Gastroenteritis
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Health and medicine
| Gastroenteritis Classification and external resources |
|
| ICD- 10 | A 09., J 10.8, K 52. |
|---|---|
| ICD- 9 | 009.0, 009.1, 558 |
| DiseasesDB | 30726 |
| eMedicine | emerg/213 |
| MeSH | D005759 |
Gastroenteritis (also known as gastro, gastric flu, and stomach flu although unrelated to influenza) is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, involving both the stomach and the small intestine (see also gastritis and enteritis) and resulting in acute diarrhea. The inflammation is caused most often by infection with certain viruses, less often by bacteria or their toxins, parasites, or adverse reaction to something in the diet or medication. Worldwide, inadequate treatment of gastroenteritis kills 5 to 8 million people per year, and is a leading cause of death among infants and children under 5.
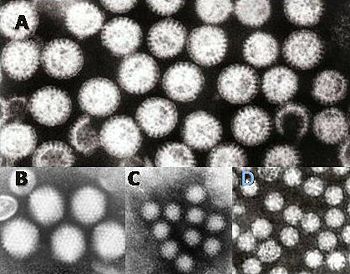
At least 50% of cases of gastroenteritis as foodborne illness are due to norovirus. Another 20% of cases, and the majority of severe cases in children, are due to rotavirus. Other significant viral agents include adenovirus and astrovirus.
Many different bacteria can cause gastroenteritis, including Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium, Escherichia coli, Yersinia, and others. Some sources of the infection are improperly prepared food, reheated meat dishes, seafood, dairy, and bakery products. Each organism causes slightly different symptoms but all result in diarrhea. Colitis, inflammation of the large intestine, may also be present.
Risk factors are consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water and travel or residence in areas of poor sanitation. The incidence is 1 in 1,000 people.
Epidemiology
Globally, gastroenteritis caused 4.6 million deaths in children in 1980 alone, most of these in the third world, where the lack of adequate safe water and sewage treatment capacity contribute to the spread of infectious gastroenteritis. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine estimates the current total figure to be 2.4 to 2.9 million per year. The global death rate has now come down significantly to approximately 1.5 million deaths annually, largely due to global introduction of proper oral rehydration therapy.
The incidence in the developed countries is as high as 1-2.5 cases per child per year and a major cause of hospitalisation in this age group.
Age, living conditions, hygiene and cultural habits are important factors. Aetiological agents vary depending on the climate. Furthermore, most cases of gastroenteritis are seen during the winter in temperate climates and during summer in the tropics.
History
Before the 20th century, the term "gastroenteritis" was not commonly used. What would now be diagnosed as gastroenteritis may have instead been diagnosed more specifically as typhoid fever or "cholera morbus", among others, or less specifically as "griping of the guts", "surfeit", "flux", "colic", "bowel complaint", or any one of a number of other archaic names for acute diarrhea. Historians, genealogists, and other researchers should keep in mind that gastroenteritis was not considered a discrete diagnosis until fairly recently.
Symptoms and signs
Gastroenteritis often involves stomach pain or spasms (sometimes to the point of being crippling), diarrhea and/or vomiting, with noninflammatory infection of the upper small bowel, or inflammatory infections of the colon.
It usually is of acute onset, normally lasting fewer than 10 days and self-limiting.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal cramps
- Bloody stools ( dysentery - suggesting infection by amoeba, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella or some pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli)
- Fainting and Weakness
The main contributing factors include poor feeding in infants. Diarrhea is common, and may be (but not always) followed by vomiting. Viral diarrhea usually causes frequent watery stools, whereas blood stained diarrhea may be indicative of bacterial colitis. In some cases, even when the stomach is empty, bile can be vomited up.
A child with gastroenteritis may be lethargic, suffer lack of sleep, run a low fever, have signs of dehydration (which include dry mucous membranes), tachycardia, reduced skin turgor, skin colour discoloration, sunken fontanelles, sunken eyeballs, darkened eye circles, glassy eyes, poor perfusion and ultimately shock.
Symptoms occur for up to 6 days on average. Given appropriate treatment, bowel movements will return to normal within a week after that.
Signs and Tests
- Stool culture positive for the organism that causes the infection
- White blood cells in the stool
- Examination of food for toxin and bacteria
This disease may also alter the results of the following tests:
- Stool gram stain
- Fecal smear
Differential diagnosis
It is important to consider infectious gastroenteritis as a diagnosis per exclusionem. A few loose stools and vomiting may be the result of systemic infection such as pneumonia, septicemia, urinary tract infection and even meningitis. Surgical conditions such as appendicitis, intussusception and, rarely, even Hirschsprung's disease may mislead the clinician.
Non-infectious causes to consider are poisoning with heavy metals (e.g. arsenic, cadmium), seafood (e.g. ciguatera, scombroid, toxic encephalopathic shellfish poisoning) or mushrooms (e.g. Amanita phalloides). Secretory tumours (e.g. carcinoid, medullary tumour of the thyroid, vasoactive intestinal peptide-secreting adenomas) and endocrine disorders (e.g. thyrotoxicosis and Addison's disease) are disorders that can cause diarrhea. Also, pancreatic insufficiency, short bowel syndrome, Whipple's disease, coeliac disease, and laxative abuse should be excluded as possibilities. Infectious gastroenteritis is caused by a wide variety of bacteria and viruses. For a list of bacteria causing gastroenteritis, see above. Pseudomembranous colitis is an important cause of diarrhea in patients often recently treated with antibiotics. Viruses causing gastroenteritis include rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus and astrovirus.
If gastroenteritis in a child is severe enough to require admission to a hospital, then it is important to distinguish between bacterial and viral infections. Bacteria, Shigella and Campylobacter, for example, and parasites like Giardia can be treated with antibiotics, but viruses do not respond to antibiotics and infected children usually make a full recovery after a few days. Children admitted to hospital with gastroenteritis routinely are tested for rotavirus A to gather surveillance data relevant to the epidemiological effects of rotavirus vaccination programs. These children are routinely tested also for norovirus, which is extraordinarily infectious and requires special isolation procedures to avoid transmission to other patients. Other methods, electron microscopy and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, are used in research laboratories.
Treatment
The objective of treatment is to replace lost fluids and electrolytes. Oral rehydration is the preferred treatment of fluid and electrolyte losses caused by diarrhea in children with mild to moderate dehydration .
Rehydration
Regardless of cause, the principal treatment of gastroenteritis (and of all other diarrheal illnesses) in both children and adults is rehydration, i.e. replenishment of water lost in the stools. Depending on the degree of dehydration, this can be done by giving the person oral rehydration therapy (ORT) or through intravenous delivery. ORT can begin before dehydration occurs, and continue until the person's urine and stool output return to normal.
People taking diuretics ("water pills") need to be cautious with diarrhea and may need to stop taking the medication during an acute episode, as directed by the health care provider.
Dietary therapy
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations for infants and children include: Breastfed infants should continue to be nursed on demand. Formula-fed infants should continue their usual formula immediately upon rehydration in amounts sufficient to satisfy energy and nutrient requirements, and at the usual concentration. Lactose-free or lactose-reduced formulas usually are unnecessary. Children receiving semisolid or solid foods should continue to receive their usual diet during episodes of diarrhea. Foods high in simple sugars should be avoided because the osmotic load might worsen diarrhea; therefore, substantial amounts of soft drinks (carbonated or flat), juice, gelatin desserts, and other highly sugared liquids should be avoided. Fatty foods should not be avoided, because maintaining adequate calories without fat is difficult, and fat might have an added benefit of reducing intestinal motility. The practice of withholding food for more than 24 hours is inappropriate.
Probiotics
Probiotics have been shown to be beneficial in preventing and treating various forms of gastroenteritis.
Zinc
The World Health Organization recommends that infants and children receive a dietary supplement of zinc for up to 2 weeks after onset of gastroenteritis.
Drug therapy
Antibiotics
When the symptoms are severe one usually starts empirical antimicrobial therapy, i.e. a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Pseudomembranous colitis is treated by discontinuing the causative agent and starting with metronidazole or vancomycin.
Antibiotics usually are not given for gastroenteritis, although they may be given due to some bacteria.
Antidiarrheal agents
Loperamide is an opioid analogue commonly used for symptomatic treatment of diarrhea. It slows down gut motility, but does not cross the mature blood-brain barrier to cause the central nervous effect of other opioids. In too high doses, loperamide may cause constipation and significant slowing down of passage of feces, but an appropriate single dose will not slow down the duration of the disease. Although antimotility drugs have the risk of exacerbating the condition, this fear is not supported by clinical experience. Nevertheless, others discourage the use of antiperistaltic agents and opiates in febrile dysentery, since they may mask, or exacerbate the symptoms. All these sources agree that in severe colitis antimotility drugs should not be used.
Loperamide prevents the body from flushing toxins from the gut, and should not be used when an active fever is present or there is a suspicion that the diarrhea is associated with organisms that can penetrate the intestinal walls, such as E. coli O157:H7 or Salmonella.
Loperamide is also not recommended in children, especially in children younger than 2 years of age, as it may cause systemic toxicity due to an immature blood brain barrier, and oral rehydration therapy remains the main stay treatment for children.
Bismuth subsalicylate (BSS), an insoluble complex of trivalent bismuth and salicylate, is another drug that can be used in mild-moderate cases.
Combining an antimicrobial drug and an antimotility drug, seems to be effective more rapidly.
Antiemetic drugs
If vomiting is severe, antiemetic drugs may be helpful. However, these drugs are not recommended for treatment of acute gastroenteritis in children.
Complications
The most serious complication is dehydration, usually due to severe diarrhea but sometimes made worse due to improper treatment such as withholding fluids until diarrhea stops. Severe dehydration can be lethal and requires prompt medical care. The most common complication, especially in infants, is malabsorption of certain sugars in the diet, and consequent food intolerances. This complication may persist for weeks, during which time it causes mild diarrhea to return when the patient resumes their normal diet. Malabsorption of lactose, the principal sugar in milk, is the most common. Its consequent milk intolerance is caused by lactase deficiency, and the diarrhea is caused by bacterial fermentation of excess lactose in the gut. However, this is not reason to discontinue breastfeeding. In children with viral gastroenteritis (usually rotavirus), the viral infection also can cause a high fever, which in turn can cause febrile convulsion. Gastroenteritis sometimes is followed by pneumonia.
Rare complications of gastroenteritis caused by bacteria include sepsis (treated with antibiotics), anaemia, renal (kidney) failure, arthritis, and new onset of irritable bowel syndrome.