17th century
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General history
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 16th century · 17th century · 18th century |
| Decades: | 1600s 1610s 1620s 1630s 1640s 1650s 1660s 1670s 1680s 1690s |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 17th Century was that century which lasted from 1601- 1700 in the Gregorian calendar.
The 17th Century falls into the Early Modern period of Europe and was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the French Grand Siècle dominated by Louis XIV, and the beginning of modern science and philosophy, including the contributions of Galileo Galilei, René Descartes, Blaise Pascal, Isaac Newton; Europe was torn by warfare throughout the century, by the Thirty Years' War, the Great Turkish War, the end of the Dutch Revolt and the English Civil War among others, while European colonization of the Americas began in earnest.

In the east, the 17th Century saw the flowering of the Ottoman, Safavid and Mughal empires, the beginning of the Edo period in feudal Japan, and the violent transition from the Ming to the Qing Dynasty in China.
Events
1600s
- 1600: Charles I of England born to James VI of Scotland and Anne of Denmark.
- 1601: Battle of Kinsale, one of the most important battles in Irish history, fought.
- 1602: Dutch East India Company founded. Its success contributes to the Dutch Golden Age.
- 1603: Elizabeth I of England dies and is succeeded by her cousin King James VI of Scotland, uniting the crowns of Scotland and England.
- 1603: Tokugawa Ieyasu seizes control of Japan and establishes the Tokugawa Shogunate which rules the country until 1868.
- 1603- 23: After modernizing his army, Abbas I expands the Safavid Empire by capturing territory from the Ottomans and the Portuguese.
- 1605: Gunpowder Plot failed in England.
- 1606: The Long War between the Ottoman Empire and Austria is ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok.
- 1606: Captain Willem Janszoon and his crew aboard the Dutch East India Company ship Duyfken becomes the first recorded Europeans to sight and make landfall in Australia.
- 1607: Jamestown, Virginia, is settled as what would become the first permanent English colony in North America.
- 1608: Quebec City founded by Samuel de Champlain in New France (present-day Canada).
- 1609: The Netherlands and Spain agree to a Twelve Years' Truce in the Eighty Years' War.
- 1609: Pedro de Peralta, a later governor of New Mexico, establishes the settlement of Santa Fe.
- 1609: Maximilian of Bavaria establishes the Catholic League.
1610s
- 1613: The Time of Troubles in Russia ends with the establishment of the House of Romanov which rules until 1917.
- 1618: The Bohemian Revolt precipitates the Thirty Years' War which devastates Europe in the years 1618- 48.
- 1618: The Manchus start invading China. Their conquest eventually topples the Ming Dynasty.
1620s
- 1620: Emperor Ferdinand II defeats the Bohemian rebels in the Battle of White Mountain.
- 1620: The Puritan Pilgrims arrive in the Mayflower at Plymouth Rock, Cape Cod.
- 1624- 42: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu centralizes power in France.
- 1625: New Amsterdam founded by the Dutch West India Company in North America.
- 1626: St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican completed.
- 1627: Cardinal Richelieu lays siege to Protestant La Rochelle which eventually capitulates.
- 1629: Cardinal Richelieu allies with Swedish Protestant forces in the Thirty Years' War to counter Ferdinand II's expansion.
1630s
- 1632: Battle of Lützen, death of king of Sweden Gustav II Adolf.
- 1633: Galileo Galilei arrives in Rome for his trial before the Inquisition.
- 1634: Battle of Nördlingen results in Catholic victory.
- 1636: Harvard University is founded in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- 1639: Naval Battle of the Downs - Republic of the United Provinces fleet decisevely defeats a Spanish fleet in English waters.
- 1639- 51: Wars of the Three Kingdoms, civil wars throughout Scotland, Ireland, and England.
1640s
- 1640: King Charles was compelled to summon Parliament due to the revolt of the Scots.
- 1640- 68: The Portuguese Restoration War led to the end of the Iberian Union.
- 1640: Torture is outlawed in England.
- 1641: The Tokugawa Shogunate institutes Sakoku- foreigners are expelled and no one is allowed to enter or leave Japan.
- 1641: The Irish Rebellion.
- 1642: Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman achieves the first recorded European sighting of New Zealand.
- 1642- 49: Civil War in England; Charles I is beheaded by Cromwell
- 1644: The Manchu conquer China ending the Ming Dynasty. The subsequent Qing Dynasty rules until 1912.
- 1644- 1674: The Mauritanian Thirty-Year War.
- 1645: The death of Miyamoto Musashi, legendary Japanese Samurai warrior of natural causes.
- 1647- 1652: The Great Plague of Seville.
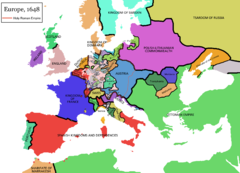
- 1648: The Peace of Westphalia ends the Thirty Years' War and the Eighty Years' War and marks the ends of Spain and the Holy Roman Empire as major European powers.
- 1648- 53: Fronde civil war in France.
- 1648- 67: The Deluge wars leave Poland in ruins.
- 1648- 69: The Ottomans capture Crete from the Venetians after the Siege of Candia.
- 1649- 1653: The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland.
1650s
- 1652: Cape Town founded by the Dutch East India Company in South Africa.
- 1652: Anglo-Dutch Wars begin.
- 1655- 61: The Northern Wars cement Sweden's rise as a Great Power.
- 1648: After his father Shah Jahan completes the Taj Mahal, his son Aurangzeb deposes him as ruler of the Mughal Empire.
1660s
- 1660: The Commonwealth of England ends and the monarchy is brought back during the English Restoration.
- 1660: Royal Society of London for the Improvement of Natural Knowledge founded.
- 1661: The reign of the Kangxi Emperor of China begins.
- 1662: Koxinga captures Taiwan from the Dutch and founds the Kingdom of Tungning which rules until 1683.
- 1662: Jacques Aymar-Vernay, who later reintroduced Dowsing into popular use in Europe, is born.
- 1663: France takes full political and military control over its colonial possessions in New France. Hooke's microscope discovers cells
- 1664: British troops capture New Amsterdam and rename it New York.
- 1665: The Great Plague of London.
- 1665: Portugal defeats the Kongo Empire.
- 1666: The Great Fire of London.
- 1667- 99: The Great Turkish War halts the Ottoman Empire's expansion into Europe.
- 1668- Peace Treaty of Lisbon between Spain and Portugal recognizes Portugal as independent country.
1670s
- 1670: The Hudson's Bay Company is founded in Canada.
- 1672- 1676: Polish-Ottoman War
- 1672: Rampjaar in the Netherlands - Combined attack by France, England and two German states on the Republic of the United Provinces
- 1672: Lynching of Johan de Witt and his brother Cornelis de Witt in the Hague - William III of Orange takes power.
- 1672- 78: Franco-Dutch War
- 1674: Maratha Empire founded in India by Shivaji.
- 1676: Russia and the Ottoman Empire commence the Russo-Turkish Wars.
1680s
- 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico until 1692.
- 1682: Peter the Great becomes joint ruler of Russia (sole tsar in 1696).
- 1682: La Salle explores the length of the Mississippi River and claims Louisiana for France.
- 1683: China conquers the Kingdom of Tungning and annexes Taiwan.

- 1683: The Battle of Vienna finishes the Ottoman Empire's hegemony in south-eastern Europe.
- 1685: Edict of Fontainebleau outlaws Protestantism in France. King Charles II dies
- 1687: Isaac Newton publishes Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica.
- 1688- 89: After the Glorious Revolution, England becomes a constitutional monarchy and the Dutch Republic goes into decline.
- 1688- 97: The Grand Alliance sought to stop French expansion during the Nine Years War.
- 1689: The Treaty of Nerchinsk established a border between Russia and China.
- 1689: The Battle of Killiecrankie is fought between Jacobite and Williamite forces in Highland Perthshire
1690s
- 1692: Salem witch trials in Massachusetts.
- 1693- 1694: Famine in France kills 2 million.
- 1696- 1697: Famine in Finland wipes out almost a third of the population.
Significant people
- Anne of Austria, Queen consort and regent of France ( 1601 - 1666)
- Gustavus Adolphus, King of Sweden ( 1594- 1632)
- Françoise-Athénaïs, marquise de Montespan, lover of Louis XIV ( 1641 - 1707)
- Françoise d'Aubigné, Marquise de Maintenon, second wife of Louis XIV ( 1635 - 1719)

- Guru Teg Bahadur, 9th Sikh Guru ( 1621 - 1675)
- Gabriel Bethlen, Hungarian prince of Transylvania ( 1580- 1629)
- Shivaji Bhonsle, Hindu king, 1st Maratha ruler, established Hindavi Swaraj ( 1630- 1680)
- Queen Christina of Sweden, high profile Catholic convert, matron of arts ( 1626 - 1689)
- Charles I of England ( 1600 - 1649)
- Charles II of England ( 1630 - 1685)
- Oliver Cromwell, Lord Protector of England, Scotland and Ireland ( 1599 - 1658)
- Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector of England, Scotland and Ireland ( 1626 - 1712)
- Elizabeth I of England ( 1533 - 1603)
- Tokugawa Ieyasu, The founder and first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, ( 1543 - 1616)
- James I of England ( 1566 - 1625)
- James II of England ( 1633 - 1701)

- Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor ( 1640 - 1705)
- Louis XIV, King of France ( 1638 - 1715)
- Mary II of England ( 1662 - 1694)
- Cardinal Mazarin, French cardinal and politician of Italian origin ( 1602 - 1661)

- André Le Nôtre, French landscape architect ( 1613 - 1700)
- Peter the Great, Russian tsar ( 1672 - 1725)
- Philip IV of Spain, Spanish king ( 1605 - 1665)
- Popé, Tewa religious leader, led the Pueblo Revolt (ca. 1630 - ca. 1688)
- Samarth Ramdas, Hindu saint ( 1608 - 1681)
- Cardinal Richelieu, French cardinal, duke, and politician ( 1585 - 1642)

- Michiel de Ruyter, Dutch admiral ( 1607 - 1676)
- Jan III Sobieski, King of Poland ( 1629 - 1696)
- Tessouat, Chief of the Algonquin
- Imre Thököly, prince of Transylvania, leader of the anti-Habsburg uprising in Hungary ( 1657 - 1705)
- Sant Tukaram, Hindu saint ( 1600 - 1650)
- Albrecht von Wallenstein, Catholic German general in the Thirty Years' War ( 1583 - 1634)
- William III of England ( 1650 - 1702), Stadtholder of the main provinces of the Republic of the United Provinces and King of England
- Johan de Witt, Grand Pensionary of the Republic of the United Provinces - 1625 - 1672
Musicians and Composers
- Johann Christoph Bach, Composer and great-uncle of the genius, ( 1642– 1703)
- Johann Sebastian Bach, German composer of genius( 1685-1750)
- Georg Friedrich Handel, German Composer ( 1685-1759)
- Jean-Baptiste Lully, Italian-born French composer ( 1632 - 1687)
- Claudio Monteverdi, Italian composer of Renaissance and Baroque music, and possibly the first opera ever ( 1567 - 1643)
- Johann Pachelbel ( 1653– 1706), German composer
- Henry Purcell, English composer ( 1659 - 1695)
- Monsieur de Sainte-Colombe, French composer and the subject of a 1991 film Tous les matins du monde (c. 1640 - 1700)
- Antonio Vivaldi Italian composer (four seasons concerti) ( 1678- 1741)
Visual artists
- Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Italian sculptor, architect ( 1598 - 1680)
- Francesco Borromini, Italian sculptor, architect ( 1599- 1667)
- Frans Hals ( 1580- 1666)
- Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, Spanish painter ( 1617 - 1682)
- José de Ribera, Lo Spagnoletto (1591 - 1652)
- Rembrandt van Rijn, Dutch painter ( 1606 - 1669)
- Peter Paul Rubens, Flemish painter, 1577 – 1640
- Jan Steen ( 1626- 1679)
- Ruisdael ( 1628- 1682)
- Jiang Tingxi, Chinese painter, calligrapher, encyclopedist, foreign delegate to Japan ( 1669 - 1732)
- Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez, Spanish painter ( 1599- 1660)
- Johannes Vermeer, Dutch Painter ( 1632 - 1675)
- Francisco Zurbarán, Spanish Painter (1598 - 1664)
Literature
- Pedro Calderón de la Barca, Spanish dramatist ( 1600 - 1681)
- Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra, Spanish author ( 1574 - 1616)
- Pierre Corneille, French dramatist ( 1606 - 1684)
- Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux, French poet and critic ( 1636 - 1711)
- Daniel Defoe, English writer, novelist ( 1659 or 1661 - 1731)
- John Donne, English metaphysical poet ( 1572 - 1631)
- John Dryden, English poet, literary critic, translator, and playwright ( 1631 - 1700)
- Jean de La Fontaine, French poet ( 1621 - 1695)
- Andreas Gryphius, German poet and dramatist ( 1616 - 1664)
- John Milton, English author and poet ( 1608 - 1674)
- Molière, French dramatist, actor, director ( 1622 - 1673)
- Miyamoto Musashi, famous Samurai warrior in Japan, author of ' The Book of Five Rings,' a treatise on strategy and martial combat, poet, painter, ( 1584 - 1645)
- Samuel Pepys, English civil servant and diarist ( 1633 - 1703)
- Francisco de Quevedo, Spanish writer ( 1580 - 1645)
- Jean Racine, French dramatist ( 1639 - 1699)
- William Shakespeare, English author and poet ( 1564 - 1616)
- Félix Lope de Vega, Spanish playwrigth and poet ( 1562 - 1635)
- John Wilmot, 2nd Earl of Rochester, English poet ( 1647 - 1680)
Educators
- Seathrún Céitinn, Irish historian (ca. 1569 - ca. 1644)
- Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh, Irish historian and genealogist (d. 1671)
- Xu Xiake, Chinese geographer ( 1587- 1641)
- Song Yingxing, Chinese encyclopedist ( 1587- 1666)
Exploration
- Samuel De Champlain, French Explorer
- Evliya Çelebi, Ottoman Explorer
- Henry Hudson, ( 1570? – 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator in the early 17th century.
- Abel Janszoon Tasman, Dutch seafarer and explorer ( 1603 - 1659)
- Luis Váez de Torres, (c.1565-1607), Portuguese or Spanish Explorer. 16th-17th century exploration of the Pacific for Spain.
Science and Philosophy
- Francis Bacon, English philosopher and politician ( 1561- 1626)
- Sir Thomas Browne, English author, philosopher and scientist ( 1605- 1682)
- Abraham Darby I, English Ironmaster, Introduced the first coke-consuming blast furnace ( 1678 – 1717)
- René Descartes, French philosopher and mathematician ( 1596 - 1650)
- Pierre de Fermat, French lawyer and mathematician 1601 – 1665
- Galileo Galilei, Italian natural philosopher ( 1564 - 1642)
- William Harvey, medical doctor ( 1578 – 1657)
- Thomas Hobbes, English philosopher and mathematician ( 1588 - 1679)
- Christiaan Huygens, Dutch mathematician, physicist and astronomer ( 1629 - 1695)
- Johannes Kepler, German astronomer ( 1571 - 1630)
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, the first person to use a microscope to view bacteria ( 1632 - 1723)
- Gottfried Leibniz, German philosopher and mathematician ( 1646 - 1716)
- John Locke, English philosopher ( 1632 - 1704)
- Isaac Newton, English physicist and mathematician ( 1642 - 1727)
- Blaise Pascal, French theologian, mathematician and physicist ( 1623 - 1662]]
- Baruch Spinoza, Dutch philosopher ( 1632 - 1677)
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
List of 17th century inventions
Major changes in philosophy and science take place, often characterized as the Scientific revolution.
- Banknotes reintroduced in Europe.

- Ice cream
- Tea and coffee become popular in Europe.
- Central Banking in France and modern Finance by Scottish economist John Law
- 1604: Supernova SN 1604 is observed in the Milky Way
- 1605: Johannes Kepler starts investigating elliptical orbits of planets
- 1608: Hans Lippershey constructs a refracting telescope, the first for which sufficient evidence exists
- 1609: Johann Carolas of Germany publishes the 'Relation', the first newspaper
- 1610: The Orion Nebula is identified by Nicolas de Peiresc of France
- 1610: Galileo Galilei and Simon Marius observe Jupiter's Galilean moons
- 1611: King James Bible or 'Authorized Version' first published
- c. 1612: The first flintlock musket likely created for Louis XIII of France by gunsmith Marin de Bourgeoys
- 1614: John Napier introduces the logarithm to simplify calculations
- 1620: Cornelius Drebbei, funded by James I of England, builds the first 'submarine' made of wood and greased leather
- 1623: The first English dictionary, 'English Dictionarie' is published by Henry Cockeram, listing difficult words with definitions
- 1628: William Harvey publishes and elucidates his earlier discovery of the circulatory system
- 1637: Dutch Bible published
- 1637: Teatro San Cassiano, the first public opera house, opened in Venice
- 1637: Pierre de Fermat formulates his so-called Last Theorem, unsolved until 1995
- 1637: Although Chinese naval mines were earlier described in the 14th century Huolongjing, the Tian Gong Kai Wu book of Ming Dynasty scholar Song Yingxing describes naval mines wrapped in a lacquer bag and ignited by an ambusher pulling a rip cord on the nearby shore that triggers a steel-wheel flint mechanism.
- 1642: Blaise Pascal builds an early mechanical calculator for addition and subtraction
- 1642: Mezzotint engraving introduces grey tones to printed images
- 1643: Evangelista Torricelli of Italy invents the mercury barometer
- 1645: Giacomo Torelli of Venice, Italy invents the first rotating stage
- 1651: Giovanni Riccioli renames the Lunar mare
- 1656: Christiaan Huygens describes the true shape of the rings of Saturn
- 1657: Christiaan Huygens develops the first functional pendulum clock based on the learnings of Galileo Galilei
- 1659: Christiaan Huygens first to observe surface details of Mars
- 1663: The first reflecting telescope is built by James Gregory based on suggestions of Italian astronomer Niccolo Zucchi
- c. 1670: Monk Dom Perignon discovers Champagne in France
- 1676: Antoni van Leeuwenhoek discovers Bacteria
- 1676: First measurement of the speed of light
- 1679: Binary system developed by Gottfried Leibnitz
- 1684: Calculus independently developed by both Gottfried Leibnitz and Sir Issac Newton and used to formulate classical mechanics
Decades and years
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||