Sassanid Empire
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Ancient History, Classical History and Mythology
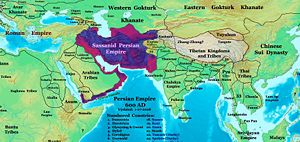
 Sassanid Empire under Khosrau II in 620 Sassanid Empire under Khosrau II in 620 |
|
| Dark green: Traditional borders. Medium green: Contested territory. Light green: Territory annexed in the east, or during war with the Byzantines (7th century). |
|
| Royal standard - Symbol of state | The Derafsh Kaviani |
| Official languages | Middle Persian |
| Capitals | Ctesiphon, in the early years of the empire Ardashir-Khwarrah |
| Government | Monarchy |
| Head of state | Shahanshah (شاهنشاه) |
| Deliberative Body | Council of Ministers |
| Establishment | 226 |
| Dissolution | Arab invasion during the Muslim conquests and death of Yazdegerd III in Merv on 651. |
| First emperor | Ardashir I (226-241) |
| Last Emperor | Yazdegerd III (632-651) |
| Preceding state | Parthian Empire |
| Succeeding states | Caliphate |
| Area | 3.5 million km² (under Khosrau II in 550) |
| Currency | Drachma |
The Sassanid Empire or Sassanid Persian Empire or Sassanian Dynasty ( Persian: ساسانیان [sɒsɒnijɒn]) is the name used for second Persian Empire (226–651). The Sassanid dynasty was founded by Ardashir I after defeating the last Parthian (Arsacid) king, Artabanus IV ( Persian: اردوان Ardavan) and ended when the last Sassanid Shahanshah (King of Kings), Yazdegerd III (632–651), lost a 14-year struggle to drive out the early Arab Caliphate, the first of the Islamic empires. The Sassanid Empire's traditional territory encompassed all of today's Iran, Iraq, Armenia, Afghanistan, eastern parts of Turkey, and parts of Syria, Pakistan, Caucasia, Central Asia and Arabia. The Sassanids called their empire Eranshahr "Empire of the Aryans ( Persians)".
The Sassanid era, encompassing the length of the Late Antiquity period, is considered to be one of Iran's most important and influential historical periods. In many ways the Sassanid period witnessed the highest achievement of Persian civilization, and constituted the last great Iranian Empire before the Muslim conquest and adoption of Islam. Persia influenced Roman civilization considerably during the Sassanids' times, and the Romans reserved for the Sassanid Persians alone the status of equals, exemplified in the letters written by the Roman Emperor to the Persian Shahanshah, which were addressed to "my brother." Their cultural influence extended far beyond the empire's territorial borders, reaching as far as Western Europe, Africa, China and India and played a prominent role in the formation of both European and Asiatic medieval art.
This influence carried forward to the early Islamic world with the Muslim conquest of Iran, especially the dynasty's unique, aristocratic culture. Zarinkoob even goes to the extent of claiming that much of what later became known as Islamic culture, architecture, writing and other skills was borrowed mainly from the Sassanid Persians and propagated throughout the broader Muslim world, although this assertion has not been corroborated by other scholars.
History
Origins and early history (205–310)

The last years of the Arsacids, and the rise of the Sassanids (or Sassanians) are not well-known because of scanty and conflicting information in the sources. The Sassanid Dynasty was established by Ardashir I, a descendant of a line of the priests of goddess Anahita in Istakhr, who at the beginning of the third century had acquired the governorship of Persis. There is, however, a problem about the origin of Ardashir and his relationship to his ancestors, Sassan and Papag. It is unclear whether he was a natural or adopted son of Papag, and whether Sasan was the eponymous founder of the dynasty or Ardashir's real father or father-in-law. In general, sources are not consistent as far as the relationships between the early Sassanids (Sassan, Papag, Ardashir and Shapur) are concerned.
Papag was originally the ruler of a small town called Kheir, but had managed by 200 to depose Gocihr, the last king of the Bazrangids (the local rulers of Persis as a client of the Arsacids) and appointed himself as the new ruler. His mother, Rodhagh, was the daughter of the provincial governor of Persis. Papag and his eldest son Shapur managed to expand their power over all of Persis. The subsequent events are unclear, due to the sketchy nature of the sources. It is however certain that following the death of Pabag, Ardashir who at the time was the governor of Darabgird, got involved in a power struggle of his own with his elder brother Shapur. The sources tell us that Shapur, leaving for a meeting with his brother, was killed when the roof of a building collapsed on him; by 208 over the protests of his other brothers, who were put to death, Ardashir declared himself ruler of Persis.
At this point, Ardashir moved his capital further to the south of Persis and founded Ardashir-Khwarrah (formerly Gur, modern day Firouzabad). The city, well supported by high mountains and easily defendable through narrow passes, became the centre of Ardashir's efforts to gain more power. The city was surrounded by a high, circular wall, probably copied from that of Darabgird, and on the north-side included a large palace, remains of which still survive. After establishing his rule over Persis, Ardashir I rapidly extended his territory, demanding fealty from the local princes of Fars, and gaining control over the neighboring provinces of Kerman, Isfahan, Susiana, and Mesene. This expansion quickly came to the attention of Artabanus IV, the Parthian king, who initially ordered the governor of Khuzestan to march against Ardashir in 224, but this ended up in a major victory for Ardashir. Artabanus himself marched a second time against Ardashir I in 224, but, after their armies clashed at Hormozgan, where Artabanus was killed, Ardashir I went on to invade the western provinces of the now defunct Parthian Empire.
Factors that aided the rise to supremacy of the Sassanids were the Artabanus- Vologases dynastic struggle for the Parthian throne, which probably allowed Ardashir to consolidate his authority in the south with little or no interference from the Parthians, and the geography of the Fars province, which separated it from the rest of Iran. Crowned in 224 at Ctesiphon as the sole ruler of Persia, Ardashir took the title Shahanshah, or "King of Kings" (the inscriptions mention Adhur-Anahid as his "Queen of Queens", but her relationship with Ardashir is not established), bringing the 400-year-old Parthian Empire to an end and beginning four centuries of Sassanid rule.
Over the next few years, following local rebellions around the empire, Ardashir I further expanded his new empire to the east and northwest, conquering the provinces of Sistan, Gorgan, Khorasan, Margiana (in modern Turkmenistan), Balkh, and Chorasmia. He also added Bahrain and Mosul to Sassanid possessions. Later Sassanid inscriptions also claim the submission of the Kings of Kushan, Turan, and Mekran to Ardashir, although based on numismatic evidence, it is more likely that these actually submitted to Ardashir's son, the future Shapur I. In the west, assaults against Hatra, Armenia, and Adiabene met with less success. In 230 he raided deep into Roman territory, and a Roman counter-offensive two years later ended inconclusively, although the Roman emperor, Alexander Severus, celebrated a triumph in Rome.
Ardashir I's son Shapur I continued the expansion of the empire, conquering Bactria and the western portion of the Kushan Empire, while leading several campaigns against Rome. Invading Roman Mesopotamia, Shapur I captured Carrhae and Nisibis, but in 243 the Roman general Timesitheus defeated the Persians at Rhesaina and regained the lost territories. The emperor Gordian III's (238–244) subsequent advance down the Euphrates was defeated at Meshike (244), leading to Gordian's murder by his own troops and enabling Shapur to conclude a highly advantageous peace treaty with the new emperor Philip the Arab, by which he secured the immediate payment of 500,000 denari and further annual payments. Shapur soon resumed the war, defeated the Romans at Barbalissos (252), and then probably took and plundered Antioch. Roman counter-attacks under the emperor Valerian ended in disaster when the Roman army was defeated and besieged at Edessa and Valerian was captured by Shapur, remaining his prisoner for the rest of his life. Shapur celebrated his victory by carving the impressive rock reliefs in Naqsh-e Rostam and Bishapur, as well as a monumental inscription in Persian and Greek in the vicinity of Persepolis. He exploited his success by advancing into Anatolia (260), but withdrew in disarray after defeats at the hands of the Romans and their Palmyrene ally Odaenathus, suffering the capture of his harem and the loss of all the Roman territories he had occupied.

Shapur had intensive development plans; he founded many cities, some settled in part by emigrants from the Roman territories, including Christians who could exercise their faith freely under Sassanid rule. Two cities, Bishapur and Nishapur, are named after him. He particularly favored Manichaeism, protected Mani (who dedicated one of his books, the Shabuhragan, to him) and sent many Manichaean missionaries abroad. He also befriended a Babylonian rabbi called Shmuel. This friendship was advantageous for the Jewish community and gave them a respite from the oppressive laws enacted against them. Later kings reversed Shapur's policy of religious tolerance. Under pressure from Zoroastrian Magi and influenced by the high-priest Kartir, Bahram I killed Mani and persecuted his followers. Bahram II was, like his father, amenable to the wishes of the Zoroastrian priesthood. During his reign the Sassanid capital Ctesiphon was sacked by the Romans under emperor Carus, and most of Armenia, after half a century of Persian rule, was ceded to Diocletian.
Succeeding Bahram III (who ruled briefly in 293), Narseh embarked on another war with the Romans. After an early success against the Emperor Galerius near Callinicum on the Euphrates in 296, Narseh was decisively defeated in an ambush while he was with his harem in Armenia in 298. In the treaty that concluded this war, the Sassanids ceded five provinces east of the Tigris and agreed not to interfere in the affairs of Armenia and Georgia. Following this crushing defeat, Narseh resigned in 301 and died in grief a year later. Narseh's son Hormizd II suppressed revolts in Sistan and Kushan, but was unable to control the nobles; he was killed by Bedouins while hunting in 309.
First Golden Era (309–379)
Following Hormizd II's death, Arabs from the south started to ravage and plunder the southern cities of the empire, even attacking the province of Fars, the birthplace of the Sassanid kings. Meanwhile, Persian nobles killed Hormizd II's eldest son, blinded the second, and imprisoned the third (who later escaped to Roman territory). The throne was reserved for, Shapur II, the unborn child of one of Hormizd II's wives who was crowned in utero: the crown was placed upon his mother's stomach. During his youth the empire was controlled by his mother and the nobles. Upon Shapur II's coming of age, he assumed power and quickly proved to be an active and effective ruler.
Shapur II first led his small but disciplined army south against the Arabs, whom he defeated, securing the southern areas of the empire. He then started his first campaign against the Romans in the west, where Persian forces won a series of battles but were unable to make territorial gains due to the failure of repeated sieges of the key frontier city of Nisibis and Roman success in retaking the cities of Singara and Amida after they fell to the Persians. These campaigns were halted by nomadic raids along the eastern borders of the empire, which threatened Transoxiana, a strategically critical area for control of the Silk Road. Shapur therefore marched east toward Transoxiana to meet the eastern nomads, leaving his local commanders to mount nuisance raids on the Romans. He crushed the Central Asian tribes, and annexed the area as a new province. He completed the conquest of the area now known as Afghanistan. Cultural expansion followed this victory, and Sassanid art penetrated Turkistan, reaching as far as China. Shapur, along with the nomad King Grumbates, started his second campaign against the Romans in 359, and soon succeeded in taking Singara and Amida again. In response to this, the Roman emperor Julian struck deep into Persian territory and defeated Shapur's forces at Ctesiphon, but having failed to take the capital, he was killed while trying to retreat back to Roman territory. His successor Jovian, trapped on the east bank of the Tigris, had to agree to hand over all the provinces which the Persians had ceded to Rome in 298 as well as Nisibis and Singara, in order to secure safe conduct for his army out of Persia.
Shapur II pursued a harsh religious policy. Under his reign the collection of the Avesta, the sacred texts of Zoroastrianism, was completed, heresy and apostasy were punished, and Christians were persecuted. The latter was a reaction against the Christianization of the Roman Empire by Constantine the Great. Shapur II, like Shapur I, was amicable towards Jews, who lived in relative freedom and gained many advantages in his period (see also Raba (Talmud)). At the time of Shapur's death, the Persian Empire was stronger than ever, with its enemies to the east pacified and Armenia under Persian control.
Second Golden Era (498–622)
The second golden era began after the second reign of Kavadh I. With the support of the Hephtalites, Kavadh I launched a campaign against the Romans. In 502, he took Theodosiopolis (Erzurum) in Modern Turkey, but lost it soon afterwards. In 503 he took Amida (Diarbekr) on the Tigris. In 504, an invasion of Armenia by the western Huns from the Caucasus led to an armistice, the return of Amida to Roman control and a peace treaty in 506. In 521/2 Kavadh lost control of Lazica, whose rulers switched their allegiance to the Romans; an attempt by the Iberians in 524/5 to do likewise triggered a war between Rome and Persia. In 527 a Roman offensive against Nisibis was repulsed and Roman efforts to fortify positions near the frontier were thwarted. In 530, Kavadh sent an army under Firouz the Mirranes to attack the important Roman frontier city of Dara. The army was met by the Roman general Belisarius, and though superior in numbers, was defeated at the Battle of Dara. In the same year, a second Persian army under Mihr-Mihroe was defeated at Satala by Roman forces under Sittas and Dorotheus, but in 531 a Persian army accompanied by a Lakhmid contingent under al-Mundhir IV defeated Belisarius at the Battle of Callinicum, and in 532 an "eternal" peace was concluded. Although he could not free himself from the yoke of the Ephthalites, Kavadh succeeded in restoring order in the interior and fought with general success against the Eastern Romans, founded several cities, some of which were named after him, and began to regulate the taxation and internal administration.
After Kavadh I, his son Khosrau I, also known as Anushirvan ("with the immortal soul"; ruled 531–579), ascended to the throne. He is the most celebrated of the Sassanid rulers. Khosrau I is most famous for his reforms in the aging governing body of Sassanids. In his reforms he introduced a rational system of taxation, based upon a survey of landed possessions, which his father had begun and tried in every way to increase the welfare and the revenues of his empire. Previous great feudal lords fielded their own military equipment, followers and retainers. Khosrau I developed a new force of dehkans or "knights" paid and equipped by the central government and the bureaucracy, tying the army and bureaucracy more closely to the central government than to local lords. (For more about Khosrau I's reforms, visit ).
Although the Emperor Justinian I (527–565) had paid him a bribe of 440,000 pieces of gold to keep the peace, in 540 Khosrau I broke the "eternal peace" of 532 and invaded Syria, where he sacked the city of Antioch and extorted large sums of money from a number of other cities. Further successes followed: in 541 Lazica defected to the Persian side, and in 542 a major Byzantine offensive in Armenia was defeated at Anglon. A five-year truce agreed in 545 was interrupted in 547 when Lazica again switched sides and eventually expelled its Persian garrison with Byzantine help; the war resumed, but remained confined to Lazica, which was retained by the Byzantines when peace was concluded in 562.
In 565, Justinian I died and was succeeded by Justin II (565–578), who resolved to stop subsidies to Arab chieftains to restrain them from raiding Byzantine territory in Syria. A year earlier the Sassanid governor of Armenia, of the Suren family, built a fire temple at Dvin near modern Yerevan, and he put to death an influential member of the Mamikonian family, touching off a revolt which led to the massacre of the Persian governor and his guard in 571, while rebellion also broke out in Iberia. Justin II took advantage of the Armenian revolt to stop his yearly payments to Khosrau I for the defense of the Caucasus passes. The Armenians were welcomed as allies, and an army was sent into Sassanid territory which besieged Nisibis in 573. However, dissension among the Byzantine generals not only led to an abandonment of the siege, but they in turn were besieged in the city of Dara, which was taken by the Persians who then ravaged Syria, causing Justin II to agree to make annual payments in exchange for a five-year truce on the Mesopotamian front, although the war continued elsewhere. In 576 Khosrau I led his last campaign, an offensive into Anatolia which sacked Sebasteia and Melitene, but ended in disaster: defeated outside Melitene, the Persians suffered heavy losses as they fled across the Euphrates under Byzantine attack. Taking advantage of Persian disarray, the Byzantines raided deep into Khosrau's territory, even mounting amphibious attacks across the Caspian Sea. Khosrau sued for peace, but he decided to continue the war after a victory by his general Tamkhosrau in Armenia in 577 and fighting resumed in Mesopotamia. The Armenian revolt came to an end with a general amnesty, which brought Armenia back into the Sassanid Empire.
Around 570 "Ma 'd-Karib", half-brother of the King of Yemen, requested Khosrau I's intervention. Khosrau I sent a fleet and a small army under a commander called Vahriz to the area near present Aden, and they marched against the capital San'a'l, which was occupied. Saif, son of Mard-Karib, who had accompanied the expedition, became King sometime between 575 and 577. Thus the Sassanids were able to establish a base in south Arabia to control the sea trade with the east. Later the south Arabian kingdom renounced Sassanid overlordship, and another Persian expedition was sent in 598 that successfully annexed southern Arabia as a Sassanid province, which lasted until the time of troubles after Khosrau II.
Khosrau I's reign witnessed the rise of the dihqans (literally, village lords), the petty landholding nobility who were the backbone of later Sassanid provincial administration and the tax collection system. Khosrau I was a great builder, embellishing his capital, founding new towns, and constructing new buildings. He rebuilt the canals and restocked the farms destroyed in the wars. He built strong fortifications at the passes and placed subject tribes in carefully chosen towns on the frontiers to act as guardians against invaders. He was tolerant of all religions, though he decreed that Zoroastrianism should be the official state religion, and was not unduly disturbed when one of his sons became a Christian.
After Khosrau I, Hormizd IV (579–590) took the throne. The war with the Byzantines continued to rage intensely but inconclusively until the general Bahram Chobin, dismissed and humiliated by Hormizd, rose in revolt in 589. The following year Hormizd was overthrown by a palace coup and his son Khosrau II (590–628) placed on the throne, but this change of ruler failed to placate Bahram, who defeated Khosrau, forcing him to flee to Byzantine territory, and seized the throne for himself as Bahram VI. With the aid of troops provided by the Byzantine emperor Maurice (582–602), Khosrau II raised a new rebellion against Bahram, and the combined armies of Khosrau and the Byzantine generals Narses and John Mystacon won a decisive victory over Bahram at Ganzak (591), restoring Khosrau to power. In return for Maurice's help, Khosrau was obliged to return all Byzantine territory occupied during the war and to hand over control of the western parts of Armenia and Iberia.
When Maurice was overthrown and killed by Phocas (602–610) in 602, Khosrau II used the murder of his benefactor as a pretext to begin a new invasion, which benefited from continuing civil war in the Byzantine Empire and met little effective resistance. Khosrau's generals systematically subdued the heavily fortified frontier cities of Byzantine Mesopotamia and Armenia, laying the foundations for unprecedented expansion. Syria was overrun and Antioch captured in 611, and in 613 a major counter-attack led in person by the Byzantine emperor Heraclius (602–610) was decisively defeated outside Antioch by the Persian generals Shahrbaraz and Shahin. Thereafter the Persian advance continued unchecked. Jerusalem fell in 614, Alexandria in 619 and the rest of Egypt by 621. The Sassanid dream of restoring the Achaemenid boundaries was close to completion. This remarkable peak of expansion was paralleled by a blossoming of Persian art, music, and architecture. The Byzantine Empire was on the verge of collapse and the borders of the Achaemenid Empire came close to being restored on all fronts.
Decline and fall (622–651)
Although hugely successful at first glance, Khosrau II's campaign had in fact overextended the Persian army and overtaxed the people. The Byzantine emperor Heraclius (610–641) drew on all his diminished and devastated empire's remaining resources, reorganised his armies and mounted a remarkable counter-offensive. Between 622 and 627 he campaigned against the Persians in Anatolia and the Caucasus, winning a string of victories against Persian forces under Khosrau, Shahrbaraz, Shahin and Shahraplakan, sacking the great Zoroastrian temple at Ganzak and securing assistance from the Khazars and Western Turkic Khaganate. In 626 Constantinople was besieged by Slavic and Avar forces which were supported by a Persian army under Shahrbaraz on the far side of the Bosphorus, but attempts to ferry the Persians across were blocked by the Byzantine fleet and the siege ended in failure. In 627-8 Heraclius mounted a winter invasion of Mesopotamia and, despite the departure of his Khazar allies, defeated a Persian army commanded by Rhahzadh in the Battle of Nineveh. He then marched down the Tigris, devastating the country and sacking Khosrau's palace of Dastagerd. He was prevented from attacking Ctesiphon by the destruction of the bridges on the Nahrawan Canal and conducted further raids before withdrawing up the Diyala into north-western Iran.
The impact of Heraclius's victories, the devastation of the richest territories of the Sassanid Empire and the humiliating destruction of high-profile targets such as Ganzak and Dastagerd fatally undermined Khosrau's prestige and his support among the Persian aristocracy, and early in 628 he was overthrown and murdered by his son Kavadh II (628), who immediately brought an end to the war, agreeing to withdraw from all occupied territories. In 629 AD Heraclius restored the True Cross to Jerusalem in a majestic ceremony. Kavadh died within months and chaos and civil war followed. Over a period of four years and five successive kings, including two daughters of Khosrau II and spahbod Shahrbaraz, the Sassanid Empire weakened considerably. The power of the central authority passed into the hands of the generals. It would take several years for a strong king to emerge from a series of coups, and the Sassanids never had time to recover fully.
In the spring of 632, a grandson of Khosrau I who had lived in hiding, Yazdegerd III, ascended the throne. The same year, the first raiders from the Arab tribes, newly united by Islam, arrived in Persian territory. Years of warfare had exhausted both the Byzantines and the Persians. The Sassanids were further weakened by economic decline, heavy taxation, religious unrest, rigid social stratification, the increasing power of the provincial landholders, and a rapid turnover of rulers. These factors facilitated the Islamic conquest of Persia.
The Sassanids never mounted a truly effective resistance to the pressure applied by the initial Arab armies. Yazdegerd was a boy at the mercy of his advisers and incapable of uniting a vast country crumbling into small feudal kingdoms, despite the fact that the Byzantines, under similar pressure from the newly expansive Arabs, no longer threatened. The first encounter between Sassanids and Muslim Arabs was in the Battle of the Bridge in 634 which resulted in a Sassanid victory, however the Arab threat did not stop there and reappeared shortly from the disciplined armies of Khalid ibn Walid, once one of Muhammad's chosen companions-in-arms and leader of the Arab army. Under the Caliph `Umar ibn al-Khattāb, a Muslim army defeated a larger Persian force lead by general Rostam Farrokhzad at the plains of al-Qādisiyyah in 637 and besieged Ctesiphon. Ctesiphon fell after a prolonged siege. Yazdgerd fled eastward from Ctesiphon, leaving behind him most of the Empire's vast treasury. The Arabs captured Ctesiphon shortly afterward, leaving the Sassanid government strapped for funds and acquiring a powerful financial resource for their own use. A number of Sassanid governors attempted to combine their forces to throw back the invaders, but the effort was crippled by the lack of a strong central authority, and the governors were defeated at the Battle of Nihawānd; the empire, with its military command structure non-existent, its non-noble troop levies decimated, its financial resources effectively destroyed, and the Asawaran (Azatan) knightly caste destroyed piecemeal, was now utterly helpless in the face of the invaders.
Upon hearing the defeat in Nihawānd, Yazdgerd along with most of Persian nobilities fled further inland to the eastern province of Khorasan. He was assassinated by a miller in Merv in late 651 while the rest of the nobles settled in central Asia where they contributed greatly in spreading Persian culture and language in those regions and the establishment of the first native Iranian Islamic dynasty, the Samanid dynasty, which sought to revive and resuscitate Sassanid traditions and culture after the invasion of Islam.
The abrupt fall of Sassanid Empire was completed in a period of five years, and most of its territory was absorbed into the Islamic caliphate; however, many Iranian cities resisted and fought against the invaders several times. Cities such as Rayy, Isfahan and Hamadan were exterminated thrice by Islamic caliphates in order to suppress revolts. The local population either willingly accepted Islam, stayed as dhimmi subjects of the Muslim state and paid a poll tax ( jizya), or were forced to convert by the invading armies. The latter measure is usually disputed in its use though as most conversion took place primarily in the Abbasids caliphate. Invaders destroyed the Academy of Gundishapur and its library, burning piles of books. Most Sassanid records and literary works were destroyed. A few that escaped this fate were later translated into Arabic and later to Modern Persian. During the Islamic invasion many Iranian cities were destroyed or deserted, palaces and bridges were ruined and many magnificent imperial Persian gardens were burned to the ground. Persian poets such as Ferdowsi lamented the downfall of the Sassanids in their work:
| “ |
کجا آن بزرگان ساسانیان kojā ān bozorgān-e Sāsānīyān "To where have the great Sassanids gone? |
” |
Government
The Sassanids established an empire roughly within the frontiers achieved by the Achaemenids, with the capital at Ctesiphon in the Khvarvaran province. In administering this empire, Sassanid rulers, took the title of Shāhanshāh (King of Kings), became the central overlords and also assumed guardianship of the sacred fire, the symbol of the national religion. This symbol is explicit on Sassanid coins where the reigning monarch, with his crown and regalia of office, appears on the obverse, backed by the sacred fire, the symbol of the national religion, on the coin's reverse. Sassanid queens had the title of Banebshenan banebshen (the Queen of Queens).
On smaller scale the territory might also be ruled by a number of petty rulers from Sassanid royal family, known as Shahrdar (شهردار) overseen directly by Shahanshah. Sassanid rule was characterized by considerable centralization, ambitious urban planning, agricultural development, and technological improvements. Below the king a powerful bureaucracy carried out much of the affairs of government; The head of the bureaucracy and Vice-Chancellor, was the "Vuzorg (Bozorg) Farmadar" (بزرگ فرمادار). Within this bureaucracy the Zoroastrian priesthood was immensely powerful. The head of the Magi priestly class, the Mobadan (موبدان), along with the commander in chief, the Iran (Eran) Spahbod (ايران سپهد), the head of traders and merchants syndicate "Ho Tokhshan Bod" (هوتوخشان بد) and minister of agriculture "Vastrioshansalar" (واستریوشانسالار) who was also head of farmers, were below the emperor the most powerful men of the Sassanid state.
The Sassanid monarch usually acted with the advice of his ministers, who composed a council of state. Masudi, the Muslim historian, praised the "excellent administration of the [Sassanid] kings, their well-ordered policy, their care for their subjects, and the prosperity of their domains."
In normal times the monarchical office was hereditary, but might be transmitted by the king to a younger son; in two instances the supreme power was held by queens. When no direct heir was available, the nobles and prelates chose a ruler, but their choice was restricted to members of the royal family.
The Sassanid nobility was a mixture of old Parthian clans, Persian aristocratic families, and noble families from subjected territories. Many new noble families had risen after the dissolution of the Parthian dynasty, while several of the once-dominant Seven Parthian clans remained of high importance. At the court of Ardashir I, the old Arsacid families of the House of Karen and the House of Suren, along with several Persian families, the Varazes and Andigans, held positions of great honour. Alongside these Iranian and non-Iranian noble families, the kings of Merv, Abarshahr, Carmania, Sakastan, Iberia, and Adiabene, who are mentioned as holding positions of honour amongst the nobles, appeared at the court of the Shahanshah. Indeed, the extensive domains of the Surens, Karens, and Varazes had become part of the original Sassanid state as semi-independent states. Thus, the noble families that attended at the court of the Sassanid empire continued to be ruling lines in their own right, although subordinate to the Shahanshah.
In general, Bozorgan from Persian families held the most powerful positions in the imperial administration, including governorships of border provinces ( Marzban مرزبان). Most of these positions were patrimonial, and many were passed down through a single family for generations. Those Marzbans of greatest seniority were permitted a silver throne, while Marzbans of the most strategic border provinces, such as the Caucasus province, were allowed a golden throne. In military campaigns the regional Marzbans could be regarded as field marshals, while lesser spahbods could command a field army.
Culturally, the Sassanids implemented a system of social stratification. This system was supported by Zoroastrianism, which was established as the state religion. Other religions appear to have been largely tolerated (although this claim is the subject of heated discussion; see, for example, Wiesehöfer, Ancient Persia, or the Cambridge History of Iran, vol. 3). Sassanid emperors consciously sought to resuscitate Persian traditions and to obliterate Greek cultural influence.
Sassanid army
The backbone of the Persian army (Spah) in the Sassanid era was composed of two types of heavy cavalry units: Clibanarii and Cataphracts. This cavalry force, composed of elite noblemen trained since youth for military service, was supported by light cavalry, infantry, and archers. Sassanid tactics centered around disrupting the enemy with archers, war elephants, and other troops, thus opening up gaps the cavalry forces could exploit.
Unlike their predecessors, the Parthians, the Sassanids developed advanced siege engines. This development served the empire well in conflicts with Rome, in which success hinged upon the ability to seize cities and other fortified points; conversely, the Sassanids also developed a number of techniques for defending their own cities from attack. The Sassanid army was famous for its heavy cavalry, which was much like the preceding Parthian army, albeit only some of the Sassanid heavy cavalry were equipped with lances. The Greek historian Ammianus Marcellinus's description of Shapur II's clibanarii cavalry manifestly shows how heavily equipped it was, and how only a portion were spear equipped:
All the companies were clad in iron, and all parts of their bodies were covered with thick plates, so fitted that the stiff-joints conformed with those of their limbs; and the forms of human faces were so skillfully fitted to their heads, that since their entire body was covered with metal, arrows that fell upon them could lodge only where they could see a little through tiny openings opposite the pupil of the eye, or where through the tip of their nose they were able to get a little breath. Of these some who were armed with pikes, stood so motionless that you would have thought them held fast by clamps of bronze.
The Byzantine emperor Maurikios also emphasizes in his Strategikon that many of the Sassanid heavy cavalry did not carry spears, relying on their bows as their primary weapons.
The amount of money involved in maintaining a warrior of the Asawaran (Azatan) knightly caste required a small estate, and the Asawaran (Azatan) knightly caste received that from the throne, and in return, were the throne's most notable defenders in time of war.
Conflicts
The Sassanids, like the Parthians, were in constant hostilities with the Roman Empire. Following the division of the Roman Empire in 395, the Eastern Roman Empire, with its capital at Constantinople, replaced the Roman Empire as Persia's principle western enemy. Hostilities between the two empires became more frequent. The Sassanids, similar to the Roman Empire, were in a constant state of conflict with neighboring kingdoms and nomadic hordes. Although the threat of nomadic incursions could never be fully resolved, the Sassanids generally dealt much more successfully with these matters than did the Romans, due to their policy of making coordinated campaigns against threatening nomads.
In the west, Sassanid territory abutted that of the large and stable Roman state, but to the east its nearest neighbors were the Kushan Empire and nomadic tribes such as the White Huns. The construction of fortifications such as Tus citadel or the city of Nishapur, which later became a centre of learning and trade, also assisted in defending the eastern provinces from attack.
In the south and central Arabia, Bedouin Arab tribes occasionally raided the Sassanid empire. The Kingdom of Al-Hirah, a Sassanid vassal kingdom, was established to form a buffer zone between the empire's mainland and the Bedouin tribes. The dissolution of the Kingdom of Al-Hirah by Pervaiz(King) Khosrau II in 602 contributed greatly to decisive Sassanid defeats suffered against Bedouin Arabs later in the century. These defeats resulted in a sudden takeover of the Sassanid empire by Bedouin tribes under the Islamic banner.
In the north, Khazars and other Turkic nomads frequently assaulted northern provinces of the empire. They plundered the territory of the Medes in 634. Shortly thereafter, the Persian army defeated them and drove them out. The Sassanids built numerous fortifications in the Caucasus region to halt these attacks.
Interactions with Eastern states
Relations with China
Like their predecessors the Parthians, the Sassanid Empire carried out active foreign relations with China, and ambassadors from Persia frequently traveled to China. Chinese documents report on thirteen Sassanid embassies to China. Commercially, land and sea trade with China was important to both the Sassanid and Chinese Empires. Large numbers of Sassanid coins have been found in southern China, confirming maritime trade.
On different occasions Sassanid kings sent their most talented Persian musicians and dancers to the Chinese imperial court at Luoyang during the Jin and Northern Wei dynasties and to Chang'an during the Sui and Tang dynasties. Both empires benefited from trade along the Silk Road, and shared a common interest in preserving and protecting that trade. They cooperated in guarding the trade routes through central Asia, and both built outposts in border areas to keep caravans safe from nomadic tribes and bandits.
Politically, we hear of several Sassanid and Chinese efforts in forging alliances against the common enemy who were the Hephthalites. Upon the rise of the nomadic Gokturk Empire in Inner Asia, we also see what looks like a collaboration between China and the Sassanid to defuse the Turkic advances. The documents from Mt. Mogh also talk about the presence of a Chinese general in the service of the king of Sogdiana at the time of the Arab invasions.
Following the invasion of Iran by Muslim Arabs, Pirooz, son of Yazdegerd III, escaped along with a few Persian nobles and took refuge in the Chinese imperial court. Both Piroz and his son Narseh (Chinese neh-shie) were given high titles at the Chinese court. At least in two occasions, the last possibly in 670, Chinese troops were sent with Peroz in order to restore him to the Sassanid throne with mixed results, one possibly ending up in a short rule of Peroz in Sistan ( Sakestan) from which we have a few remaining numismatic evidences. Narseh later attained the position of commander of the Chinese imperial guards and his descendants lived in China as respected princes.
Expansion to India
After the Sassanids had secured Iran and its neighboring regions under Ardashir I, the second emperor, Shapur I (240–270), extended his authority eastwards into what is today Pakistan and northwestern India. The previously autonomous Kushans were obliged to accept his suzerainty. Although the Kushan empire declined at the end of the 3rd century, to be replaced by the northern Indian Gupta Empire in the 4th century, it is clear that Sassanid influence remained relevant in India's northwest throughout this period.
Persia and northwestern India engaged in cultural as well as political intercourse during this period, as certain Sassanid practices spread into the Kushan territories. In particular, the Kushan's were influenced by the Sassanid conception of kingship, which spread through the trade of Sassanid silverware and textiles depicting emperors hunting or dispensing justice.
This cultural interchange did not, however, spread Sassanid religious practices or attitudes to the Kushans. While the Sassanids always adhered to a stated policy of religious proselytization, and sporadically engaged in persecution or forced conversion of minority religions, the Kushans preferred to adopt a policy of religious tolerance.
Lower-level cultural interchanges also took place between India and Persia during this period. For example, Persians imported chess from India and changed the game's name from chaturanga to chatrang. In exchange, Persians introduced Backgammon to India.
During Khosrau I's reign many books were brought from India and translated into Pahlavi, the language of the Sassanid Empire. Some of these later found their way into the literature of the Islamic world. A notable example of this was the translation of the Indian Panchatantra by one of Khosrau's ministers, Burzoe; this translation, known as the Kelileh va Demneh, later made its way into Arabia and Europe. The details of Burzoe's legendary journey to India and his daring acquirement of Panchatantra is written in full details in Ferdowsi's Shahnameh.
Iranian society under the Sassanids

Sassanid society and civilization were among the most flourishing of their time, rivaled in their region only by the Byzantine civilisation. The amount of scientific and intellectual exchange between the two empires is witness to the competition and cooperation of these cradles of civilization.
The most striking difference between Parthian and Sassanid society was renewed emphasis on charismatic and centralized government. In Sassanid theory, the ideal society was one which could maintain stability and justice and the necessary instrument for this was a strong monarch. Sassanid society was immensely complex, with separate systems of social organization governing numerous different groups within the empire. Historians believe that society was divided into four classes: Priests (Atorbanan in Persian: آتروبانان), Warriors (Arteshtaran in Persian: ارتشتاران), Secretaries (Dabiran in Persian: دبيران), and Commoners (Vasteryoshan-Hootkheshan in Persian: هوتخشان-واستريوشان). At the centre of the Sassanid caste system was the Shahanshah, ruling over all the nobles. The royal princes, petty rulers, great landlords, and priests together constituted a privileged stratum, and were identified as Bozorgan بزرگان, or nobles. This social system appears to have been fairly rigid.
Membership in a class was based on birth, although it was possible for an exceptional individual to move to another class on the basis of merit. The function of the king was to ensure that each class remained within its proper boundaries, so that the strong did not oppress the weak, nor the weak the strong. To maintain this social equilibrium was the essence of royal justice, and its effective functioning depended on the glorification of the monarchy above all other classes.
On a lower level, Sassanid society was divided into Azatan (Azadan) آزادان (freemen), who jealously guarded their status as descendants of ancient Aryan conquerors, and the mass of originally non-Aryan peasantry. The Azatan formed a large low-aristocracy of low-level administrators, mostly living on small estates. The Azatan provided the cavalry backbone of Sassanid army.
Art, science and literature
The Sassanid kings were enlightened patrons of letters and philosophy. Khosrau I had the works of Plato and Aristotle translated into Pahlavi taught at Gundishapur, and even read them himself. During his reign many historical annals were compiled, of which the sole survivor is the Karnamak-i Artaxshir-i Papakan (Deeds of Ardashir), a mixture of history and romance that served as the basis of the Iranian national epic, the Shahnama. When Justinian I closed the schools of Athens, seven of their professors fled to Persia and found refuge at Khosrau's court. In time they grew homesick, and in his treaty of 533 with Justinian, the Sassanid king stipulated that the Greek sages should be allowed to return and be free from persecution.
Under Khosrau I the college of Gundishapur, which had been founded in the 4th century, became "the greatest intellectual centre of the time," drawing students and teachers from every quarter of the world. Nestorian Christians were received there, and brought Syriac translations of Greek works in medicine and philosophy. Neoplatonists, too, came to Gundishapur, where they planted the seeds of Sufi mysticism; the medical lore of India, Persia, Syria, and Greece mingled there to produce a flourishing school of therapy.
Artistically, the Sassanid period witnessed some of the highest achievements of Persian civilization. Much of what later became known as Muslim culture, including architecture and writing, was originally drawn from Persian culture. At its peak the Sassanid Empire stretched from Syria to northwest India, but its influence was felt far beyond these political boundaries. Sassanid motifs found their way into the art of Central Asia and China, the Byzantine Empire, and even Merovingian France. Islamic art however, was the true heir to Sassanid art, whose concepts it was to assimilate while, at the same time instilling fresh life and renewed vigor into it. According to Will Durant:
"Sasanian art exported its forms and motifs eastward into India, Turkestan, and China, westward into Syria, Asia Minor, Constantinople, the Balkans, Egypt, and Spain. Probably its influence helped to change the emphasis in Greek art from classic representation to Byzantine ornament, and in Latin Christian art from wooden ceilings to brick or stone vaults and domes and buttressed walls."
Sassanid carvings at Taq-e Bostan and Naqsh-e Rustam were colored; so were many features of the palaces; but only traces of such painting remain. The literature, however, makes it clear that the art of painting flourished in Sasanian times; the prophet Mani is reported to have founded a school of painting; Firdowsi speaks of Persian magnates adorning their mansions with pictures of Iranian heroes; and the poet al-Buhturi describes the murals in the palace at Ctesiphon. When a Sasanian king died, the best painter of the time was called upon to make a portrait of him for a collection kept in the royal treasury.
Painting, sculpture, pottery, and other forms of decoration shared their designs with Sasanian textile art. Silks, embroideries, brocades, damasks, tapestries, chair covers, canopies, tents, and rugs were woven with patience and masterly skill, and were dyed in warm tints of yellow, blue, and green. Every Persian but the peasant and the priest aspired to dress above his class; presents often took the form of sumptuous garments; and great colorful carpets had been an appendage of wealth in the East since Assyrian days. The two dozen Sasanian textiles that have survived are among the most highly valued fabrics in existence. Even in their own day, Sasanian textiles were admired and imitated from Egypt to the Far East; and during the Middle Ages they were favored for clothing the relics of Christian saints. When Heraclius captured the palace of Khosru Parvez at Dastagird, delicate embroideries and an immense rug were among his most precious spoils. Famous was the "Winter Carpet", also known as "Khosro's Spring" (Spring Season Carpet قالى بهارستان) of Khosru Anushirvan, designed to make him forget winter in its spring and summer scenes: flowers and fruits made of inwoven rubies and diamonds grew, in this carpet, beside walks of silver and brooks of pearls traced on a ground of gold. Harun al-Rashid prided himself on a spacious Sasanian rug thickly studded with jewelry. Persians wrote love poems about their rugs.
Studies on Sassanid remains show over 100 types of crowns being worn by Sassanid kings. The various Sassanid crowns demonstrate the cultural, economic, social, and historical situation in each period. The crowns also show the character traits of each king in this era. Different symbols and signs on the crowns, the moon, stars, eagle, and palm, each illustrate the wearer's religious faith and beliefs. (For more on Sassanid crowns please visit )
The Sassand Dynasty, like the Achaemenid, originated in the province of Persis ( Fars). The Sassanids saw themselves as successors of the Achaemenids, after the Hellenistic and Parthian interlude, and believed that it was their destiny to restore the greatness of Persia.
In reviving the glories of the Achaemenid past, the Sassanids were no mere imitators. The art of this period reveals an astonishing virility, in certain respects anticipating key features of Islamic art. Sassanid art combined elements of traditional Persian art with Hellenistic elements and influences. The conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great had inaugurated the spread of Hellenistic art into Western Asia. Though the East accepted the outward form of this art, it never really assimilated its spirit. Already in the Parthian period, Hellenistic art was being interpreted freely by the peoples of the Near East. Throughout the Sassanid period there was reaction against it. Sassanid art revived forms and traditions native to Persia, and in the Islamic period, these reached the shores of the Mediterranean. According to Fergusson:
With the accession of the [Sassanids], Persia regained much of that power and stability to which she had been so long a stranger… The improvement in the fine arts at home indicates returning prosperity, and a degree of security unknown since the fall of the Achaemenidae.
Surviving palaces illustrate the splendor in which the Sassanid monarchs lived. Examples include palaces at Firouzabad and Bishapur in Fars and the capital city of Ctesiphon in Khvarvaran province, Iraq. In addition to local traditions, Parthian architecture influenced Sassanid architectural characteristics. All are characterized by the barrel-vaulted iwans introduced in the Parthian period. During the Sassanid period, these reached massive proportions, particularly at Ctesiphon. There, the arch of the great vaulted hall, attributed to the reign of Shapur I (241–272), has a span of more than 80 feet (24 m) and reaches a height of 118 feet (36 m). This magnificent structure fascinated architects in the centuries that followed and has been considered one of the most important examples of Persian architecture. Many of the palaces contain an inner audience hall consisting, as at Firuzabad, of a chamber surmounted by a dome. The Persians solved the problem of constructing a circular dome on a square building by employing squinches, or arches built across each corner of the square, thereby converting it into an octagon on which it is simple to place the dome. The dome chamber in the palace of Firouzabad is the earliest surviving example of the use of the squinch, suggesting that this architectural technique was probably invented in Persia.
The unique characteristic of Sassanid architecture was its distinctive use of space. The Sassanid architect conceived his building in terms of masses and surfaces; hence the use of massive walls of brick decorated with molded or carved stucco. Stucco wall decorations appear at Bishapur, but better examples are preserved from Chal Tarkhan near Rayy (late Sassanid or early Islamic in date), and from Ctesiphon and Kish in Mesopotamia. The panels show animal figures set in roundels, human busts, and geometric and floral motifs.
At Bishapur some of the floors were decorated with mosaics showing scenes of banqueting. The Roman influence here is clear, and the mosaics may have been laid by Roman prisoners. Buildings were decorated with wall paintings. Particularly fine examples have been found on Mount Khajeh in Sistan.
Industry and trade
Persian industry under the Sassanids developed from domestic to urban forms. Guilds were numerous, and some towns had a revolutionary proletariat. Silk weaving was introduced from China; Sassanid silks were sought after everywhere, and served as models for the textile art in Byzantium, China, and Japan. Chinese merchants came to thriving Iranian ports such as Siraf to sell raw silk and buy rugs, jewels, rouge; Armenians, Syrians, and Jews connected Persia, Byzantium, and Rome in slow exchange. Good roads and bridges, well patrolled, enabled state post and merchant caravans to link Ctesiphon with all provinces; and harbors were built in the Persian Gulf to quicken trade with India. Sassanid merchants ranged far and wide and gradually ousted Romans from lucrative Indian ocean trade routes. The recent Archeological discovery has shown an interesting fact that Sassanids used special labels (commercial labels) on goods as a way of promoting their brands and distinguish between different qualities.
Khosrau I further extended the already vast trade network. The Sassanid state now tended toward monopolistic control of trade, with luxury goods assuming a far greater role in the trade than heretofore, and the great activity in building of ports, caravanserais, bridges, and the like was linked to trade and urbanization. The Persians dominated international trade, both in the Indian Ocean and in Central Asia and South Russia in the time of Khosrau, although competition with the Byzantines was at times intense. Sassanian settlements in Oman and Yemen testify to the importance of trade with India, but the silk trade with China was mainly in the hands of Sassanid vassals and the Iranian people, the Sogdians.
The main exports of the Sassanids were silk, woolen and golden textile, carpets and rugs, skin, leather and pearls from the Persian gulf. Also there were goods in transit from China (paper, silk) and India (spices) which Sassanid customs imposed taxes upon and which were re-exported from the Empire to Europe.
It was also a time of increased metallurgical production, so Iran earned a reputation as the "armory of Asia". Most of the Sassanid mining centers were at the fringes of the Empire, in Armenia, the Caucasus and above all Transoxania. The extraordinary mineral wealth of the Pamir Mountains on the eastern horizon of the Sassanid empire led to a legend among the Tajiks, an Iranian people living there, which is still told today. It said when God was creating the world, he tripped over Pamirs, dropping his jar of minerals which spread across the region.
Religion

The religion of the Sassanid state was Zoroastrianism, but Sassanid Zoroastrianism had clear distinctions from the practices laid out in the Avesta, the holy books of Zoroastrianism. Sassanid Zoroastrian clergy modified the religion in a way to serve themselves, causing substantial religious uneasiness. Sassanid religious policies contributed to the flourishing of numerous religious reform movements, the most important of these being the Mani and Mazdak religions.
Extreme and pronounced dualism constituted the most noticeable feature of Zoroastrianism. Ormazd and Ahriman, the principles of Good and Evil, were expressly declared to be "twins" who had "in the beginning come together to create Life and Death, and to settle how the world was to be." There was no priority of existence of the one over the other, and no decided superiority. The two, being coeval, had contended since the beginning of time and would continue to contend until the end of the world, when Good would triumph over Evil (see also Zoroastrian eschatology).
These two principles were represented as persons. Ormazd was "the creator of life, the earthly and the spiritual," he who "made the celestial bodies, earth, water, and trees." He was "good," "holy," "pure," "true," "the Holy God," "the Holiest," "the Essence of Truth," "the father of all truth," "the being best of all," "the master of purity." He was supremely "happy," being possessed of every blessing, "health, wealth, virtue, wisdom, immortality." From him came every good gift enjoyed by man; on the pious and the righteous he bestowed, not only earthly advantages, but precious spiritual gifts, truth, devotion, "the good mind," and everlasting happiness; and, as he rewarded the good, so he also punished the bad, though this was an aspect in which he was but seldom represented.
Zoroastrian worship was intimately connected with fire-temples and fire-altars. A fire-temple was maintained in every important city throughout the empire; and in these a sacred flame, believed to have been lighted from heaven, was kept perpetually alight by the priests, and was spoken of as "unextinguishable". Fire-altars probably also existed independently of temples; throughout Sassanid history a freestanding fire-altar was given a prominent place on coinage as the main impress on the reverse. It was represented with the flame rising from it, and sometimes with a head in the flame; its stem was ornamented with garlands or fillets; and on either side, as protectors or as worshippers, were represented two figures, sometimes watching the flame, sometimes turned from it, guarding it apparently from external enemies.
Alongside Zoroastrianism other religions, primarily Judaism, Christianity and Buddhism existed in Sassanid society, and were largely free to practice and preach their beliefs. A very large Jewish community flourished under Sassanid rule, with thriving centers at Isfahan, Babylon and Khorasan, and with its own semiautonomous Exilarchate leadership based in Mesopotamia. This community would, in fact, continue to flourish until the advent of Zionism. Jewish communities suffered only occasional persecution. They enjoyed a relative freedom of religion, and were granted privileges denied to other religious minorities. Shapur I (Shabur Malka in Aramaic) was a particular friend to the Jews. His friendship with Shmuel produced many advantages for the Jewish community. He even offered the Jews in the Sassanid empire a fine white Nisaean horse, just in case the Messiah, who was thought to ride a donkey or a mule, would come. Shapur II, whose mother was Jewish, had a similar friendship with a Babylonian rabbi named Raba. Raba's friendship with Shapur II enabled him to secure a relaxation of the oppressive laws enacted against the Jews in the Persian Empire. Moreover, in the eastern portion of the empire, various Buddhist places of worship, notably in Bamiyan were active as Buddhism gradually became more popular in that region.
Christians in Iran at this time belonged mainly to the Nestorian and Jacobite branches of Christianity, also known as respectively the Assyrian Church of the East and the Syriac Orthodox Church. Although these churches originally maintained ties with the Christian churches in the Roman Empire, they were indeed quite different from them. One of the most important reasons for this, is that the Church language of the Nestorian and Jacobite churches was the Aramaic language, which is also the language spoken by the Jews in Judea and Galilee at the time of Jesus. This language was not used by the vast majority of the Christians in the Roman Empire, who mainly spoke Latin, Koine Greek, or Coptic.
Another reason that the churches within the Persian Empire did not maintain such close ties with their counterparts in the Roman Empire, was the continuous rivalry between these two great empires. And quite often, Christians in Persia were (often falsely) accused of sympathizing with the Romans, especially when the Roman emperor Theodosius I declared Christianity the state religion of the Roman Empire.
But it was not until the Council of Ephesus in 431 that the vast majority of Christians in Persia broke their ties with the churches in the Roman Empire. At this council, Nestorius, a theologian of Syrian/Assyrian origin and the patriarch of Constantinople, taught a different view of the Christology that was rejected and regarded as heretical by the majority of Greek, Roman and Coptic Christians. One of the differences in Nestorius' teachings, was that he refused to call Mary, the mother of Jesus Christ " Theotokos" or Mother of God. The Assyrian Church, however, disagreed with the other churches, and refused to condemn Nestorius' teachings.
Nestorius eventually lost the debate, and was deposed as patriarch. He was forced to flee with a number of his followers to the Sassanid Persian Empire where he was allowed to settle in Persian territories. He and his followers were welcomed into the Assyrian Church in Mesopotamia. Several Persian emperors also used this opportunity to strengthen Nestorius' position within the Assyrian Church (which made up the vast majority of the Christians in the Persian Empire) by eliminating the most important pro-catholic clergymen in Persia and making sure that their places were taken by Nestorians. This was to assure that the only loyalty these Christians would have would be to the Persian Empire. (see also Sassanid Church)
Most of the Christians in the Sassanid empire lived on the western edge of the empire, predominantly in Mesopotamia, but there were also important communities on the island of Tylos (present day Bahrain), the southern coast of the Persian Gulf, the area of the Arabian kingdom of Lakhm and the Persian part of Armenia. Some of these areas were the earliest to be Christianized; the kingdom of Armenia became the first independent Christian state in the world in 301 while a number of Assyrian territories had almost become fully Christianized even earlier during the 3rd century; they never became independent nations.
Most Christians in the Persian Empire belonged to a number of predominantly Christian ethnic groups. Some of these groups were the Assyrians, the Arabs of southern Mesopotamia, and the Armenians, as well as some smaller ethnic groups such as the Monophysite Syriacs. The latter group was taken to Persia as prisoners of war from the many conflicts with the Roman Empire. Conversion did take place among ethnic Persians and other ethnicities residing in the empire. Among them were certain small Caucasian and Kurdish tribes which had converted to Christianity.
Legacy and Importance
The influence of the Sassanids continues long after they ceased to exist:
In Europe
Sassanids had a significant influence on Roman civilization. The character of the Roman army was affected by the methods of Persian warfare. In a modified form, the Roman Imperial autocracy imitated the royal ceremonies of the court of the Sassanids at Ctesiphon, and those in turn had an influence on the ceremonial traditions of the courts of modern Europe. The origin of the formalities of European diplomacy is attributed to the diplomatic relations between the Persian governments and Roman Empire.
Through the late Roman Empire's adoption of Cataphract cavalry, the principles of the European knighthood (heavily armoured cavalry) of the Middle Ages can be traced to the Sassanid Asawaran (Azatan) knightly caste with whom it also shares a number of similarities.
In Jewish history
From the perspective of Jewish history, the Sassanid Empire was highly significant when it became the centre of the Jewish world after the destruction of the Second Commonwealth in 70 AD. The period saw major developments in Judaism, including the making of the Babylonian Talmud, when the great Talmudic Academies in Babylonia flourished during the Rabbinic era of the Amoraim.
In India
Following the collapse of the Sassanid Empire, after which Zoroastrianism was supplanted by Islam, Zoroastrians increasingly became a persecuted minority, and a number of them chose to emigrate. According to the Qissa-i Sanjan, one group of those refugees landed in what is now Gujarat, India, where they were allowed greater freedom to observe their old customs and to preserve their faith. The descendants of those Zoroastrians, now known as the Parsis, would play a significant role in the development of India. Today there are around 70,000 Parsis in India.
The Parsis, as Zoroastrians, still use a variant of the religious calendar instituted under the Sassanids. That calendar still marks the number of years since the accession of Yazdegerd III, just as it did in 632. (See also: Zoroastrian calendar)
Sassanid Empire chronology
| Ruler | Year |
|---|---|
| Ardashir I | 224 to 241 |
| Shapur I | 241 to 272 |
| Hormizd I | 272 to 273 |
| Bahram I | 273 to 276 |
| Bahram II | 276 to 293 |
| Bahram III | 293 |
| Narseh | 293 to 302 |
| Hormizd II | 302 to 310 |
| Shapur II | 310 to 379 |
| Ardashir II | 379 to 383 |
| Shapur III | 383 to 388 |
| Bahram IV | 388 to 399 |
| Yazdegerd I | 399 to 420 |
| Bahram V | 420 to 438 |
| Yazdegerd II | 438 to 457 |
| Hormizd III | 457 to 459 |
| Peroz I | 457 to 484 |
| Balash | 484 to 488 |
| Kavadh I | 488 to 531 |
| Djamasp | 496 to 498 |
| Khosrau I | 531 to 579 |
| Hormizd IV | 579 to 590 |
| Bahram Chobin | 590 to 591 |
| Khosrau II | 591 to 628 |
| Kavadh II | 628 |
| Ardashir III | 628 to 630 |
| Shahrbaraz | 630 |
| Purandokht (Empress) | 630 to 631 |
| Azarmidokht (Empress) | 631- |
| Hormizd VI | 631 to 632 |
| Yazdgerd III | 632 to 651 |
226–241: Reign of Ardashir I:
- 224–226: Overthrow of Parthian Empire.
- 229–232: War with Rome
- Zoroastrianism is revived as official religion.
- The collection of texts known as the Zend Avesta is assembled.
241–271: Reign of Shapur I:
- 241–244: War with Rome.
- 252–261: War with Rome. Capture of Roman emperor Valerian.
- 215–271: Mani, founder of Manicheanism.
271–301: A period of dynastic struggles.
283: War with Rome. Romans sack Ctesiphon
296-8: War with Rome. Persia cedes five provinces east of the Tigris to Rome.
309–379: Reign of Shapur II "the Great":
- 337–350: First war with Rome with relatively little success.
- 359–363: Second war with Rome. Rome returns trans-Tigris provinces and cedes Nisibis and Singara to Persia.
387: Armenia partitioned into Roman and Persian zones.
399–420: Reign of Yazdegerd I "the Sinner":
- 409: Christian are permitted to publicly worship and to build churches.
- 416–420: Persecution of Christians as Yazdegerd revokes his earlier order.
420–438: Reign of Bahram V:
- 420–422: War with Rome.
- 424: Council of Dad-Ishu declares the Eastern Church independent of Constantinople.
- 428: Persian zone of Armenia annexed to Sassanid Empire.
438–457: Reign of Yazdegerd II:
- 441: War with Rome.
- 449-451: Armenian revolt.
482-3: Armenian and Iberian revolt.
483: Edict of Toleration granted to Christians.
484: Peroz I defeated and killed by Hephthalites.
491: Armenian revolt. Armenian Church repudiates the Council of Chalcedon:
- Nestorian Christianity becomes dominant Christian sect in Sassanid Empire.
502-506: War with Constantinople.
526-532: War with Constantinople.
531–579: Reign of Khosrau I, "with the immortal soul" (Anushirvan)
540–562: War with Constantinople.
572-591: War with Constantinople. Persia cedes much of Armenia and Iberia to Constantinople.
590–628: Reign of Khosrau II
603–628: War with Byzantium. Persia occupies Byzantine Mesopotamia, Syria, Palestine, Egypt and the Transcaucasus, before being driven to withdraw to pre-war frontiers by Byzantine counter-offensive.
610: Arabs defeat a Sassanid army at Dhu-Qar.
626: Unsuccessful siege of Constantinople by Avars and Persians.
627: Byzantine Emperor Heraclius invades Assyria and Mesopotamia. Decisive defeat of Persian forces at the Battle of Nineveh.
628–632: Chaotic period of multiple rulers.
632–642: Reign of Yazdegerd III.
636: Decisive Sassanid defeat at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah during the Islamic conquest of Iran.
642: Final victory of Arabs when Persian army destroyed at Nahavand (Nehavand).
651: Last Sassanid ruler Yazdegerd III was captured and beheaded by Arabian army invaders at Merv, present-day Turkmenistan, ending the dynasty. His son Pirooz and many others went into exile in China.