Federal Reserve System
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Economics
| Federal Reserve System | |||||
|
|||||
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman | Ben Bernanke | ||||
| Central Bank of | United States | ||||
| Currency | U.S. dollar | ||||
| ISO 4217 Code | USD | ||||
| Base borrowing rate | 2% | ||||
| Base deposit rate | 3.5% | ||||
| Website | federalreserve.gov | ||||
The Federal Reserve System (also the Federal Reserve; informally The Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. Created in 1913 by the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, it is a quasi-public ( government entity with private components) banking system composed of (1) the presidentially appointed Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System in Washington, D.C.; (2) the Federal Open Market Committee; (3) 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks located in major cities throughout the nation acting as fiscal agents for the U.S. Treasury, each with its own nine-member board of directors; (4) numerous private U.S. member banks, which subscribe to required amounts of non-transferable stock in their regional Federal Reserve Banks; and (5) various advisory councils. As of 2008, Ben Bernanke serves as the Chairman of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
History
In 1863, in order to help finance the Civil War, a system of national banks was instituted by the National Currency Act. The banks each had the power to issue standardized national bank notes based on United States bonds held by the bank. The early national banking system had two main weaknesses: an "inelastic" currency; and a lack of liquidity. During the last quarter of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century the United States economy went through a series of financial panics. A particularly severe panic in 1907 provided the motivation for renewed demands for banking and currency reform. The following year Congress enacted the Aldrich-Vreeland Act which provided for an emergency currency and established the National Monetary Commission to study banking and currency reform.
The Federal Reserve Act
The chief of the bipartisan National Monetary Commission was financial expert and Senate Republican leader Nelson Aldrich. Aldrich set up two commissions — one to study the American monetary system in depth and the other, headed by Aldrich himself, to study the European central-banking systems and report on them. Aldrich went to Europe opposed to centralized banking, but after viewing Germany's banking system came away believing that a centralized bank was better than the government-issued bond system that he had previously supported. Centralized banking was met with much opposition from politicians, who were suspicious of a central bank and who charged that Aldrich was biased due to his close ties to wealthy bankers such as J.P. Morgan and his daughter's marriage to John D. Rockefeller, Jr.
Aldrich fought for a private bank with little government influence, but conceded that the government should be represented on the Board of Directors. Most Republicans favored the Aldrich Plan, but it lacked enough support in the bipartisan Congress to pass. Progressive Democrats instead favored a reserve system owned and operated by the government and out of control of the "money trust", ending Wall Street's control of American currency supply. Conservative Democrats fought for a privately owned, yet decentralized, reserve system, which would still be free of Wall Street's control. The Federal Reserve Act passed Congress in late 1913 on a mostly partisan basis, with most Democrats in support and most Republicans against it.
Post Bretton Woods era
In July 1979, Paul Volcker was nominated, by President Carter, as Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board amid roaring inflation. He tightened the money supply, and by 1986 inflation had fallen sharply. In October 1979 the Federal Reserve announced a policy of "targeting" money aggregates and bank reserves in its struggle with double-digit inflation.
In January 1987, with retail inflation at only 1%, the Federal Reserve announced it was no longer going to use money-supply aggregates, such as M2, as guidelines for controlling inflation, even though this method had been in use from 1979, apparently with great success. Before 1980, interest rates were used as guidelines; inflation was severe. The Fed complained that the aggregates were confusing. Volcker was chairman until August 1987, whereupon Alan Greenspan assumed the mantle, seven months after monetary aggregate policy had changed.
Purpose
The purpose of the Federal Reserve System is formally stated in the Federal Reserve Act:
-
To provide for the establishment of Federal reserve banks, to furnish an elastic currency, to afford means of rediscounting commercial paper, to establish a more effective supervision of banking in the United States, and for other purposes.
The primary motivation for creating the Federal Reserve was to address banking panics. The Federal Reserve briefly describes the circumstances that led to its creation, the purpose for creating it, and functions of the system in The Federal Reserve in Plain English:
-
Just before the founding of the Federal Reserve, the nation was plagued with financial crises. At times, these crises led to “panics,” in which people raced to their banks to withdraw their deposits. A particularly severe panic in 1907 resulted in bank runs that wreaked havoc on the fragile banking system and ultimately led Congress in 1913 to write the Federal Reserve Act. Initially created to address these banking panics, the Federal Reserve is now charged with a number of broader responsibilities, including fostering a sound banking system and a healthy economy.
The purpose and functions of the Federal Reserve System include:
- To address banking panics
- To serve as the central bank for the United States
- To strike a balance between private interests of banks and the centralized responsibility of government
- supervising and regulating banking institutions
- protect the credit rights of consumers
- To manage the nation's money supply through monetary policy
- maximum employment
- stable prices
- moderate long-term interest rates
- Maintain the stability of the financial system and containing systemic risk in financial markets
- Providing financial services to depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign official institutions, including playing a major role in operating the nation’s payments system
- facilitate the exchange of payments among regions
- to be responsive to local liquidity needs
- Strengthen U.S. standing in the world economy
Addressing the problem of bank panics
Bank runs occur because banking systems are usually fractional reserve lending institutions and do not have enough cash in reserves to give to all of their depositors simultaneously. Bank runs can lead to a multitude of social and economic problems. The Federal Reserve was designed as an attempt to prevent this from occurring.
Elastic currency
One way to prevent bank runs is to have a money supply that can expand when money is needed. The term "elastic currency" in the Federal Reserve Act doesn't just mean the ability to expand the money supply, but also to contract it. Some economic theories have been developed that support the idea of expanding or shrinking a money supply as economic conditions warrant. Elastic currency is defined by the Federal Reserve as:
Currency that can, by the actions of the central monetary authority, expand or contract in amount warranted by economic conditions.
Monetary policy of the Federal Reserve System is based partially on the theory that it is best overall to expand or contract the money supply as economic conditions change.
Check clearing system
Because some banks refused to clear checks from certain other banks during times of economic uncertainty, which increased financial problems, a check-clearing system was created in the Federal Reserve System. It is briefly described in The Federal Reserve System - Purposes and Functions:
By creating the Federal Reserve System, Congress intended to eliminate the severe financial crises that had periodically swept the nation, especially the sort of financial panic that occurred in 1907. During that episode, payments were disrupted throughout the country because many banks and clearinghouses refused to clear checks drawn on certain other banks, a practice that contributed to the failure of otherwise solvent banks. To address these problems, Congress gave the Federal Reserve System the authority to establish a nationwide check-clearing system. The System, then, was to provide not only an elastic currency—that is, a currency that would expand or shrink in amount as economic conditions warranted—but also an efficient and equitable check-collection system.
Lender of last resort
The Federal Reserve has the authority and financial resources to act as “lender of last resort” by extending credit to depository institutions or to other entities in unusual circumstances involving a national or regional emergency, where failure to obtain credit would have a severe adverse impact on the economy.
Through its discount and credit operations, Reserve Banks provide liquidity to banks to meet short-term needs stemming from seasonal fluctuations in deposits or unexpected withdrawals. Longer term liquidity may also be provided in exceptional circumstances. The rate the Fed charges banks for these loans is the discount rate (officially the primary credit rate).
In making these loans, the Fed serves as a buffer against unexpected day-to-day fluctuations in reserve demand and supply. This contributes to the effective functioning of the banking system, alleviates pressure in the reserves market and reduces the extent of unexpected movements in the interest rates.
Central bank
In its role as the central bank of the United States, the Fed serves as a 'banker's bank' and as the government's bank. As the banker's bank, it helps to assure the safety and efficiency of the payments system. As the government's bank, or fiscal agent, the Fed processes a variety of financial transactions involving trillions of dollars. Just as an individual might keep an account at a bank, the U.S. Treasury keeps a checking account with the Federal Reserve through which incoming federal tax deposits and outgoing government payments are handled. As part of this service relationship, the Fed sells and redeems U.S. government securities such as savings bonds and Treasury bills, notes and bonds. It also issues the nation's coin and paper currency. The U.S. Treasury, through its Bureau of the Mint and Bureau of Engraving and Printing, actually produces the nation's cash supply; the Fed Banks then distribute it to financial institutions.
Federal funds
Federal funds are the reserve balances that private banks keep at their local Federal Reserve Bank. These reserve balances are the "reserves" in "federal reserve", hence the name of the system. The purpose of keeping funds at a Federal Reserve Bank is to have a mechanism through which private banks can lend funds to one another. This market for funds plays an important role in the Federal Reserve System as it is what inspired the name of the system and it is what is used as the basis for monetary policy. Monetary policy works by influencing how much money the private banks charge each other for the lending of these funds.
Balance between private banks and responsibility of government
The system was designed out of a compromise between the competing philosophies of privatization and government regulation. While planning the design of the system, some people wanted the system to have generally private aspects whereas others wanted more government involvement. The system that resulted ended up being a compromise between these two philosophies. Donald L. Kohn, vice chairman of the Board of Governors, gave a summary of this compromise:
Agrarian and progressive interests, led by William Jennings Bryan, favored a central bank under public, rather than banker, control. But the vast majority of the nation's bankers, concerned about government intervention in the banking business, opposed a central bank structure directed by political appointees. The legislation that Congress ultimately adopted in 1913 reflected a hard-fought battle to balance these two competing views and created the hybrid public-private, centralized-decentralized structure that we have today.
In the current system, private banks are for-profit businesses but there are restrictions on what they can do. These restrictions placed on private banks are government regulations. The Federal Reserve System is the part of government that regulates the private banks. The balance between privatization and government involvement is also seen in the structure of the system. Private banks elect members of the board of directors at their regional Federal Reserve Bank while the members of the Board of Governors are selected by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. The private banks give input to the government officials about their economic situation and these government officials use this input in Federal Reserve policy decisions. In the end, private banking businesses are able to freely run a profitable business while the U.S. government, through the Federal Reserve System, oversees and regulates the activities of the private banks.
Government regulation and supervision
The Board of Governors is the part of the Federal Reserve System that is responsible for supervising the private banks. A general description of the types of regulation and supervision involved is given by the Federal Reserve:
- The Board also plays a major role in the supervision and regulation of the U.S. banking system. It has supervisory responsibilities for state-chartered banks that are members of the Federal Reserve System, bank holding companies (companies that control banks), the foreign activities of member banks, the U.S. activities of foreign banks, and Edge Act and agreement corporations (limited-purpose institutions that engage in a foreign banking business). The Board and, under delegated authority, the Federal Reserve Banks, supervise approximately 900 state member banks and 5,000 bank holding companies. Other federal agencies also serve as the primary federal supervisors of commercial banks; the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency supervises national banks, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation supervises state banks that are not members of the Federal Reserve System.
- Some regulations issued by the Board apply to the entire banking industry, whereas others apply only to member banks, that is, state banks that have chosen to join the Federal Reserve System and national banks, which by law must be members of the System. The Board also issues regulations to carry out major federal laws governing consumer credit protection, such as the Truth in Lending, Equal Credit Opportunity, and Home Mortgage Disclosure Acts. Many of these consumer protection regulations apply to various lenders outside the banking industry as well as to banks.
- Members of the Board of Governors are in continual contact with other policy makers in government. They frequently testify before congressional committees on the economy, monetary policy, banking supervision and regulation, consumer credit protection, financial markets, and other matters.
- The Board has regular contact with members of the President’s Council of Economic Advisers and other key economic officials. The Chairman also meets from time to time with the President of the United States and has regular meetings with the Secretary of the Treasury. The Chairman has formal responsibilities in the international arena as well.
Preventing asset bubbles
The board of directors of each Federal Reserve Bank District also have regulatory and supervisory responsibilities. For example, a member bank (private bank) is not permitted to give out too many loans to people who cannot pay them back. This is because too many defaults on loans will lead to a bank run. If the board of directors has judged that a member bank is performing or behaving poorly, it will report this to the Board of Governors. This policy is described in United States Code, Title 12, Chapter 3, subchapter 7, section 301:
Each Federal reserve bank shall keep itself informed of the general character and amount of the loans and investments of its member banks with a view to ascertaining whether undue use is being made of bank credit for the speculative carrying of or trading in securities, real estate, or commodities, or for any other purpose inconsistent with the maintenance of sound credit conditions; and, in determining whether to grant or refuse advances, rediscounts, or other credit accommodations, the Federal reserve bank shall give consideration to such information. The chairman of the Federal reserve bank shall report to the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System any such undue use of bank credit by any member bank, together with his recommendation. Whenever, in the judgment of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, any member bank is making such undue use of bank credit, the Board may, in its discretion, after reasonable notice and an opportunity for a hearing, suspend such bank from the use of the credit facilities of the Federal Reserve System and may terminate such suspension or may renew it from time to time.
The punishment for making false statements or reports which overvalue an asset is stated in U.S. Code, Title 18, Part 1, Chapter 47, Section 1014:
Whoever knowingly makes any false statement or report, or willfully overvalues any land, property or security, for the purpose of influencing in any way...shall be fined not more than $1,000,000 or imprisoned not more than 30 years, or both.
These aspects of the Federal Reserve System are the parts intended to prevent or minimize speculative asset bubbles which ultimately lead to severe market corrections.
Structure
Independent within government
The Federal Reserve System is an independent government institution that has private aspects, but is neither a private organization, nor operates for a profit. It derives its authority and public purpose from the Federal Reserve Act passed by Congress in 1913. As an independent institution, the Federal Reserve has the authority to act on its own without prior approval from Congress or the President. The members of its Board of Governors are appointed for long, staggered terms, limiting the influence of day-to-day political considerations. The Federal Reserve’s unique structure also provides internal checks and balances, ensuring that its decisions and operations are not dominated by any one part of the system. It also generates revenue independently without need for Congressional funding. Congressional oversight and statue, which can alter the Fed's responsibilities and control, allows the government to keep the Federal Reserve in check. Since it was designed to be independent while also remaining within the government of the United States, it is often said to be "independent within the government."
The 12 Federal Reserve banks provide the financial means to operate the Federal Reserve. Each reserve bank is organized much like a private corporation so that it can provide the necessary revenue to cover operational expenses and implement the demands of the board. Member banks are privately owned banks that must buy a certain amount of stock in the Reserve Bank within its region to be a member of the Federal Reserve System. This stock "may not be sold, traded, or pledged as security for a loan" and all member banks receive a 6% annual dividend. These member banks must maintain fractional reserves either as vault cash or on account at its Reserve Bank; member banks earn no interest on either of these. The dividends paid by the Federal Reserve Banks to member banks are considered partial compensation for the lack of interest paid on the required reserves. All profit after expenses is returned to the U.S. Treasury or contributed to the surplus capital of the Federal Reserve Banks (and since shares in ownership of the Federal Reserve Banks are redeemable only at par, the nominal "owners" do not benefit from this surplus capital); the Federal Reserve system contributed over $29 billion to the Treasury in 2006.
Outline
The Federal Reserve System as a whole
- The nation's central bank
- A regional structure with 12 districts
- Subject to general Congressional authority and oversight
- Operates on its own earnings
Board of Governors
- 7 members serving staggered 14-year terms
- Appointed by the U.S. President and confirmed by the Senate
- Oversees System operations, makes regulatory decisions, and sets reserve requirements
Federal Open Market Committee
- The System's key monetary policymaking body
- Decisions seek to foster economic growth with price stability by influencing the flow of money and credit
- Composed of the 7 members of the Board of Governors and the Reserve Bank presidents, 5 of whom serve as voting members on a rotating basis
Federal Reserve Banks
- 12 regional banks with 25 branches
- Each independently incorporated with a 9-member board of directors, of whom 6 are from the private sector and 3 are designated by the Board of Governors.
- Set discount rate, subject to approval by Board of Governors.
- Monitor economy and financial institutions in their districts and provide financial services to the U.S. government and depository institutions.
Member banks
- Private banks
- Hold stock in their local Federal Reserve Bank
- Elect six of the nine members of Reserve Banks’ boards of directors.
Advisory Committees
- carry out varied responsibilities
Board of Governors
The seven-member Board of Governors is the main governing body of the Federal Reserve System. It is charged with overseeing the 12 District Reserve Banks and with helping implement national monetary policy. Governors are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate., one on Jan. 31 of every even-numbered year, for staggered, 14-year terms. As an independent federal government agency, the Board of Governors does not receive funding from Congress, and the terms of the seven members of the Board span multiple presidential and congressional terms. Once a member of the Board of Governors is appointed by the president, he or she functions mostly independently. The Board is required to make an annual report of operations to the Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives. It also supervises and regulates the operations of the Federal Reserve Banks, and US banking system in general.
Membership is generally limited to one term. However, if someone is appointed to serve the remainder of another member's uncompleted term, he or she may be reappointed to serve an additional 14-year term. Conversely, a governor may serve the remainder of another governor's term even after he or she has completed a full term. The law provides for the removal of a member of the Board by the President "for cause."
The current members of the Board of Governors are:
- Ben Bernanke, Chairman
- Donald Kohn, Vice-Chairman
- Frederic Mishkin
- Kevin Warsh
- Randall Kroszner
(*Because the Senate Banking Committee has refused to hold hearings on appointments to fill the two vacant positions until a new President takes office, there are currently two vacancies. Governor Kroszner's term has also expired, but the law allows him to remain in office until a successor is confirmed)
All current members of the Board of Governors have taken office during the presidency of George W. Bush.
Federal open market committee
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) created under comprises the seven members of the board of governors and five representatives selected from the regional Federal Reserve Banks. The FOMC is charged under law with overseeing open market operations, the principal tool of national monetary policy. These operations affect the amount of Federal Reserve balances available to depository institutions, thereby influencing overall monetary and credit conditions. The FOMC also directs operations undertaken by the Federal Reserve in foreign exchange markets. The representative from the Second District, New York, (currently Timothy Geithner) is a permanent member, while the rest of the banks rotate at two- and three-year intervals. All the presidents participate in FOMC discussions, contributing to the committee’s assessment of the economy and of policy options, but only the five presidents who are committee members vote on policy decisions. The FOMC, under law, determines its own internal organization and by tradition elects the Chairman of the Board of Governors as its chairman and the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York as its vice chairman. Formal meetings typically are held eight times each year in Washington, D.C. Nonvoting Reserve Bank presidents also participate in Committee deliberations and discussion. The FOMC generally meets eight times a year in Telephone consultations and other meetings are held when needed.
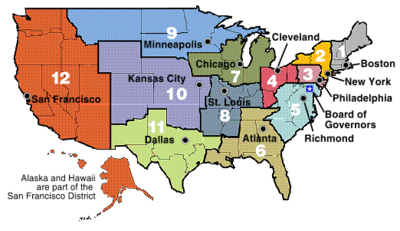
Federal Reserve Banks
There are 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks (not to be confused with the "member banks") with 25 branches, which serve as the operating arms of the system. Each Federal Reserve Bank is subject to oversight by a Board of Governors. Each Federal Reserve Bank has a board of directors, whose members work closely with their Reserve Bank president to provide grassroots economic information and input on management and monetary policy decisions. These boards are drawn from the general public and the banking community and oversee the activities of the organization. They also appoint the presidents of the Reserve Banks, subject to the approval of the Board of Governors. Reserve Bank boards consist of nine members: six serving as representatives of nonbanking enterprises and the public (nonbankers) and three as representatives of banking. Each Federal Reserve branch office has its own board of directors, composed of three to seven members, that provides vital information concerning the regional economy.
The Reserve Banks opened for business on November 16, 1914. Federal Reserve Notes were created as part of the legislation, to provide a supply of currency. The notes were to be issued to the Reserve Banks for subsequent transmittal to banking institutions. The various components of the Federal Reserve System have differing legal statuses.
The Federal Reserve Banks have an intermediate status, with some features of private corporations and some features of public federal agencies. Each member bank owns nonnegotiable shares of stock in its regional Federal Reserve Bank—but these shares of stock give the member banks only limited control over the actions of the Federal Reserve Banks, and the charter of each Federal Reserve Bank is established by law and cannot be altered by the member banks. While it is unusual, private individuals and non-bank corporations (with proof of a resolution of the board of directors indicating it intends to do so) may also purchase one or more shares of stock of any of the Federal Reserve Banks. The stock is the same nonnegotiable stock as banks receive, cannot be sold and pays a small dividend. In Lewis v. United States, the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit stated that "the Reserve Banks are not federal instrumentalities for purposes of the FTCA [the Federal Tort Claims Act], but are independent, privately owned and locally controlled corporations." The opinion also stated that "the Reserve Banks have properly been held to be federal instrumentalities for some purposes." Another decision is Scott v. Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City in which the distinction between the Federal Reserve Banks and the Board of Governors is made.
Board of directors
The nine member board of directors of each district is made up of 3 classes, designated as classes A, B, and C. The directors serve a term of 3 years. The makeup of the boards of directors is outlined in U.S. Code, Title 12, Chapter 3, Subchapter 7:
Class A:
- three members
- chosen by and representative of the stockholding banks.
- member banks are divided into 3 groups based on size - large, medium, and small banks. Each group elects one member of Class A.
Class B:
- three members
- represent the public with due but not exclusive consideration to the interests of agriculture, commerce, industry, services, labor, and consumers.
- member banks are divided into 3 groups based on size - large, medium, and small banks. Each group elects one member of Class B.
- No director of class B shall be an officer, director, or employee of any bank
Class C:
- three members
- designated by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. They shall be elected to represent the public, and with due but not exclusive consideration to the interests of agriculture, commerce, industry, services, labor, and consumers.
- No director of class C shall be an officer, director, employee, or stockholder of any bank
- Shall have been for at least two years residents of the district for which they are appointed, one of whom shall be designated by said board as chairman of the board of directors of the Federal reserve bank and as Federal reserve agent.
List of Federal Reserve Banks
The Federal Reserve Districts are listed below along with their identifying letter and number. These are used on Federal Reserve Notes to identify the issuing bank for each note. The 25 branches are also listed.
| Federal Reserve Bank | Letter | Number | Branches | Website | President |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boston | A | 1 | http://www.bos.frb.org/ | Eric S. Rosengren | |
| New York | B | 2 | Buffalo, New York (will be closing after 31 October 2008) | http://www.newyorkfed.org/ | Timothy F. Geithner |
| Philadelphia | C | 3 | http://www.philadelphiafed.org/ | Charles I. Plosser | |
| Cleveland | D | 4 | Cincinnati, Ohio / Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania | http://www.clevelandfed.org/ | Sandra Pianalto |
| Richmond | E | 5 | Baltimore, Maryland / Charlotte, North Carolina | http://www.richmondfed.org/ | Jeffrey M. Lacker |
| Atlanta | F | 6 | Birmingham, Alabama / Jacksonville, Florida / Miami, Florida / Nashville, Tennessee / New Orleans, Louisiana | http://www.frbatlanta.org/ | Dennis P. Lockhart |
| Chicago | G | 7 | Detroit, Michigan | http://www.chicagofed.org/ | Charles Evans |
| St Louis | H | 8 | Little Rock, Arkansas / Louisville, Kentucky / Memphis, Tennessee | http://www.stlouisfed.org/ | James B. Bullard |
| Minneapolis | I | 9 | Helena, Montana | http://www.minneapolisfed.org/ | Gary H. Stern |
| Kansas City | J | 10 | Denver, Colorado / Oklahoma City, Oklahoma / Omaha, Nebraska | http://www.kansascityfed.org/ | Thomas M. Hoenig |
| Dallas | K | 11 | El Paso, Texas / Houston, Texas / San Antonio, Texas | http://www.dallasfed.org/ | Richard W. Fisher |
| San Francisco | L | 12 | Los Angeles, California / Portland, Oregon / Salt Lake City, Utah / Seattle, Washington | http://www.frbsf.org/ | Janet L. Yellen |
Member banks
Each member bank is a private bank (e.g., a privately owned corporation) that holds stock in one of the twelve regional Federal Reserve banks. All of the commercial banks in the United States can be divided into three types according to which governmental body charters them and whether or not they are members of the Federal Reserve System:
- national banks - Those chartered by the federal government (through the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency in the Department of the Treasury); by law, they are members of the Federal Reserve System
- state member banks - Those chartered by the states who are members of the Federal Reserve System.
- state nonmember banks - Those chartered by the states who are not members of the Federal Reserve System.
All nationally chartered banks hold stock in one of the Federal Reserve banks. State-chartered banks may choose to be members (and hold stock in a regional Federal Reserve bank), upon meeting certain standards.
Holding stock in a Federal Reserve bank is not, however, like owning publicly traded stock. The stock cannot be sold or traded. Member banks receive a fixed, 6 percent dividend annually on their stock, and they do not directly control the applicable Federal Reserve bank as a result of owning this stock. They do, however, elect six of the nine members of Reserve banks’ boards of directors. Federal statute provides (in part):
Every national bank in any State shall, upon commencing business or within ninety days after admission into the Union of the State in which it is located, become a member bank of the Federal Reserve System by subscribing and paying for stock in the Federal Reserve bank of its district in accordance with the provisions of this chapter and shall thereupon be an insured bank under the Federal Deposit Insurance Act [. . . .]"
Other banks may elect to become member banks. According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston:
Any state-chartered bank (mutual or stock-formed) may become a member of the Federal Reserve System. The twelve regional Reserve Banks supervise state member banks as part of the Federal Reserve System’s mandate to assure strength and stability in the nation’s domestic markets and banking system. Reserve Bank supervision is carried out in partnership with the state regulators, assuring a consistent and unified regulatory environment. Regional and community banking organizations constitute the largest number of banking organizations supervised by the Federal Reserve System.
For example, as of October 2006 the member banks in New Hampshire included Community Guaranty Savings Bank; The Lancaster National Bank; The Pemigewasset National Bank of Plymouth; and other banks. In California, member banks (as of September 2006) included Bank of America California, National Association; The Bank of New York Trust Company, National Association; Barclays Global Investors, National Association; and many other banks.
Lists of member banks
A list of all U.S. commercial banks can be found at the website of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Some of the banks in this list are members of the Federal Reserve System. As of May 22, 2008, there were a total of 8,508 FDIC insured institutions. This list also includes the total assets of each bank and where the headquarters is located.
Summary of all FDIC insured banks:
| FDIC Insured Institutions | |
|---|---|
| Number as of 5/22/08 | 8,508 |
| Assets as of 12/31/2007 | $13,055,375 |
| Deposits as of 12/31/2007 | $8,423,971 |
| (dollar amounts in millions of dollars) | |
Advisory Committees
The Federal Reserve System uses advisory committees in carrying out its varied responsibilities. Three of these committees advise the Board of Governors directly:
- Federal Advisory Council
- Consumer Advisory Council
- Thrift Institutions Advisory Council
The Federal Reserve Banks also use advisory committees. Of these advisory committees, perhaps the most important are the committees (one for each Reserve Bank) that advise the Banks on matters of agriculture, small business, and labor. Biannually, the Board solicits the views of each of these committees by mail.
Monetary policy
The term " monetary policy" refers to the actions undertaken by a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve, to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to help promote national economic goals. What happens to money and credit affects interest rates (the cost of credit) and the performance of the U.S. economy. The Federal Reserve Act of 1913 gave the Federal Reserve responsibility for setting monetary policy.
Interbank lending is the basis of policy
The Federal Reserve implements monetary policy by influencing the interbank lending of excess reserves. Interbank lending occurs when too many withdrawals have been made at a bank and it needs to borrow funds from another bank to make up the difference. The rate that banks charge each other for these loans is determined by the markets but the Federal Reserve influences this rate through the three tools of monetary policy which are described in the "Tools of monetary policy" section below. A summary of the basis and implementation of monetary policy is stated by the Federal Reserve:
The Federal Reserve implements U.S. monetary policy by affecting conditions in the market for balances that depository institutions hold at the Federal Reserve Banks...By conducting open market operations, imposing reserve requirements, permitting depository institutions to hold contractual clearing balances, and extending credit through its discount window facility, the Federal Reserve exercises considerable control over the demand for and supply of Federal Reserve balances and the federal funds rate. Through its control of the federal funds rate, the Federal Reserve is able to foster financial and monetary conditions consistent with its monetary policy objectives.
This influences the economy through its effect on the quantity of reserves that banks use to make loans. Policy actions that add reserves to the banking system encourage lending at lower interest rates thus stimulating growth in money, credit, and the economy. Policy actions that absorb reserves work in the opposite direction. The Fed's task is to supply enough reserves to support an adequate amount of money and credit, avoiding the excesses that result in inflation and the shortages that stifle economic growth.
Goals of monetary policy
The goals of monetary policy include:
- maximum employment
- stable prices
- moderate long-term interest rates
- promotion of sustainable economic growth
Tools of monetary policy
There are three main tools of monetary policy that the Federal Reserve uses to influence the amount of reserves in private banks:
- open market operations: purchases and sales of U.S. Treasury and federal agency securities—the Federal Reserve's principal tool for implementing monetary policy. The Federal Reserve's objective for open market operations has varied over the years. During the 1980s, the focus gradually shifted toward attaining a specified level of the federal funds rate (the rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans of federal funds, which are the reserves held by banks at the Fed), a process that was largely complete by the end of the decade.
- discount rate: the interest rate charged to commercial banks and other depository institutions on loans they receive from their regional Federal Reserve Bank's lending facility--the discount window.
- reserve requirements: the amount of funds that a depository institution must hold in reserve against specified deposit liabilities.
In order to address problems related to the subprime mortgage crisis, three new tools have been created. The first new tool, called the Term Auction Facility, was added on December 12, 2007. It was first announced as a temporary tool but there have been suggestions that this new tool may remain in place for a prolonged period of time. Creation of the second new tool, called the Term Securities Lending Facility, was announced on March 11, 2008. The main difference between these two facilities is that the Term Auction Facility is used to inject cash into the banking system whereas the Term Securities Lending Facility is used to inject treasury securities into the banking system. Creation of the third tool, called the Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF), was announced on March 16, 2008. The PDCF was a fundamental change in Federal Reserve policy because now the Fed is able to lend directly to primary dealer's, which was previously against Fed policy. The differences between these 3 new facilities is described by the Federal Reserve:
The Term Auction Facility program offers term funding to depository institutions via a bi-weekly auction, for fixed amounts of credit. The Term Securities Lending Facility will be an auction for a fixed amount of lending of Treasury general collateral in exchange for OMO-eligible and AAA/Aaa rated private-label residential mortgage-backed securities. The Primary Dealer Credit Facility now allows eligible primary dealers to borrow at the existing Discount Rate for up to 120 days.
Open market operations
Open market operations put money in and take money out of the banking system. This is done through the sale and purchase of U.S. government treasury securities. When the U.S. government sells securities, it gets money from the banks and the banks get a piece of paper (I.O.U.) that says the U.S. government owes the bank money. This drains money from the banks. When the U.S. government buys securities, it gives money to the banks and the banks give the I.O.U. back to the U.S. government. This puts money back into the banks. The Federal Reserve education website describes open market operations as follows:
- Open market operations involve the buying and selling of U.S. government securities (federal agency and mortgage-backed). The term 'open market' means that the Fed doesn’t decide on its own which securities dealers it will do business with on a particular day. Rather, the choice emerges from an 'open market' in which the various securities dealers that the Fed does business with—the primary dealers—compete on the basis of price. Open market operations are flexible and thus, the most frequently used tool of monetary policy.
- Open market operations are the primary tool used to regulate the supply of bank reserves. This tool consists of Federal Reserve purchases and sales of financial instruments, usually securities issued by the U.S. Treasury, Federal agencies and government-sponsored enterprises. Open market operations are carried out by the Domestic Trading Desk of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York under direction from the FOMC. The transactions are undertaken with primary dealers.
- The Fed’s goal in trading the securities is to affect the federal funds rate, the rate at which banks borrow reserves from each other. When the Fed wants to increase reserves, it buys securities and pays for them by making a deposit to the account maintained at the Fed by the primary dealer’s bank. When the Fed wants to reduce reserves, it sells securities and collects from those accounts. Most days, the Fed does not want to increase or decrease reserves permanently so it usually engages in transactions reversed within a day or two. That means that a reserve injection today could be withdrawn tomorrow morning, only to be renewed at some level several hours later. These short-term transactions are called repurchase agreements (repos) – the dealer sells the Fed a security and agrees to buy it back at a later date.
A simpler description is described in The Federal Reserve in Plain English:
How do open market operations actually work? Currently, the FOMC establishes a target for the federal funds rate (the rate banks charge each other for overnight loans). Open market purchases of government securities increase the amount of reserve funds that banks have available to lend, which puts downward pressure on the federal funds rate. Sales of government securities do just the opposite—they shrink the reserve funds available to lend and tend to raise the funds rate. By targeting the federal funds rate, the FOMC seeks to provide the monetary stimulus required to foster a healthy economy. After each FOMC meeting, the funds rate target is announced to the public.
Repurchase agreements
To smooth temporary or cyclical changes in the monetary supply, the desk engages in repurchase agreements (repos) with its primary dealers. Repos are essentially secured, short-term lending by the Fed. On the day of the transaction, the Fed deposits money in a primary dealer’s reserve account, and receives the promised securities as collateral. When the transaction matures, the process unwinds: the Fed returns the collateral and charges the primary dealer’s reserve account for the principal and accrued interest. The term of the repo (the time between settlement and maturity) can vary from 1 day (called an overnight repo) to 65 days.
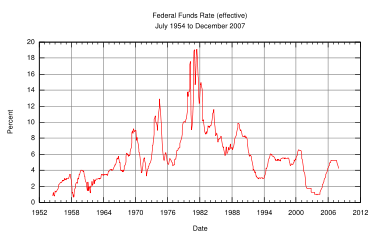
Federal funds rate and discount rate
The Federal Reserve System implements monetary policy largely by targeting the federal funds rate. This is the rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans of federal funds, which are the reserves held by banks at the Fed. This rate is actually determined by the market and is not explicitly mandated by the Fed. The Fed therefore tries to align the effective federal funds rate with the targeted rate by adding or subtracting from the money supply through open market operations. The late economist Milton Friedman consistently criticized this reverse method of controlling inflation by seeking an ideal interest rate and enforcing it through affecting the money supply since nowhere in the widely accepted money supply equation are interest rates found.
The Federal Reserve System also directly sets the "discount rate", which is the interest rate that banks pay the Fed to borrow directly from it. This rate is generally set at a rate close to 100 points above the target federal funds rate. The idea is to encourage banks to seek alternative funding before using the "discount rate" option.
Both of these rates influence the prime rate which is usually about 3 percentage points higher than the federal funds rate.
Lower interest rates stimulate economic activity by lowering the cost of borrowing, making it easier for consumers and businesses to buy and build, but at the cost of promoting the expansion of the money supply and thus greater inflation. Higher interest rates slow the economy by increasing the cost of borrowing. (See monetary policy for a fuller explanation.)
The Federal Reserve System usually adjusts the federal funds rate by 0.25% or 0.50% at a time.
The Federal Reserve System might also attempt to use open market operations to change long-term interest rates, but its "buying power" on the market is significantly smaller than that of private institutions. The Fed can also attempt to "jawbone" the markets into moving towards the Fed's desired rates, but this is not always effective.
Reserve requirements
Another instrument of monetary policy adjustment employed by the Federal Reserve System is the fractional reserve requirement, also known as the required reserve ratio. The required reserve ratio sets the balance that the Federal Reserve System requires a depository institution to hold in the Federal Reserve Banks, which depository institutions trade in the federal funds market discussed above. The required reserve ratio is set by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
| Table: Reserve Requirements in the U.S. Federal Reserve System | ||
| Type of liability | Requirement | |
|
|
Percentage of liabilities | Effective date |
| Net transaction accounts | ||
| $0 to $9.3 million | 0 | 12/20/07 |
| More than $9.3 million to $43.9 million | 3 | 12/20/07 |
| More than $43.9 million | 10 | 12/20/07 |
|
|
||
| Nonpersonal time deposits | 0 | 12/27/90 |
|
|
||
| Eurocurrency liabilities | 0 | 12/27/90 |
Term auction facility
The Term Auction Facility is a program in which the Federal Reserve auctions term funds to depository institutions. The creation of this facility was announced by the Federal Reserve on December 12, 2007 and was done in conjunction with the Bank of Canada, the Bank of England, the European Central Bank, and the Swiss National Bank to address elevated pressures in short-term funding markets. The reason it was created is because banks were not lending funds to one another and banks in need of funds were refusing to go to the discount window. Banks were not lending money to each other because there was a fear that the loans would not be paid back. Banks refused to go to the discount window because it is usually associated with the stigma of bank failure. Under the Term Auction Facility, the identity of the banks in need of funds is protected in order to avoid the stigma of bank failure. Foreign exchange swap lines with the European Central Bank and Swiss National Bank were opened so the banks in europe could have access to U.S. dollars. Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke briefly described this facility to the U.S. House of Representatives on January 17, 2008:
the Federal Reserve recently unveiled a term auction facility, or TAF, through which prespecified amounts of discount window credit can be auctioned to eligible borrowers. The goal of the TAF is to reduce the incentive for banks to hoard cash and increase their willingness to provide credit to households and firms...TAF auctions will continue as long as necessary to address elevated pressures in short-term funding markets, and we will continue to work closely and cooperatively with other central banks to address market strains that could hamper the achievement of our broader economic objectives.
It is also described in the Term Auction Facility FAQ:
The TAF is a credit facility that allows a depository institution to place a bid for an advance from its local Federal Reserve Bank at an interest rate that is determined as the result of an auction. By allowing the Federal Reserve to inject term funds through a broader range of counterparties and against a broader range of collateral than open market operations, this facility could help ensure that liquidity provisions can be disseminated efficiently even when the unsecured interbank markets are under stress. In short, the TAF will auction term funds of approximately one-month maturity. All depository institutions that are judged to be in sound financial condition by their local Reserve Bank and that are eligible to borrow at the discount window are also eligible to participate in TAF auctions. All TAF credit must be fully collateralized. Depositories may pledge the broad range of collateral that is accepted for other Federal Reserve lending programs to secure TAF credit. The same collateral values and margins applicable for other Federal Reserve lending programs will also apply for the TAF.
Term securities lending facility
The Term Securities Lending Facility is a 28-day facility that will offer Treasury general collateral to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s primary dealers in exchange for other program-eligible collateral. It is intended to promote liquidity in the financing markets for Treasury and other collateral and thus to foster the functioning of financial markets more generally. Like the Term Auction Facility, the TSLF was done in conjunction with the Bank of Canada, the Bank of England, the European Central Bank, and the Swiss National Bank. The resource allows dealers to switch debt that is less liquid for U.S. government securities that are easily tradable. It is anticipated by Federal Reserve officials that the primary dealers, which include Goldman Sachs Group. Inc., Bear Stearns Cos. and Merrill Lynch & Co., will lend the Treasuries on to other firms in return for cash. That will help the dealers finance their balance sheets. The currency swap lines with the European Central Bank and Swiss National Bank were increased.
Primary dealer credit facility
The Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF) is an overnight loan facility that will provide funding to primary dealers in exchange for a specified range of eligible collateral and is intended to foster the functioning of financial markets more generally. This new facility marks a fundamental change in Federal Reserve policy because now primary dealers can borrow directly from the Fed when this previously was not permitted.
Measurement of economic variables
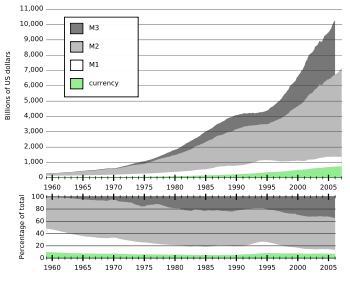
The money supply
The most common measures are named M0 (narrowest), M1, M2, and M3. In the United States they are defined by the Federal Reserve as follows:
- M0: The total of all physical currency, plus accounts at the central bank that can be exchanged for physical currency.
- M1: M0 + those portions of M0 held as reserves or vault cash + the amount in demand accounts ("checking" or "current" accounts).
- M2: M1 + most savings accounts, money market accounts, and small denomination time deposits ( certificates of deposit of under $100,000).
- M3: M2 + all other CDs, deposits of eurodollars and repurchase agreements.
The Federal Reserve ceased publishing M3 statistics in March 2006, explaining that it cost a lot to collect the data but did not provide significantly useful information. The other three money supply measures continue to be provided in detail.
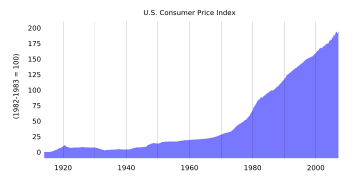
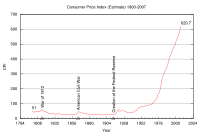
Consumer price index
The consumer price index is used to measure the value of the money. It is defined as:
A measure of the average price level of a fixed basket of goods and services purchased by consumers as determined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Monthly changes in the CPI represent the rate of inflation. Core CPI excludes volatile components, i.e., food and energy prices.
The data consists of the US city average of consumer prices and can be found at The US Department of Labor - Bureau of Labor Statistics
The CPI has powerful political ramifications, and Administrations of both parties have been tempted to change the basis for its calculation, progressively underestimating the true rate of decline in purchasing power.
One of the Fed's main roles is to maintain price stability. This means that the change in the consumer price index over time should be as small as possible. The ability to maintain a low inflation rate is a long-term measure of the Fed's success. Although the Fed usually tries to keep the year-on-year change in CPI between 2 and 3 percent, there has been debate among policy makers as to whether or not the Federal Reserve should have a specific inflation targeting policy.
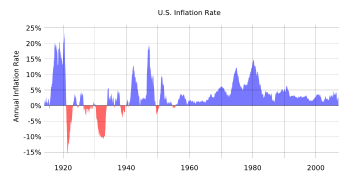
Inflation and the economy
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general level of prices, which is equivalent to a decline in the value or purchasing power of money. If the supply of money and credit increases too rapidly over many months, the result will be inflation. With inflation, a dollar buys less and less over time.
The effects of inflation include:
- Inflation might make people worse off if their incomes don’t rise as rapidly as prices.
- Lenders might lose because they will be repaid with dollars that aren't worth as much.
- Savers might lose because the dollar they save today will not buy as much when they are ready to spend it.
- Businesses will find it harder to plan and therefore may decrease investment in future projects.
- Owners of financial assets suffer.
- Interest rate-sensitive industries, like mortgage companies, may suffer as inflation drives up long-term interest rates and Federal Reserve tightening raises short-term rates.
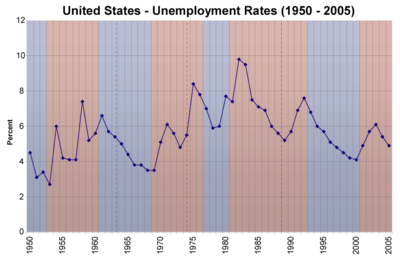
Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate statistics are collected by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Since one of the stated goals of monetary policy is maximum employment, the unemployment rate is a sign of the success of the Federal Reserve System.
Like the CPI, the unemployment rate is used as a barometer of the nation's economic health, and thus as a measure of the success of an administration's economic policies. Since 1980, both parties have made progressive changes in the basis for calculating unemployment, so that the numbers now quoted cannot be compared directly to the corresponding rates from earlier administrations, or to the rest of the world.
Budget
The Federal Reserve is self-funded. The vast majority (90%+) of Fed revenues come from open market operations, specifically the interest on the portfolio of Treasury securities as well as “capital gains/losses” that may arise from the buying/selling of the securities and their derivatives as part of Open Market Operations. The balance of revenues come from sales of financial services (check and electronic payment processing) and discount window loans.
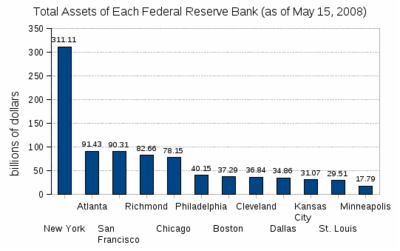
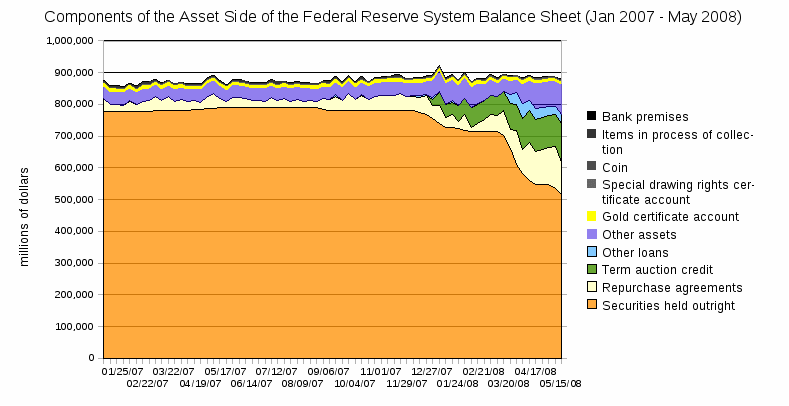
Balance sheet
One of the keys to understanding the Federal Reserve is the Federal Reserve balance sheet (or balance statement). In accordance with Section 11 of the Federal Reserve Act, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System publishes once each week the "Consolidated Statement of Condition of All Federal Reserve Banks" showing the condition of each Federal Reserve bank and a consolidated statement for all Federal Reserve banks.
Below is the balance sheet as of May 15, 2008 (in millions of dollars):
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analyzing the Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet reveals a number of facts:
- The Fed has over $11 billion in gold which is a holdover from the days the government used to back US Notes and Federal Reserve Notes with gold.. The value reported here is based on a statutory valuation of $42 2/9 per fine troy ounce.
- The Fed holds almost a billion dollars in coinage not as a liability but as an asset. The Treasury Department is actually in charge of creating coins and US Notes. The Fed then buys coinage from the Treasury by increasing the liability assigned to the Treasury's account.
- The Fed holds at least $515 billion of the national debt. The "securities held outright" value used to directly represent the Fed's share of the national debt, but after the creation of new facilities in the winter of 2007-2008, this number has been reduced and the difference is shown with values from some of the new facilities.
- The Fed has about $100 billion in assets from Overnight Repurchase agreements. Repurchase agreements are the primary asset of choice for the Fed in dealing in the Open Market. Repo assets are bought by creating 'Depository institution' liabilities and directed to the bank the Primary Dealer uses when they sell into the Open Market.
- The $982 billion in Federal Reserve Note liabilities represents the total value of all dollar bills in existence; over $200 billion is held by the Fed (not in circulation); and the "net" figure of $780 billion represents the total face value of Federal Reserve Notes in circulation.
- The $10.5 billion in deposit liabilities of 'Depository institutions' shows that dollar bills are not the only source of government money. Banks can swap 'Deposit Liabilities' of the Fed for 'Federal Reserve Notes' back and forth as needed to match demand from customers, and the Fed can have the 'Bureau of Engraving and Printing' create the paper bills as needed to match demand from banks for paper money. The amount of money printed has no relation to the growth of the monetary base (M0).
- The $4 billion in Treasury liabilities shows that the Treasury Department does not use a private banks but rather uses the Fed directly (the lone exception to this rule is Treasury Tax and Loan because government worries that pulling too much money out of the private banking system during tax time could be disruptive).
- The $97 million Foreign liability represents the amount of foreign central bank deposits with the Federal Reserve.
- The $2.7 billion in 'Other liabilities and accrued dividends' represents partly the amount of money owed so far in the year to member banks for the 6% dividend on the 3% of their net capital they are required to contribute in exchange for nonvoting stock their regional Reserve Bank in order to become a member. Member banks are also subscribed for an additional 3% of their net capital, which can be called at the Federal Reserve's discretion. All nationally-chartered banks must be members of a Federal Reserve Bank, and state-chartered banks have the choice to become members or not.
- Total capital represents the profit the Fed has earned which comes mostly from the assets they purchase with the deposit and note liabilities they create. Excess capital is then turned over to the Treasury Department and Congress to be included into the Federal Budget as "Miscellaneous Revenue".
In addition, the balance sheet also indicates which assets are held as collateral against Federal Reserve Notes.
| Federal Reserve Notes and collateral | ||
|---|---|---|
| Federal Reserve notes outstanding | 982,744 | |
| Less: Notes held by F.R. Banks | 201,956 | |
| Federal Reserve notes to be collateralized | 780,789 | |
| Collateral held against Federal Reserve notes | 780,789 | |
| Gold certificate account | 11,037 | |
| Special drawing rights certificate account | 2,200 | |
| U.S. Treasury and agency securities pledged | 576,601 | |
| Other assets pledged | 190,951 | |
Criticisms
A large and varied group of criticisms has been directed against the Federal Reserve System. One critique, typified by the Austrian School, is that the Federal Reserve is an unnecessary and counterproductive interference in the economy. Other critiques include arguments in favour of the gold standard (usually coupled with the charge that the Federal Reserve System is unconstitutional) or beliefs that the centralized banking system is doomed to fail (due to the fractional reserve system's strong resemblance of the unsustainable pyramid scheme scam). Some critics argue that the Fed lacks accountability and transparency or that there is a culture of secrecy within the Reserve.
Historical criticisms
Criticisms of the Federal Reserve System are not new, and some historical criticisms are reflective of current concerns.
At one end of the spectrum are economists from the Austrian School and the Chicago School who want the Federal Reserve System abolished. They criticize the Federal Reserve System’s expansionary monetary policy in the 1920s, arguing that the policy allowed misallocations of capital resources and supported a massive stock price bubble. They also cite politically motivated expansions or tightening of currency in the 1970s and 1980s.
Handling of The Great Depression
Milton Friedman, leader of the Chicago School, argued that the Federal Reserve System did not cause the Great Depression, but made it worse by contracting the money supply at the very moment that markets needed liquidity. Since its entire existence was predicated on its mission to prevent events like the Great Depression, it had failed in what the 1913 bill tried to enact. Friedman explains his hypothesis on the cause of The Great Depression and the role the Federal Reserve played in it in his book and documentary series Free to Choose. An excerpt of his hypothesis:
the recession only became a crisis when these failures spread to New York and in particular to this building, then the headquarters of the Bank of United States. The failure of this bank had far reaching effects and need never have happened...Only a few blocks away is the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. It was here that the Bank of United States could have been saved. Indeed, the Federal Reserve System had been set up 17 years earlier precisely to prevent the worst consequences of bank failures...It was all a question of reassuring the public that they could get their money. The Federal Reserve System was there to ensure that this happened by supplying cash to the banks...Why didn't this system prevent The Great Depression after 1929? Because from 1929 to 1930 after the stock market crashed, the Federal Reserve system allowed the quantity of money to decline slowly thereby throttling the monetary structure...If the Federal Reserve had stepped in, bought government securities on a large scale, provided the cash, the depositors would have found that they could've got their money and they would have stopped asking for it...Despite excellent advice from New York, the system refused to buy government bonds, something which would have provided cash to the commercial banks with which they could have met more easily the insisted demands of their depositors. Instead, believe it or not, the system stood idly by while banks crashed on all sides. As the head of one of the banks put it, the reserve system had to keep its powder dry for a real emergency.
This is also the current conventional wisdom on the matter, as both Ben Bernanke and other economists such as the late John Kenneth Galbraith- the latter being an ardent Keynesian- have upheld this reasoning. In an interview with Peter Jaworski (The Journal, Queen's University, March 15, 2002 - Issue 37, Volume 129) Friedman also said that ideally he would "prefer to abolish the federal reserve system altogether" rather than try to reform it, because it was a flawed system in the first place. He later said he would like to "abolish the Federal Reserve and replace it with a computer", meaning that it would be a mechanical system in nature that would keep the quantity of money going up at a steady rate. Friedman also believed that, ideally, the issuing power of money should rest with the Government instead of private banks issuing money through fractional reserve lending.
Ben Bernanke agreed that the Fed had made the Great Depression worse, saying in a 2002 speech:
I would like to say to Milton [Friedman] and Anna [J. Schwartz]: Regarding the Great Depression. You're right, we did it. We're very sorry. But thanks to you, we won't do it again."
Inflation
One major area of criticism focuses on the failure of the Federal Reserve System to stop inflation; this is seen as a failure of the Fed's legislatively mandated duty to maintain stable prices. These critics focus particularly on inflation's effects on wages, since workers are hurt if their wages do not keep up with inflation. They point out that wages, as adjusted for inflation, or real wages, have dropped in the past.
Milton Friedman alleged that the Fed caused the high inflation of the 1970s. When asked about the greatest economic problem of the day, he said the most pressing was how to get rid of the Federal Reserve. Friedman discusses the high inflation rate of the 1970s and other periods in Free to Choose:
Inflation is just like alcoholism. In both cases when you start drinking or when you start printing too much money, the good effects come first. The bad effects only come later...That's why in both cases there is a strong temptation to overdo it. To drink too much and to print too much money. When it comes to the cure, it's the other way around. When you stop drinking or when you stop printing money, the bad effects come first and the good effects only come later. That's why it's so hard to persist with the cure. In the United States, four times in the 20 years after 1957, we undertook the cure. But each time we lacked the will to continue. As a result, we had all the bad effects and none of the good effects.
United States Congressman Ron Paul, ranking member of the Subcommittee on Domestic and International Monetary Policy (of the House Banking Committee), has also criticized Federal Reserve policy for creating and downplaying excessive inflation:
This decline in the value of the dollar is simple to explain. The dollar loses value as the direct result of the Federal Reserve and U.S. Treasury increasing the money supply. Inflation, as the late Milton Friedman explained, is always a monetary phenomenon. The federal government consistently wants to spend more than it can tax and borrow, so Congress turns to the Fed for help in covering the difference. The result is more dollars, both real and electronic-- which means the value of every existing dollar goes down...when the Fed sets interest rates artificially low, the cost of borrowing becomes cheap. Individuals incur greater amounts of debt, while businesses overextend themselves and grow without real gains in productivity. The bubble bursts quickly once the credit dries up and the bills cannot be paid...the Fed steadily increased the monetary supply throughout the 1990s by printing money. Recent Fed numbers show double-digit annual increases in the M2 money supply. These new dollars may make Americans feel richer, but the net result of monetary inflation has to be the devaluation of savings and purchasing power.
Monetary policy uncertainties
A few of the uncertainties involved in monetary policy decision making are described by the federal reserve:
- While these policy choices seem reasonably straightforward, monetary policy makers routinely face certain notable uncertainties. First, the actual position of the economy and growth in aggregate demand at any point in time are only partially known, as key information on spending, production, and prices becomes available only with a lag. Therefore, policy makers must rely on estimates of these economic variables when assessing the appropriate course of policy, aware that they could act on the basis of misleading information. Second, exactly how a given adjustment in the federal funds rate will affect growth in aggregate demand—in terms of both the overall magnitude and the timing of its impact—is never certain. Economic models can provide rules of thumb for how the economy will respond, but these rules of thumb are subject to statistical error. Third, the growth in aggregate supply, often called the growth in potential output, cannot be measured with certainty.
- In practice, as previously noted, monetary policy makers do not have up-to-the-minute information on the state of the economy and prices. Useful information is limited not only by lags in the construction and availability of key data but also by later revisions, which can alter the picture considerably. Therefore, although monetary policy makers will eventually be able to offset the effects that adverse demand shocks have on the economy, it will be some time before the shock is fully recognized and—given the lag between a policy action and the effect of the action on aggregate demand—an even longer time before it is countered. Add to this the uncertainty about how the economy will respond to an easing or tightening of policy of a given magnitude, and it is not hard to see how the economy and prices can depart from a desired path for a period of time.
- The statutory goals of maximum employment and stable prices are easier to achieve if the public understands those goals and believes that the Federal Reserve will take effective measures to achieve them.
- Although the goals of monetary policy are clearly spelled out in law, the means to achieve those goals are not. Changes in the FOMC’s target federal funds rate take some time to affect the economy and prices, and it is often far from obvious whether a selected level of the federal funds rate will achieve those goals.
Opacity
Some argue that the Federal Reserve System is shrouded in excessive secrecy. Meetings of some components of the Fed are held behind closed doors, and the transcripts are released five years after the meeting was held. Even expert policy analysts are unsure about the logic behind Fed decisions. Critics argue that such opacity leads to greater market volatility, because the markets must guess, often with only limited information, about how the Fed is likely to change policy in the future. The jargon-laden fence-sitting opaque style of Fed communication, especially under the previous Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan, has often been called "Fed speak."
The Federal Reserve System has also been considered reserved in its relations with the media in an effort to maintain its carefully crafted image and resents any public information that runs contrary to this notion. Maria Bartiromo reported on CNBC that during a conversation at the White House Correspondents’ Dinner in April 2006, Federal Reserve Board Chairman Ben Bernanke stated investors had misinterpreted his recent congressional remarks as an indication the Fed was nearly done raising rates. This triggered a drop in stock prices just when the market was about to close.
In 1993, Rep. Henry Gonzalez confirmed that the Fed did have tapes and transcripts of the meetings and could have complied with the FOIA requests, but had misrepresented the existence of the transcripts and chosen to ignore questions from Congress. After the existence of the transcripts was revealed, the Fed agreed to release the transcripts on a five-year time lag. The time period has been extended, so that for example 1992's transcripts were not released until 1998.
Some critics believe the Fed exacerbated this idea when it decided to stop publishing the M3 aggregate of financial data, which details the total amount of money in circulation at a time. Some of them argue that it is a way the Fed could hide an impending economic disaster from the public if it felt the need. The Fed said that economists did not need M3 when they had M2, despite the fact that the M3 was the only aggregate to contain information regarding the most extravagant monetary exchanges, and therefore would be needed to have a complete understanding of the overall monetary policy in the United States.
Business cycles, libertarian philosophy and free markets
Economists of the Austrian School such as Ludwig von Mises contend that the Federal Reserve's operation amounts to an artificial manipulation of the money supply and has led to the boom/bust business cycle occurring over the last century. Many economic libertarians, such as Austrian School economist Murray Rothbard, believe that the Federal Reserve's manipulation of the money supply to stop "gold flight" from England caused, or was instrumental in causing, the Great Depression. See Austrian Business Cycle Theory. In general, laissez-faire advocates of free banking argue that there is no better judge of the proper interest rate and money supply than the market.
Many libertarians also contend that the Federal Reserve Act is unconstitutional. Congressman Ron Paul (ranking member of the House Subcommittee on Domestic Monetary Policy), for example, argues that:
"The United States Constitution grants to Congress the authority to coin money and regulate the value of the currency. The Constitution does not give Congress the authority to delegate control over monetary policy to a central bank. Furthermore, the Constitution certainly does not empower the federal government to erode the American standard of living via an inflationary monetary policy."
Congress
Congressman Louis T. McFadden, Chairman of the House Committee on Banking and Currency from 1920–31, accused the Federal Reserve of deliberately causing the Great Depression. In several speeches made shortly after he lost the chairmanship of the committee, McFadden claimed that the Federal Reserve was run by Wall Street banks and their affiliated European banking houses. On June 10, 1932, McFadden said:
Mr. Chairman, we have in this country one of the most corrupt institutions the world has ever known. I refer to the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve Banks. The Federal Reserve Board, a Government board, has cheated the Government of the United States and the people of the United States out of enough money to pay the national debt. These twelve private credit monopolies were deceitfully and disloyally foisted upon this country by the bankers who came here from Europe and repaid us for our hospitality by undermining our American institutions...The people have a valid claim against the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve banks.
Quite a few Congressmen who have been involved in the House and Senate Banking and Currency Committees have been open critics of the Federal Reserve. Currently, Congressman Paul is the ranking member of the Monetary Policy Subcommittee and he is a staunch opponent of the Federal Reserve System. During each Congress Paul introduces a bill to abolish the Federal Reserve System (H.R. 2755 - 110th Congress, H.R. 2778 - 108th Congress, H.R. 5356 - 107th Congress, H.R. 1148 - 106th Congress), although he has yet to have any hearings held on his legislation or even to gather any cosponsors. It has often been said that the Federal Reserve is a creature of Congress and it is the fluctuating opinion of that body that it answers to.