his name, they became known as three lions. They are now drawn to look more like lions. Leopards are traditionally depicted lying down whereas lions were drawn standing on all fours or up on their hind legs attacking, as in the Scottish Lion Rampant.
- England (and sometimes Britain) has been personified as the character John Bull, although this character is rarely used in modern times.
- The oak tree and the rose have long been a widely used proxy for the visual representation of English identity. The red rose is the emblem of the England national rugby union team and the Rugby Football Union.
- The thistle is widely used as a Scottish symbol.
- The daffodil and leek are used as Welsh symbols.
| Flag | Country | Patron saint | Flower |
|---|---|---|---|
| England | St. George | Tudor rose | |
| Scotland | St. Andrew | Thistle | |
| Wales | St. David | Leek/Daffodil | |
| Northern Ireland | St. Patrick | Shamrock/ Flax |
There is no official National flag of Northern Ireland following the Northern Ireland Constitution Act 1973 or any unofficial flag universally supported in Northern Ireland. The use of various flags in Northern Ireland is contentious. However, the Ulster Banner is often used for sporting events. See Northern Ireland flags issue and The Union Flags and flags of the United Kingdom