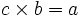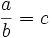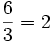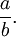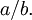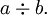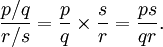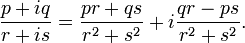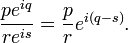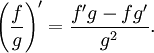Division (mathematics)
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Mathematics
In mathematics, especially in elementary arithmetic, division is an arithmetic operation which is the inverse of multiplication.
Specifically, if c times b equals a, written:
where b is not zero, then a divided by b equals c, written:
For instance,
since
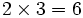 .
.
In the above expression, a is called the dividend, b the divisor and c the quotient.
Division by zero (i.e. where the divisor is zero) is not defined.
Notation
Division is most often shown by placing the dividend over the divisor with a horizontal line, also called a vinculum, between them. For example, a divided by b is written
This can be read out loud as "a divided by b" or "a over b". A way to express division all on one line is to write the dividend, then a slash, then the divisor, like this:
This is the usual way to specify division in most computer programming languages since it can easily be typed as a simple sequence of characters.
A typographical variation, which is halfway between these two forms, uses a solidus (fraction slash) but elevates the dividend, and lowers the divisor:
- a⁄b .
Any of these forms can be used to display a fraction. A fraction is a division expression where both dividend and divisor are integers (although typically called the numerator and denominator), and there is no implication that the division needs to be evaluated further.
A less common way to show division is to use the obelus (or division sign) in this manner:
This form is infrequent except in elementary arithmetic. The obelus is also used alone to represent the division operation itself, as for instance as a label on a key of a calculator.
In some non-English-speaking cultures, "a divided by b" is written a : b. However, in English usage the colon is restricted to expressing the related concept of ratios (then "a is to b").
Computing division
A person who knows the multiplication tables can divide two integers using pencil and paper and the method of long division. If the dividend has a fractional part (expressed as a decimal fraction), we can continue the algorithm past the ones place as far as desired. If the divisor has a fractional part, we can restate the problem by moving the decimal to the right in both numbers until the divisor has no fraction.
Modern computers compute division by methods that are faster than long division: see Division (digital).
A person can calculute division with an abacus by repeatedly placing the dividend on the abacus, and then subtracting the divisor the offset of each digit in the result, counting the number of divisions possible at each offset.
In modular arithmetic, some numbers have a multiplicative inverse with respect to the modulus. We can calculate division by multiplication in such a case. This approach is useful in computers that do not have a fast division instruction.
Division algorithm
The division algorithm is a theorem in mathematics which precisely expresses the outcome of the usual process of division of integers. In particular, the theorem asserts that integers called the quotient q and remainder r always exist and that they are uniquely determined by the dividend a and divisor d, with d ≠ 0. Formally, the theorem is stated as follows: There exist unique integers q and r such that a = qd + r and 0 ≤ r < | d |, where | d | denotes the absolute value of d.
Division of integers
Division of integers is not closed. Apart from division by zero being undefined, the quotient will not be an integer unless the dividend is an integer multiple of the divisor; for example 26 cannot be divided by 10 to give an integer. In such a case there are four possible approaches.
- Say that 26 cannot be divided by 10; division becomes a partial function.
- Give the answer as a decimal fraction or a mixed number, so
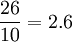 or
or 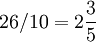 . This is the approach usually taken in mathematics.
. This is the approach usually taken in mathematics. - Give the answer as an integer quotient and a remainder, so
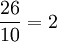 remainder 6.
remainder 6. - Give the integer quotient as the answer, so
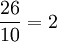 . This is sometimes called integer division.
. This is sometimes called integer division.
One has to be careful when performing division of integers in a computer program. Some programming languages, such as C, will treat division of integers as in case 4 above, so the answer will be an integer. Other languages, such as MATLAB, will first convert the integers to real numbers, and then give a real number as the answer, as in case 2 above.
Names and symbols used for integer division include div, /, \, and %. Definitions vary regarding integer division when the quotient is negative: rounding may be toward zero or toward minus infinity.
Divisibility rules can sometimes be used to quickly determine whether one integer divides exactly into another.
Division of rational numbers
The result of dividing two rational numbers is another rational number when the divisor is not 0. We may define division of two rational numbers p/q and r/s by
All four quantities are integers, and only p may be 0. This definition ensures that division is the inverse operation of multiplication.
Division of real numbers
Division of two real numbers results in another real number when the divisor is not 0. It is defined such a/b = c if and only if a = cb and b ≠ 0.
Division of complex numbers
Dividing two complex numbers results in another complex number when the divisor is not 0, defined thus:
All four quantities are real numbers. r and s may not both be 0.
Division for complex numbers expressed in polar form is simpler than the definition above:
Again all four quantities are real numbers. r may not be 0.
Division of polynomials
One can define the division operation for polynomials. Then, as in the case of integers, one has a remainder. See polynomial long division.
Division of matrices
One can define a division operation for matrices. The usual way to do this is to define A / B = AB−1, where B−1 denotes the inverse of B, but it is far more common to write out AB−1 (or B−1A) explicitly to avoid confusion.
Left and right division
Because matrix multiplication is not commutative, one can also define a left division or so-called backslash-division as A \ B = A−1B. For this to be well defined, B−1 need not exist, however A−1 does need to exist. To avoid confusion, division as defined by A / B = AB−1 is sometimes called right division or slash-division in this context.
Note that with left and right division defined this way, A/(BC) is in general not the same as (A/B)/C and nor is (AB)\C the same as A\(B\C), but A/(BC) = (A/C)/B and (AB)\C = B\(A\C).
Matrix division and pseudoinverse
To avoid problems when A−1 and/or B−1 do not exist, division can also be defined as multiplication with the pseudoinverse, i.e., A / B = AB+ and A \ B = A+B, where A+ and B+ denote the pseudoinverse of A and B.
Division in abstract algebra
In abstract algebras such as matrix algebras and quaternion algebras, fractions such as 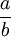 are typically defined as
are typically defined as 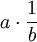 or
or 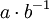 where b is presumed to be an invertible element (i.e. there exists a multiplicative inverse b − 1 such that bb − 1 = b − 1b = 1 where 1 is the multiplicative identity). In an integral domain where such elements may not exist, division can still be performed on equations of the form ab = ac or ba = ca by left or right cancellation, respectively. More generally "division" in the sense of "cancellation" can be done in any ring with the aforementioned cancellation properties. If such a ring is finite, then by an application of the pigeonhole principle, every nonzero element of the ring is invertible, so division by any nonzero element is possible in such a ring. To learn about when algebras (in the technical sense) have a division operation, refer to the page on division algebras. In particular Bott periodicity can be used to show that any real normed division algebra must be isomorphic to either the real numbers R, the complex numbers C, the quaternions H, or the octonions O.
where b is presumed to be an invertible element (i.e. there exists a multiplicative inverse b − 1 such that bb − 1 = b − 1b = 1 where 1 is the multiplicative identity). In an integral domain where such elements may not exist, division can still be performed on equations of the form ab = ac or ba = ca by left or right cancellation, respectively. More generally "division" in the sense of "cancellation" can be done in any ring with the aforementioned cancellation properties. If such a ring is finite, then by an application of the pigeonhole principle, every nonzero element of the ring is invertible, so division by any nonzero element is possible in such a ring. To learn about when algebras (in the technical sense) have a division operation, refer to the page on division algebras. In particular Bott periodicity can be used to show that any real normed division algebra must be isomorphic to either the real numbers R, the complex numbers C, the quaternions H, or the octonions O.
Division and calculus
The derivative of the quotient of two functions is given by the quotient rule:
There is no general method to integrate the quotient of two functions.