Giganotosaurus
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Dinosaurs
| Giganotosaurus Fossil range: Late Cretaceous |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Species | ||||||||||||||||||
|
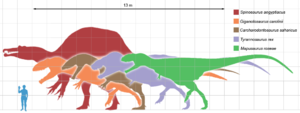
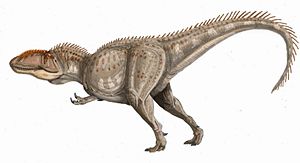
Giganotosaurus (meaning 'giant southern lizard', derived from the Ancient Greek gigas/γιγας meaning 'giant', notos/νοτος meaning 'south wind' and saurus/σαυρος meaning 'lizard') is a genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur that lived 93 to 89 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period. It is one of the largest known terrestrial carnivores, slightly larger than Tyrannosaurus, but smaller than Spinosaurus. Its fossils have been found in Argentina.
Discovery and species
Giganotosaurus carolinii was named for Ruben Carolini, an amateur fossil hunter, who discovered the fossils in the deposits of the Rio Limay Formation of Patagonia, southern Argentina, in 1993. It was published by Rodolfo Coria and Leonardo Salgado in the journal Nature in 1995.
The holotype specimen's (MUCPv-Ch1) skeleton was about 70% complete and included the skull, pelvis, leg bones and most of the backbone. It is estimated around 12.2-12.5 m (40-41 ft) in length. A second specimen (MUCPv-95), 8% larger, has also been recovered. This largest Giganotosaurus specimen is estimated to represent an individual 13.2 m (43.3 ft) long, that weighed 6.2 tons. Giganotosaurus might have had the longest known skull for a theropod dinosaur, with the holotype's skull estimated at 1.80 m (6 ft) and the second specimen's estimated at 1.95 m (6.3 ft). Giganotosaurus surpasses Tyrannosaurus rex in length by almost a meter (the upper length estimate for T. rex is 13 m).
Paleobiology
G. carolinii was slightly larger than T. rex but had a much smaller brain that was the size and shape of a banana. Its teeth were built more for cutting than crushing. A well-developed olfactory region means it probably had a good sense of smell.
Titanosaur fossils have been recovered near the remains of Giganotosaurus, leading to speculation that these carnivores may have preyed on the giant herbivores. Fossils of related carcharodontosaurid fossils grouped closely together may indicate pack hunting, a behaviour that could possibly extend to Giganotosaurus itself.
Classification

Giganotosaurus, along with relatives like Tyrannotitan, Mapusaurus and Carcharodontosaurus, are members of the carnosaur family Carcharodontosauridae. Both Giganotosaurus and Mapusaurus have been placed in their own subfamily Giganotosaurinae by Coria and Currie in 2006 as more carcharodontosaurid dinosaurs are found and described, allowing interrelationships to be calculated.
In popular culture
The original fossils of Giganotosaurus remain at the Carmen Funes Museum in Neuquen, Argentina, but replicas are common in other places, including the Australian Museum in Sydney. Despite having been discovered relatively recently, Giganotosaurus is already gaining a name for itself in popular culture. Giganotosaurus was featured in Dino Crisis 2, but was extremely exaggerated in size; the game's giganotosaur was said to be about 7 metres tall and 20 meters long, when the actual creature was about 5.5 metres tall and 14 meters long. Giganotosaurus was also shown in Turok in "Death Valley". Slade incorrectly calls it a T-Rex, but is easily differentiated from Tyrannosaurus. Giganotosaurus appears in the Chased by Dinosaurs special Land of Giants. They are seen to hunt both independently and in packs, working together to bring down an Argentinosaurus. Giganotosaurus is also featured in the IMAX movie Dinosaurs: Giants of Patagonia where Dr. Rodolfo Coria shows the sites of major discoveries in Argentina. It also has a robotic animal kit, from the popular Zoids series, released after the species known as Gojulas Giga.