Qing Dynasty
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General history
- Not to be confused with Qin Dynasty, the first dynasty of Imperial China.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of China | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | |||||||
| 3 Sovereigns and 5 Emperors | |||||||
| Xia Dynasty 2100–1600 BCE | |||||||
| Shang Dynasty 1600–1046 BCE | |||||||
| Zhou Dynasty 1122–256 BCE | |||||||
| Western Zhou | |||||||
| Eastern Zhou | |||||||
| Spring and Autumn Period | |||||||
| Warring States Period | |||||||
| IMPERIAL | |||||||
| Qin Dynasty 221 BCE–206 BCE | |||||||
| Han Dynasty 206 BCE–220 CE | |||||||
| Western Han | |||||||
| Xin Dynasty | |||||||
| Eastern Han | |||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | |||||||
| Wei, Shu & Wu | |||||||
| Jin Dynasty 265–420 | |||||||
| Western Jin | |||||||
| Eastern Jin | 16 Kingdoms 304–439 |
||||||
| Southern & Northern Dynasties 420–589 | |||||||
| Sui Dynasty 581–618 | |||||||
| Tang Dynasty 618–907 | |||||||
| ( Second Zhou 690–705 ) | |||||||
| 5 Dynasties & 10 Kingdoms 907–960 |
Liao Dynasty 907–1125 |
||||||
| Song Dynasty 960–1279 |
|||||||
| Northern Song | W. Xia Dyn. | ||||||
| Southern Song | Jin Dyn. | ||||||
| Yuan Dynasty 1271–1368 | |||||||
| Ming Dynasty 1368–1644 | |||||||
| Qing Dynasty 1644–1911 | |||||||
| MODERN | |||||||
| Republic of China 1912–1949 | |||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present 1949-1976 |
Republic of China |
||||||
| Dynasties in Chinese History Economic History of China Historiography of China History of Chinese Art History of Education in China History of Science and Technology in China Legal History of China Linguistic History of China Military History of China Naval History of China Timeline of Chinese History |
|||||||
The Qing Dynasty (Chinese: 清朝; pinyin: Qīng cháo; Wade-Giles: Ch'ing ch'ao; Manchu: ![]() Daicing gurun; Mongolian: Манж Чин Улс), also known as the Manchu Dynasty, was the last ruling dynasty of China from 1644 to 1912.
Daicing gurun; Mongolian: Манж Чин Улс), also known as the Manchu Dynasty, was the last ruling dynasty of China from 1644 to 1912.
The dynasty was founded by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in what is today northeast China ( Manchuria). Starting in 1644 it expanded into China proper and its surrounding territories, establishing the Empire of the Great Qing ( simplified Chinese: 大清国; traditional Chinese: 大清國; pinyin: dàqīngguó). The Qing Dynasty was the last Imperial dynasty of China.
Originally declared as the Later Jin Dynasty (後金 Hòu Jīn) / Amaga Aisin Gurun (![]() ), in 1616, it changed its name to "Qing", meaning "clear" or "pellucid", in 1636 and captured Beijing in 1644. By 1646 it had come into power over most of present-day China, although complete pacification of China would not be accomplished until 1683.
), in 1616, it changed its name to "Qing", meaning "clear" or "pellucid", in 1636 and captured Beijing in 1644. By 1646 it had come into power over most of present-day China, although complete pacification of China would not be accomplished until 1683.
During its reign, the Qing Dynasty became highly integrated with Chinese culture. However, its military power weakened during the 1800s, and faced with international pressure, massive rebellions and defeats in wars, the Qing Dynasty declined after the mid-19th century. The Qing Dynasty was overthrown following the Xinhai Revolution, when the Empress Dowager Longyu abdicated on behalf of the last emperor, Puyi, on February 12, 1912.
Formation of the Manchu State
The Dynasty was founded not by the Han Chinese who form the majority of the Chinese population, but the Manchus, who are today an ethnic minority within China. The Manchus are descended from Jurchens (Zh: 女真, Manchu: ![]() Jušen), a Tungusic people who lived around the region now comprising the Russian province of Primorsky Krai and the Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang and Jilin. What was to become the Manchu state was founded by Nurhaci (Zh: 努尔哈赤), the chieftain of a minor Jurchen tribe in Jianzhou (Zh: 建州), in the early 17th century. Originally a vassal of the Ming emperors, Nurhaci in 1582 embarked on an inter-tribal feud that escalated into a campaign to unify the Jianzhou Jurchen tribes. By 1616 he had sufficiently consolidated Jianzhou region to proclaim himself Khan of "Great Jin" in reference to the previous Jurchen dynasty. Historians refer to this pre-Qing entity as "Later Jin" to distinguish it from the first Jin Dynasty. Two years later Nurhaci openly renounced the sovereignty of Ming overlordship in order to complete the unification of those Jurchen tribes still allied with the Ming emperor. After a series of successful battles he relocated his capital from Hetu Ala to successively bigger captured Ming cities in the province of Liaodong (Zh: 辽东), first Liaoyang (Zh: 辽阳; Ma: dergi hecen) in 1621 and again in 1625 to Shenyang (Zh: 沈阳; later renamed Shengjing; Zh: 盛京; Ma:
Jušen), a Tungusic people who lived around the region now comprising the Russian province of Primorsky Krai and the Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang and Jilin. What was to become the Manchu state was founded by Nurhaci (Zh: 努尔哈赤), the chieftain of a minor Jurchen tribe in Jianzhou (Zh: 建州), in the early 17th century. Originally a vassal of the Ming emperors, Nurhaci in 1582 embarked on an inter-tribal feud that escalated into a campaign to unify the Jianzhou Jurchen tribes. By 1616 he had sufficiently consolidated Jianzhou region to proclaim himself Khan of "Great Jin" in reference to the previous Jurchen dynasty. Historians refer to this pre-Qing entity as "Later Jin" to distinguish it from the first Jin Dynasty. Two years later Nurhaci openly renounced the sovereignty of Ming overlordship in order to complete the unification of those Jurchen tribes still allied with the Ming emperor. After a series of successful battles he relocated his capital from Hetu Ala to successively bigger captured Ming cities in the province of Liaodong (Zh: 辽东), first Liaoyang (Zh: 辽阳; Ma: dergi hecen) in 1621 and again in 1625 to Shenyang (Zh: 沈阳; later renamed Shengjing; Zh: 盛京; Ma: ![]() Mukden).
Mukden).
Relocating his court from Jianzhou to Liaodong provided Nurhaci a bigger power base in terms of human and material resources; geographically it also brought him in close contact with the Mongol domains on the plains of Mongolia. Although by this time the once-united Mongol nation under Genghis Khan had long fragmented into individual and at times hostile tribes, these disunited tribes still presented a serious security threat to the Ming borders. Nurhaci's policy towards the Mongols was to seek their friendship and cooperation, thus securing the Jurchens' western front from a potential enemy. Furthermore, the Mongols proved a useful ally in the war, lending the Jurchens their traditional expertise as cavalry archers. To cement this new alliance Nurhaci initiated a policy of inter-marriages between Jurchen and those Mongolian nobility compliant to Jurchen leadership, while those who resisted were met with military action. This is a typical example of Nurhaci's many initiatives that eventually became official Qing government policy. Some of Nurhaci's other important contributions include ordering the creation of a written Manchu language based on Mongolian script, and the creation of the civil and military administrative system that eventually evolved into the Manchu Banners the defining element of Manchu identity, thus laying foundation for transforming the loosely knitted Jurchen tribes into a nation.
Nurhaci's unbroken series of military successes came to an end in January 1626 when he was dealt his first major military defeat by general Yuan Chonghuan while laying siege to the Ming city of Ningyuan. He died a few months later and was succeeded by his eighth son Hung Taiji who emerged after a short political struggle amongst other potential contenders as the new Khan. Although he was an experienced general and the commander of two Banners at the time of his succession, Hung Taiji's reign did not start well on the military front. The Jurchens suffered yet another defeat in 1627 at the hands of Yuan Chonghuan. As before, this defeat was the result of the superior firepower of the Ming forces' newly acquired Portuguese cannons. To redress the technological and numerical disparity Hung Taiji in 1634 created his own artillery corps (Zh: 重军, Ma: ujen chooha) from amongst his existing Han troops who casted their own cannons from European design with the help of captured Chinese artisans. In 1635 the Manchu's Mongolian allies were fully incorporated into a separate Banner hierarchy under direct Manchu command. This was followed by the creation of the first (two) Han Banners in 1637 (which eventually increased to eight in 1642). Together these military reforms enabled Hung Taiji to resoundingly defeat Ming forces in a series of battles from 1640 to 1642 for the territories of Songshan (Zh: 松山)) and Jingzhou (Zh: 锦州)). This final victory resulted in the surrender of many of the Mings' most battle hardened troops and the complete permanent withdrawal of remaining Ming forces from lands north of the Great Wall. On a geopolitical level, the victory also gave the Manchus undisputed overlordship over the Mings' Korean vassal the Joseon Dynasty.
On the civil front, Hung Taiji, on the advice of surrendered Ming officials, set up a rudimentary bureaucratic system based on the Ming model of government. Hung Taiji's bureaucracy was staffed with an unprecedented number of Han Chinese, many of them newly surrendered Ming officials. However, the Jurchens' continued dominance in government was ensured by an ethnic quota for top bureaucratic appointments. Hung Taiji's reign also saw a fundamental change of policy towards his Han Chinese subjects. Whereas under Nurhaci all captured Han Chinese were seen as a potential fifth column for the Ming Dynasty and treated as chattel— including those who eventually held important government posts– Hung Taiji in contrast incorporated them into the Jurchen "nation" as full if not first class citizens, who were also obligated to provide military service. This change of policy not only increased Hung Taiji's power base and reduced his military dependence on those banners not under his personal control, it also greatly encouraged other Han Chinese subjects of the Ming Dynasty to surrender and accept Jurchen rule when they were defeated militarily. Through these and other measures Hung Taiji was able to centralize power unto the office of the Khan, which in the long run prevented the Jurchen federation from fragmenting after his death.
One of the defining events of Hung Taiji's reign was the official adoption of the name Manchu (Zh: 满族; Ma: ![]() ) for all Jurchen people in November 1635. And when the imperial seal of the Yuan emperors was presented to Hung Taiji by Ejei Khan the son of Lingdan Khan, the last grand-Khan of the Mongols, Hung Taiji in 1636 renamed the state from "Later Jin" to "Great Qing" and elevated his position from Khan to Emperor, suggesting imperial ambitions beyond unifying Manchu territories. Some sources suggested that the name "Qing" was chosen in reaction to that of the Ming Dynasty (明) which consists of the Chinese characters for sun (日) and moon (月), which are associated with the fire element. The character Qing (清) is composed of the water (水) radical and the character for blue-green (青), which are both associated with the water element. Other suggested that the name change went a long way to rehabilitate the Manchu state in the eyes of the Ming-era Han Chinese, who, being heavily influenced by a Neo-Confucian education system, had regarded the former Jurchen Jin dynasty as foreign invaders.
) for all Jurchen people in November 1635. And when the imperial seal of the Yuan emperors was presented to Hung Taiji by Ejei Khan the son of Lingdan Khan, the last grand-Khan of the Mongols, Hung Taiji in 1636 renamed the state from "Later Jin" to "Great Qing" and elevated his position from Khan to Emperor, suggesting imperial ambitions beyond unifying Manchu territories. Some sources suggested that the name "Qing" was chosen in reaction to that of the Ming Dynasty (明) which consists of the Chinese characters for sun (日) and moon (月), which are associated with the fire element. The character Qing (清) is composed of the water (水) radical and the character for blue-green (青), which are both associated with the water element. Other suggested that the name change went a long way to rehabilitate the Manchu state in the eyes of the Ming-era Han Chinese, who, being heavily influenced by a Neo-Confucian education system, had regarded the former Jurchen Jin dynasty as foreign invaders.
Claiming the Mandate of Heaven

Hung Taiji died suddenly in September 1643 without a designated heir. Because Jurchens had traditionally "elected" their leader through a council of nobles, the Qing state did not have in place a clear succession system until the reign of Emperor Kangxi. The leading contenders for power at this time were Hung Taiji’s eldest son Hooge and Hung Taiji’s agnate half brother Dorgon. In the ensuing political impasse between two bitter political rivals a compromise candidate in the person of Hung Taiji’s five-year-old son Fulin was installed as Emperor Shunzhi, with Dorgon as regent and de facto leader of the Manchu nation. Fortunately the Manchus' nemesis the Ming Dynasty was fighting for its own survival against a long peasant rebellion and was unable to capitalise on the Qing court’s political uncertainty over the succession dispute and installation of a minor as Emperor. The Ming Dynasty's internal crisis came to a head in April 1644, when the capital at modern day Beijing was sacked by a coalition of rebel forces led by Li Zicheng, a minor Ming official turned leader of the peasant revolt. The last Ming, Emperor Chongzhen committed suicide when the city fell, marking the official end of the dynasty.
After easily taking Beijing, Li Zicheng led a coalition of rebel forces numbering 200,000 to confront Wu Sangui, the general commanding the Ming garrison at Shanhaiguan (Zh:山海關). Shanhaiguan is a pivotal pass of the Great Wall of China located fifty miles northeast of Beijing, and for years its defenses were what kept the Manchus from directly raiding the Ming capital. Wu, caught between a rebel army twice his size and a foreign enemy he had fought for years, decided to cast his lot with the Manchus with whom he was familiar, and made an alliance with Dorgon to fight the rebels. Some sources suggested that Wu's actions were influenced by news of mistreatment of his family and his concubine Chen Yuanyuan at the hands of the rebels when the capital fell. Regardless of the actual reasons for his decision, this awkward and some would say cynical alliance between Wu and his former sworn enemy was ironically made in the name of avenging the death of Emperor Chongzhen. Together, the two former enemies met and defeated Li Zicheng's rebel forces in battle on May 27, 1644. After routing Li's forces, the Manchus captured Beijing on June 6, where Emperor Shunzhi was installed as the "Son of Heaven" on October 30. The Manchus who had positioned themselves as political heir to the Ming Emperor by defeating Li Zicheng, completed the symbolic act of transition by holding a formal funeral for Emperor Chongzhen. However the process of conquest took another seventeen years of battling Ming loyalists, pretenders and rebels. The last Ming pretender, Prince Gui, sought refuge with the King of Burma, a vassal of the Ming Dynasty, but was turned over to a Qing expeditionary army commanded by Wu, who had him brought back to Yunnan province and executed in early 1662.

The first seven years of Shunzhi’s reign was dominated by the regent prince Dorgon, who, because of his own political insecurity within the Manchu power structure, followed Hung Taiji’s example of centralizing power unto himself in the name of the Emperor at the expense of other contending Manchu princes, many of whom eventually were demoted or imprisoned under one pretext or another. Although the period of his regency was relatively short, Dorgon cast a long shadow over the Qing Dynasty. Firstly the Manchus were able to enter "China Proper" only because of Dorgon’s timely decision to act on Wu Sangui’s appeal for military assistance. After capturing Beijing instead of sacking the city as the rebels had done before them, Dorgon insisted over other Manchu princes on making it Qing’s capital and largely reappointed Ming officials back to their posts. Setting the Qing capital in Beijing may seem a straightforward move in hindsight, but it was then an act of innovation because historically no major Chinese dynasty had ever "inherited" its immediate predecessor’s capital. Keeping the Ming capital and bureaucracy intact helped quickly stabilize the country and greatly sped up the Manchu process of conquest. However, not all of Dorgon’s policies were equally popular nor easily implemented.
One of Dorgon's most controversial decisions was his 1646 imperial edict (the " Queue Order") which forced all Han Chinese men, on pain of death, to adopt the Manchu style of dress, including shaving the front of their heads and combing the remaining hair into a queue. To the Manchus this policy might both be a symbolic act of submission and in practical terms an aid in identification of friend from foe, however for the Han Chinese it totally went against their traditional Confucian values. Unsurprisingly it was deeply unpopular and, together with other policies unfavourable towards the Han Chinese, might account for the increasingly steep resistance met by Qing forces after 1646. Hundreds of thousands of people were killed before all of China was brought into compliance.
Dorgon died suddenly while on a hunting expedition in 1651 marking the official start of Emperor Shunzhi’s personal rule. However, because the Emperor was only twelve years old at that time, most decisions were made on his behalf by his mother, the Empress Dowager Xiao-Zhuang, who turned out to be a skilled political operator. Although Dorgon’s “support” was essential to Shunzhi’s ascent and rule in the early years of the his reign, Dorgon had through the years centralised so much power unto his office as imperial regent to become a direct threat to the throne, so much so that upon his death Dorgon was extraordinarily bestowed the posthumous title of Emperor Yi (Zh: 義皇帝), the only instance in Qing history of a Manchu " prince of the blood" (Zh: 亲王) was so honoured. However two months into Shunzhi’s personal rule Dorgon was not only stripped of his titles, but his corpse was disinterred and mutilated to atone for multiple "crimes"—one of which was persecuting to death Shunzhi’s agnate eldest brother Hooge. More importantly Dorgon’s symbolic fall from grace also signalled a political purge of his family and associates in court thus reverting power back to the person of the Emperor. However, from a promising start, Shunzhi’s reign was cut short by his early death in 1661 at the age of twenty-four from smallpox. He was succeeded by his third son Xuan-Ye, who became Emperor Kangxi.
Kangxi emperor and consolidation
At sixty one years, Kangxi had the longest reign of any Chinese Emperor. But more importantly, apart from its length, Kangxi’s reign is also celebrated as the beginning of an era called “Kang-Qian Golden Age” (Zh: 康乾盛世) during which Qing Dynasty reached the zenith of its social, economic and military power. Kangxi’s long reign started when he was eight years old upon the untimely demise of his father. In order to prevent a repeat of Dorgon's dictatorial monopolizing of imperial powers during the period of regency, Emperor Shunzhi on his deathbed hastily appointed four senior cabinet ministers to govern on behalf of his young son. The four ministers— Sonin, Ebilun, Suksaha, and Oboi—were chosen for their long service to the crown, but also to counteract each others' influences. Most importantly, the four were not closely related to the imperial family and laid no claim to the throne. However as time passed, through chance and machination, Oboi—the most junior of the four ministers—was able to achieve political dominance to such an extent as to become a potential threat to the crown. Even though Oboi's loyalty was never an issue, his personal arrogance and political conservatism led him to come into ever escalating conflict with the young Emperor. In 1669 Kangxi, through trickery, disarmed and imprisoned Oboi—a not insignificant victory for the fifteen-year-old Emperor, as Oboi was not only a wily old politician but also an experienced military commander.
The Manchus found controlling the " Mandate of Heaven" a daunting task. The vastness of China's territory meant that there were only enough banner troops to garrison key cities forming the backbone of a defence network that relied heavily on surrendered Ming soldiers. In addition, three surrendered Ming generals were singled out for their contributions to the establishment of the Qing dynasty, ennobled as feudal princes (藩王), and given governorships over vast territories in Southern China. The chief of these was Wu Sangui (吳三桂), who was given the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou, while generals Shang Kexi (尚可喜) and Geng Zhongming (耿仲明) were given the Guangdong and Fujian provinces, respectively.
As the years went by, the three feudal lords and their territories inevitably became increasingly autonomous. Finally, in 1673, Shang Kexi petitioned Kangxi Emperor, stating his desire to retire to his hometown in Liaodong (遼東) province and nominating his son as his successor. The young emperor granted his retirement, but denied the heredity of his fief. In reaction, the two other generals decided to petition for their own retirements to test Kangxi's resolve, thinking that he would not risk offending them. The move backfired as the young emperor called their bluff by accepting their requests and ordering all three fiefdoms to be reverted back to the crown.
Faced with the stripping of their powers, Wu Sangui felt he had no choice but to rise up in revolt. He was joined by Geng Zhongming and by Shang Kexi's son Shang Zhixin (尚之信). The ensuing rebellion lasted for eight years. At the peak of the rebels' fortunes, they managed to extend their control as far north as the Yangtze River (長江). Ultimately, though, the Qing government was able to put down the rebellion and exert control over all of southern China. The rebellion would be known in Chinese history as the Revolt of the Three Feudatories.
To consolidate the empire, Kangxi Emperor personally led China on a series of military campaigns against Tibet, the Dzungars, and later Russia. He arranged the marriage of his daughter to the Mongol Khan Gordhun to avoid a military conflict. Gordhun's military campaign against the Qing failed, further strengthening the Empire. Taiwan was also conquered by Qing Empire forces in 1683 from Zheng Keshuang, grandson of Koxinga. Koxinga had conquered Taiwan from the Dutch colonists to use it as a base against the Qing Dynasty. By the end of the 17th century, China was at its greatest height of power since the early Ming Dynasty.
Kangxi Emperor also handled many Jesuit missionaries that came to China. A series of missionaries, including Matteo Ricci, Martino Martini, Johann Adam Schall von Bell, Ferdinand Verbiest and Antoine Thomas, also held significant positions as mathematicians, astronomers and advisors to the Emperor. Together they played a significant role in correcting the Chinese calendar and advancing knowledge of astronomy, science and the geography of the Chinese empire.
Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors
The reigns of the Yongzheng Emperor (r. 1723–1735) and his son the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–1796) marked the height of Qing's power. During this period, the Qing Dynasty ruled over 13 million square kilometres of territory.
After the Kangxi Emperor's death in the winter of 1722, his fourth son Prince Yong (雍親王) succeeded him as the Yongzheng Emperor. Yongzheng remained a controversial character because of rumours about him usurping the throne, and in the late Kangxi years, he was involved in great political struggles with his brothers. Yongzheng was a hardworking administrator who ruled with an iron hand. His first big step towards a stronger regime came when he brought the State Examination System back to its original standards. In 1724, he cracked down on illegal exchange rates of coins, which was being manipulated by officials to fit their financial needs. Those who were found in violation of new laws on finances were removed from office, or in extreme cases, executed.
Yongzheng showed a great amount of trust in Han officials, and appointed many of his proteges to prestigious positions. Nian Gengyao was appointed to lead a military campaign in place of his brother Yinti in Qinghai. Nian's arrogant actions, however, led to his downfall in 1726. Yongzheng's reign saw consolidation of imperial power at its height in Chinese history. More territory was incorporated in the Northwest. A toughened stance was directed towards corrupt officials, and Yongzheng led the creation of a Grand Council, which grew to become the de facto Cabinet for the rest of the dynasty.
The Yongzheng Emperor died in 1735. This was followed by the succession of his son Prince Bao (寶親王) as the Qianlong Emperor. Qianlong was known as an able general. Succeeding the throne at the age of 24, Qianlong personally led the military in campaigns near Xinjiang and Mongolia. Revolts and uprisings in Sichuan and parts of southern China were successfully put down.
Around forty years into Qianlong's reign, the Qing government saw a return of rampant corruption. The official Heshen was arguably one of the most corrupt in the entire Qing Dynasty. He was eventually forced into committing suicide by Qianlong's son, the Jiaqing Emperor (r. 1796–1820).
In 1796 open rebellion by the White Lotus Society against the Qing government broke out. The White Lotus Rebellion continued for eight years, until 1804, and shattered the myth of the military invincibility of the Manchus.
Rebellion, unrest and external pressure
A common view of 19th century China is that it was an era in which Qing control weakened and prosperity diminished. Indeed, China suffered massive social strife, economic stagnation, and explosive population growth which placed an increasing strain on the food supply. Historians offer various explanations for these events, but the basic idea is that Qing power was, over the course of the century, faced with internal problems and natural disasters which were simply too much for the antiquated Chinese government, bureaucracy, and economy to deal with.
The Taiping Rebellion in the mid-19th century was the first major instance of anti-Manchu sentiment threatening the stability of the Qing dynasty, a phenomenon that would only increase in the following years. However, the horrific number of casualties of this rebellion—as many as 30 million people—and the complete devastation of a huge area in the south of the country have to a large extent been overshadowed by another significant conflict. Although not nearly as bloody, the outside world and its ideas and technologies had a tremendous and ultimately revolutionary impact on an increasingly weak and uncertain Qing state. The Qing government would go on to face more revolts, this time by Muslims who would fight the Panthay Rebellion (1856–1873) and the Dungan revolt (1862–1877).
One of the major issues affecting nineteenth-century China was the question of how to deal with other countries. Prior to the nineteenth-century, the Chinese empire was the hegemonic power in Asia. Under its imperial theory, the Chinese emperor had the rights to rule " all under heaven". Depending on the period and dynasty, it either ruled territories directly or neighbors fell under its hierarchical tributary system. Historians often refer to the underlying concept of the Chinese empire as "an empire with no boundary". However, the 18th century saw the European empires gradually expand across the world, as European states developed stronger economies built on maritime trade. European colonies had been established in nearby India and on the islands that are now part of Indonesia, whilst the Russian Empire had annexed the areas north of China. In 1793, Great Britain attempted to forge an alliance with China, sending the Macartney Embassy to Hong Kong with gifts for the Emperor, including examples of the latest European technologies and art. When the British delegation received a letter from Beijing explaining that China was unimpressed with European achievements, and that George III was welcome to pay homage to the Chinese court, the deeply offended British government aborted all further attempts to reconcile relations with the Qing regime.
When the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815, world trade rapidly increased, and as China's vast population offered limitless markets for European goods, trade between Chinese and European merchants expanded during the early years of the 19th century. This increased trade, though, led to increasing hostility between European governments and the Qing regime.
In 1793, the Qianlong Emperor stated to the British Ambassador Lord Macartney that China had no use for European manufactured products. Consequently, leading Chinese merchants only accepted bar silver as payment for their goods. The huge demand in Europe for Chinese goods such as silk, tea, and ceramics could only be met if European companies funnelled their limited supplies of silver into China. By the late 1830s, the governments of Great Britain and France were deeply concerned about their stockpiles of precious metals and sought alternate trading schemes with China—the foremost of which was addicting China to opium. When the Qing regime tried to ban the Opium Trade in 1838, Great Britain declared war on China.
The First Opium War revealed the outdated state of the Chinese military. The Qing navy, composed entirely of wooden sailing junks, was severely outclassed by the modern tactics and firepower of the Royal Navy at its apex. British soldiers, using modern rifles and artillery, easily outmanoeuvred and outgunned Qing forces in ground battles. The Qing surrender in 1842 marked a decisive, humiliating blow to China. The Treaty of Nanking, which demanded reparation payments, allowed unrestricted European access to Chinese ports, and ceded the island of Hong Kong to Great Britain. It revealed many inadequacies in the Qing government and provoked widespread rebellions against the already hugely unpopular regime.
The Western powers, largely unsatisfied with the Treaty of Nanking, only gave grudging support to the Qing government during the Taiping and Nien Rebellions. China's income fell sharply during the wars as vast areas of farmland were destroyed, millions of lives lost, and countless armies raised and equipped to fight the rebels. In 1854, Great Britain tried to re-negotiate the Treaty of Nanking, inserting clauses allowing British commercial access to Chinese rivers and the creation of a permanent British embassy at Peking. This last clause outraged the Qing regime, who refused to sign, provoking another war with Britain. The Second Opium War ended in another crushing Chinese defeat, whilst the Treaty of Tianjin contained clauses deeply insulting to the Chinese, such as a demand that all official Chinese documents be written in English and a proviso granting British warships unlimited access to all navigable Chinese rivers.
Rule of Empress Dowager Cixi
In the late 19th century, a new leader emerged. The Empress Dowager Cixi, concubine to the Emperor Xianfeng (r. 1850–1861), the mother of child emperor Tongzhi, and Aunt of Guangxu successfully controlled the Qing government and was the de facto leader of China for 47 years. She staged a coup d'état to oust the regency led by Sushun appointed by the late Emperor. She was known for "ruling from behind the curtain" (垂簾聽政).
By the 1860s, the Qing dynasty had put down the rebellions with the help of militia organized by the gentry. The Qing government then proceeded to deal with problem of modernization, which it attempted with the Self-Strengthening Movement. Several modernized armies were formed, including the much renowned Beiyang Army; however, the fleets of "Beiyang" were annihilated in the Sino-Japanese War (1894-1895), which produced calls for greater and more extensive reform. After the start of the 20th century, the Qing Dynasty was in a dilemma. It could proceed with reform and thereby alienate the conservative gentry or it could stall reform and thereby alienate the progressive reformers. The Qing Dynasty tried to follow a middle path, and thus managed to alienate everyone.
Ten years into the reign of Guangxu (r. 1875–1908), western pressure on China was so great that she forcefully gave up all sorts of power. In 1898 Guangxu attempted the Hundred Days' Reform (百日維新/戊戌變法), in which new laws were put in place and some old rules were abolished. Newer, more progressive-minded thinkers like Kang Youwei were trusted and recognized conservative-minded people like Li Hongzhang were removed from high positions. But the ideals were stifled by Cixi and Guangxu was jailed in his own palace. Cixi concentrated on centralizing her own power base. At the occasion of her sixtieth Birthday, she spent over 30 million taels of silver for the decorations & events, funds that were originally to improve the weaponry of the Beiyang Navy.
In 1901, following the murder of the German Ambassador, the Eight-Nation Alliance (八國聯軍) entered China as a united military force for the second time. Cixi reacted by declaring war on all eight nations, only to lose Beijing under their control within a short period of time. Along with the Guangxu Emperor, she fled to Xi'an. As a military compensation, the Alliance listed scores of demands on the Qing Government, including an initial hit list which had Cixi as No. 1. Li Hongzhang was sent to negotiate and the Alliance backed down from several of the demands.
Qing government and society
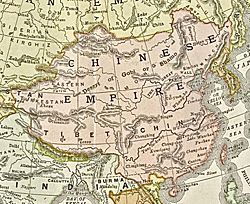
Administrative Divisions
- Outer Mongolia - 4 aimags
- Inner Mongolia - 6 leagues
- Dariganga - special region designated as Emperor's pasture
- Köbsgöl
- Tannu Urianhai
- Köke Nuur league
- Alshaa khoshuu-league (League-level khoshuu)
- Ejine khoshuu-league
- Kobdo league
- Tianshanbei
- Tianshannan
- China proper provinces
- Zhili
- Henan
- Shandong
- Shanxi
- Shaanxi
- Gansu
- Hubei
- Hunan
- Guangdong
- Guangxi
- Sichuan
- Yunnan
- Guizhou
- Jiangsu
- Jiangxi
- Zhejiang
- Fujian (incl. Taiwan until 1885)
- Anhui
Politics
The Qing were astute in stabilizing the government. The most important administrative body of the Qing dynasty was the Trung Council which was a body composed of the emperor and high officials. The Qing dynasty was characterized by a system of dual appointments by which each position in the central government had a Manchu and a Han assigned to it. During the Qianlong Emperor's reign, for example, members of his family were distinguished by garments with a small circular emblem on the back, whereas a Han wears clothing with a square emblem; this meant effectively that any guard in the court could immediately distinguish family members from the back view alone.
With respect to Mongolia, Tibet, and eastern Turkestan, like other dynasties before it the Qing maintained imperial control, with the emperor acting as Mongol khan, patron of Tibetan Buddhism and protector of Muslims. However, Qing policy changed with the establishment of Xinjiang province in 1884. In response to British and Russian military action in Xinjiang and Tibet, the Qing sent Army units which performed remarkably well against British units.
The abdication of the Qing emperor inevitably led to controversy about the status of territories in Tibet and Mongolia. It was and remains the position of Mongols and Tibetans that, because they owed allegiance to the Qing monarch, with the abdication of the Qing they owed no allegiance to the new Chinese state. This position was rejected by the Republic of China and subsequent People's Republic of China, which claim that these areas were integral parts of Chinese dynasties even before the Qing, and that Han, Manchus, Mongols, or other ethnic groups all established Sinocentric-based dynasties, thus claiming legitimacy and history as part of imperial China over two thousand years. The Western powers accepted the latter theory for their own political reasons, partly in order to prevent a scramble for China.
Bureaucracy
The Qing Dynasty inherited many important institutions from the preceding Ming dynasty. The formal structure of the Qing government centered around the Emperor as the absolute ruler, who presided over six ministries (or boards), each headed by two presidents (Ch: Shàngshū, 尚書; Ma: ![]() Aliha amban) and assisted by four vice presidents (Ch: Shìláng, 侍郎; Ma:
Aliha amban) and assisted by four vice presidents (Ch: Shìláng, 侍郎; Ma: ![]() Ashan i amban). In contrast to the Ming system, however, Qing ethnic policy dictated that appointments were split between Manchu noblemen and Han officials who had passed the highest levels of the state examinations. The Grand Secretariat (Ch: Nèigé 內閣; Ma:
Ashan i amban). In contrast to the Ming system, however, Qing ethnic policy dictated that appointments were split between Manchu noblemen and Han officials who had passed the highest levels of the state examinations. The Grand Secretariat (Ch: Nèigé 內閣; Ma: ![]() Dorgi yamun), which had been an important policy making body during Ming, lost its importance during Qing and evolved into an imperial chancery. The institutions which had been inherited from the Ming dynasty formed the core of the Qing "outer court", which handled routine matters and was located in the southern part of the Forbidden City.
Dorgi yamun), which had been an important policy making body during Ming, lost its importance during Qing and evolved into an imperial chancery. The institutions which had been inherited from the Ming dynasty formed the core of the Qing "outer court", which handled routine matters and was located in the southern part of the Forbidden City.
In order not to let the routine administration take over the running of the empire, the Manchu Qing emperors made sure that all important matters were decided in the "Inner Court", which was dominated by the imperial family and Manchu nobility and which was located in the northern part of the Forbidden City. A central part of the inner court was the Grand Council, a body initially in charge of military and intelligence matters, but which later assumed the role of supervising all government departments. Ministers posted to the Grand Council served as the emperor's privy council and they were collectively known as privy councillors.
The six ministries and their respective areas of responsibilities were as follows:
- The personnel administration of all civil officials - including evaluation, promotion, and dismissal. It was also in charge of the 'honours list'.
- The literal translation of the Chinese word 'hù'(户)is 'household'. For much of the Qing Dynasty's history, the government's main source of revenue came from taxation on landownership supplemented by official monopolies on essential household items such as salt and tea. Thus, in the predominantly agrarian Qing dynasty, the 'household' was the basis of imperial finance. The department was charged with revenue collection and the financial management of the government.
- This was responsible for all matters concerning protocol at court, which included not just the periodic worshiping of ancestors and various gods by the Emperor—in his capacity as the "Son of Heaven" (Tiānzǐ, 天子), to ensure the smooth running of the empire—but also looking after the welfare of visiting ambassadors from tributary nations. The Chinese concept of courtesy (lǐ, 禮), as taught by Confucius, was considered an integral part of education. An intellect was said to "know of books and courtesy (rites)" ("知書達禮"). Thus, the ministry's other function was to oversee the nationwide civil examination system for entrance to the bureaucracy. Because democracy was unknown to pre-Republican China, neo-Confucian philosophy saw state sponsored exams as the way to legitimize a regime by allowing the intelligentsia participation in an otherwise autocratic and unelected system.
- Unlike its Ming Dynasty predecessor, which had full control over all military matters, the Qing Dynasty Board of War had very limited powers. First, the Eight Banners were under the direct control of the Emperor and hereditary Manchu and Mongolian princes, leaving the ministry only with authority over the Green Standard Armies. Furthermore, the ministry's functions were purely administrative—campaigns and troop movements were monitored and directed by the Emperor, first through the Manchu ruling council, and later through the Grand Council.
- The Board of Punishments handled all legal matters, including the supervision of various law courts and prisons. The Qing legal framework was relatively weak compared to modern day legal systems, as there was no separation of executive and legislative branches of government. The legal system could be inconsistent, and, at times, arbitrary, because the emperor ruled by decree and had final say on all judicial outcomes. Emperors could (and did) overturn judgements of lower courts from time to time. Fairness of treatment was also an issue under the apartheid system practised by the Manchu government over the Han Chinese majority. To counter these inadequacies and keep the population in line, the Qing maintained a very harsh penal code towards the Han populace, but it was no more severe than previous Chinese dynasties.
- The Board of Works handled all governmental building projects, including palaces, temples and the repairs of waterways and flood canals. It was also in charge of minting coinage.
In addition to the six boards, there was a Court of Colonial Affairs (Chinese: Lǐfànyuàn, 理藩院; Manchu: ![]() Tulergi golo be darasa jurgan; Mongol: γadaγdu mongγul un törü-ji jasaqu jabudal-un jamun) unique to the Qing government. This institution was established to supervise the administration of Tibet and the Mongolian lands. As the empire expanded, it took over administrative responsibility of all minority ethnic groups living in and around the empire, including early contacts with Russia—then seen as a tribute nation. The office had the status of a full ministry and was headed by officials of equal rank. However, appointees were at first restricted only to candidates of Manchurian and Mongolian ethnicity. To the south, Manchuria was separated from China proper by the Inner Willow Palisade, a ditch and embankment planted with willows intended to restrict the movement of the Han Chinese into Manchuria, as the area was off-limits to the Han until the Qing started colonizing the area with them later on in the dynasty's rule.
Tulergi golo be darasa jurgan; Mongol: γadaγdu mongγul un törü-ji jasaqu jabudal-un jamun) unique to the Qing government. This institution was established to supervise the administration of Tibet and the Mongolian lands. As the empire expanded, it took over administrative responsibility of all minority ethnic groups living in and around the empire, including early contacts with Russia—then seen as a tribute nation. The office had the status of a full ministry and was headed by officials of equal rank. However, appointees were at first restricted only to candidates of Manchurian and Mongolian ethnicity. To the south, Manchuria was separated from China proper by the Inner Willow Palisade, a ditch and embankment planted with willows intended to restrict the movement of the Han Chinese into Manchuria, as the area was off-limits to the Han until the Qing started colonizing the area with them later on in the dynasty's rule.
Even though the Board of Rites and the Court of Colonial Affairs performed some duties of a foreign office, they fell short of developing into a professional foreign service. This stemmed from the traditional imperial world view of seeing China as the centre of the world and viewing all foreigners as uncivilized barbarians unworthy of equal diplomatic status. It was not until 1861—a year after losing the Second Opium War to the Anglo-French coalition—that the Qing government bowed to foreign pressure and created a proper foreign affairs office known as the Zongli Yamen. The office was originally intended to be temporary and was staffed by officials seconded from the Grand Council. However, as dealings with foreigners became increasingly complicated and frequent, the office grew in size and importance, aided by revenue from customs duties which came under its direct jurisdiction.
Military
Beginnings and early development
The development of Qing military system can be divided into two broad periods separated by the Taiping rebellion (1850–1864). Early Qing military was rooted in the Manchu banners first developed by Nurhachi as a way to organize Jurchen society beyond petty clan affiliations. There are eight banners in all, differentiated by colours. The banners in their order of precedence were as follows: yellow, bordered yellow (i.e yellow banner with red border), white, red, bordered white, bordered red, blue, and bordered blue. The yellow, bordered yellow, and white banners were collectively known as the 'Upper Three Banners' (Zh: 上三旗) and were under the direct command of the Emperor. Only Manchus belonging to the Upper Three Banners, and selected Han Chinese who had passed the highest level of martial exams were qualified to serve as the Emperor's personal bodyguards. The remaining Banners were known as "The Lower Five Banners" (Zh: 下五旗) and were commanded by hereditary Manchurian princes descended from Nurhachi's immediate family, known informally as the "Iron Cap Princes" (Zh: 鐵帽子王). Together they formed the ruling council of the Manchu nation as well as high command of the army. In 1730, the Emperor Yongzheng established the Grand Council (Zh: 軍機處; Pinyin: Jūnjīchù; Ma: ![]() Cooha nashūn-i ba) at first to direct day to day military operations, but gradually Junjichu took over other military and administrative duties and served to centralize authority unto the crown. However, the Iron Cap Princes continued to exercise considerable influence over the political and military affairs of Qing government well into the reign of the Qianlong Emperor.
Cooha nashūn-i ba) at first to direct day to day military operations, but gradually Junjichu took over other military and administrative duties and served to centralize authority unto the crown. However, the Iron Cap Princes continued to exercise considerable influence over the political and military affairs of Qing government well into the reign of the Qianlong Emperor.
As Qing power expanded north of the Great Wall in the last years of the Ming Dynasty, the Banner system was expanded by Nurhachi's son and successor Hung Taiji to include mirrored Mongolian and Han Banners. After capturing Beijing in 1644 and as the Manchu rapidly gained control of large tracts of former Ming territory, the relatively small Banner armies were further augmented by the Green Standard Army (Zh: 綠營兵) which eventually outnumbered Banner troops three to one. The Green Standard Army so-named after the colour of their battle standards was made up of those Ming troops who had surrendered to the Qing. They maintained their Ming era organization and were led by a mix of Banner and Green Standard officers. The Banners and Green Standard troops were standing armies, paid for by central government. In addition, regional governors from provincial down to village level maintained their own irregular local militias for police duties and disaster relief. These militias were usually granted small annual stipends from regional coffers for part-time service obligations. They received very limited military drill if at all and were not considered combat troops.
Peace and stagnation
Banner Armies were broadly divided along ethnic lines, namely Manchurian and Mongolian. Although it must be pointed out that the ethnic composition of Manchurian Banners was far from homogeneous as they include non-Manchu bondservants registered under the household of their Manchu masters. As the war with Ming Dynasty progressed and the Han Chinese population under Manchu rule increased, Hung Taiji created a separate branch of Han Banners to draw on this new source of manpower. However these Han bannermen were never regarded by the government as equal to the other two branches due to their relatively late addition to the Manchu cause as well as their Han Chinese ancestry. The nature of their service—mainly as infantry, artillery and sappers, was also alien to the Manchurian nomadic traditions of fighting as cavalry. Furthermore, after the conquest the military roles played by Han Bannermen were quickly subsumed by the Green Standard Army. The Han Banners ceased to exist altogether after Emperor Yongzheng's Banner registration reforms aimed at cutting down imperial expenditures.
The socio-military origins of the Banner system meant that population within each branch and their sub-divisions were hereditary and rigid. Only under special circumstances sanctioned by imperial edict were social movements between banners permitted. In contrast, the Green Standard Army was originally intended to be a professional force. However during protracted period of peace in China from the 18th to mid-19th century, recruits from farming communities dwindled, due partly to Neo-Confucianism's negative stance on military careers. In order to maintain strengths, the Green Standard Army began to internalize, and gradually became hereditary in practice.
After defeating the remnants of the Ming forces, the Manchu Banner Army of approximately 200,000 strong at the time was evenly divided; half was designated the Forbidden Eight Banner Army (禁旅八旗 Jìnlǚ Bāqí) and was stationed in Beijing. It served both as the capital's garrison and Qing government's main strike force. The remainder of the Banner troops was distributed to guard key cities in China. These were known as the Territorial Eight Banner Army (駐防八旗 Zhùfáng Bāqí). The Manchu court keenly aware its own minority status reinforced a strict policy of racial segregation between the Manchus and Mongols from Han Chinese for fear of being sinitized by the latter. This policy applied directly to the Banner garrisons, most of which occupied a separate walled zone within the cities they were stationed in. In cities where there were limitation of space such as in Qingzhou (青州), a new fortified town would be purposely erected to house the Banner garrison and their families. Beijing being the imperial seat, the Regent Dorgon had the entire Chinese population forcibly relocated to the southern suburbs which became known as the "Outer Citadel" (外城 wàichéng). The northern walled city called "Inner Citadel" (內城 nèichéng) was portioned out to the remaining Manchu eight Banners, each responsibled for guarding a section of the Inner Citadel surrounding the Forbidden City palace complex (Zh: 紫禁城 Zǐjìnchéng; Ma: ![]() Dabkūri dorgi hoton)
Dabkūri dorgi hoton)
The policy of posting Banner troops as territorial garrison was not to protect but to inspire awe in the subjugated populace at the expense of their expertise as cavalry. As a result, after a century of peace and lack of field training the Manchurian Banner troops had deteriorated greatly in their combat worthiness. Secondly, before the conquest the Manchu banner was a "citizen" army, and its members were Manchu farmers and herders obligated to provide military service to the state at times of war. The Qing government's decision to turn the banner troops into a professional force whose every welfare and need was met by state coffers brought wealth, and with it corruption, to the rank and file of the Manchu Banners and hastened its decline as a fighting force. This was mirrored by a similar decline in the Green Standard Army. During peace time, soldiering became merely a source of supplementary income. Soldiers and commanders alike neglected training in pursuit of their own economic gains. Corruption was rampant as regional unit commanders submitted pay and supply requisitions based on exaggerated head counts to the quartermaster department and pocketed the difference. When the Taiping rebellion broke out in 1850s the Qing Court found out belatedly that the Banner and Green Standards troops could neither put down internal rebellions nor keep foreign invaders at bay.
Transition and modernization
Early during the Taiping rebellion, Qing forces suffered a series of disastrous defeats culminating in the loss of the regional capital city of Nanjing (南京) in 1853. The rebels massacred the entire Manchu garrison and their families in the city and made it their capital. Shortly thereafter a Taiping expeditionary force penetrated as far north as the suburbs of Tianjin (天津) in what was considered Imperial heartlands. In desperation the court ordered a Chinese mandarin Zeng Guofan (曾國藩) to organize regional and village militias (Tuányǒng 團勇 and Xiāngyǒng 鄉勇) into a standing army to contain the rebellion. Zeng's strategy was to rely on local gentries to raise a new type of military organization from those provinces that the Taiping rebels directly threatened. This new force became known as the Xiang Army (湘軍), named after Hunan region where it was raised. The Xiang Army was a hybrid of local militia and a standing army. It was given professional training, but was paid for out of regional coffers and funds its commanders—mostly members of the Chinese gentry—could muster. The Xiang Army and its successor the Huai Army (淮軍) created by Zeng's colleague and pupil Li Hongzhang (李鴻章)were collectively called Yongying (勇營).
Prior to forming and commanding the Xiang Army, Zeng had no military experience. Being a classically educated Mandarin his blueprint for the Xiang Army was taken from a historical source—the Ming Dynasty General Qi Jiguang (戚繼光) who, because of the weakness of regular Ming troops, had decided to form his own "private" army to repel raiding Japanese pirates in the mid-16th century. Qi's doctrine was based on Neo-Confucian ideas of binding troops' loyalty to their immediate superiors and also to the regions in which they were raised. This initially gave the troops an excellent esprit de corps. However, Qi's Army was an ad hoc solution to the specific problem of combating pirates, as was Zeng's original intention for the Xiang Army, which was to eradicate the Taiping rebels. However, circumstances led to the Yongying system becoming a permanent institution within the Qing military, which in the long run created problems of its own for the beleaguered central government.
Firstly, Yongying system signalled the end of Manchu dominance in Qing military establishment. Although the Banners and Green Standard armies lingered on as parasites depleting resources, henceforth the Yongying corps became Qing government's de facto first-line troops. Secondly the Yongying corps were financed through provincial coffers and were led by regional commanders. This devolution of power weakened the central government's grip on the whole country, a weakness further aggravated by foreign powers vying to carve up autonomous colonial territories in different parts of the Empire in the later half of the 19th century. Despite these serious negative effects the measure was deemed necessary as tax revenue from provinces occupied and threatened by rebels had ceased to reach the cash-strapped central government. Finally, the nature of Yongying command structure fostered nepotism and cronyism amongst its commanders whom as they ascended the bureaucratic ranks laid the seeds to Qing's eventual demise and the outbreak of regional warlordism in China during the first half of the 20th century.
By the late 19th century, China was fast descending into a semi-colonial state. Even the most conservative elements within the Qing court could no longer ignore China's military weakness in contrast to the foreign "barbarians" literally beating down its gates. In 1860, during the Second Opium War, the capital Beijing was captured and the Summer Palaces sacked by a relatively small Anglo-French coalition force numbering 25,000. Although the Chinese invented gunpowder, and firearms had been in continual use in Chinese warfare since as far back as the Sung Dynasty, the advent of modern weaponry resulting from the European Industrial Revolution had rendered China's traditionally trained and equipped army and navy obsolete. The government attempts to modernize during the Self-Strengthening Movement were in the view of most historians with hindsight piecemeal and yielded little lasting results. Various reasons for the apparent failure of late-Qing modernization attempts have been advanced including the lack of funds, lack of political will, and unwillingness to depart from tradition. These reasons remain disputed.
Losing the Sino-Japanese War of 1894–1895 was a watershed for the Qing government. Japan, a country long regarded by the Chinese as little more than an upstart nation of pirates, had convincingly beaten its larger neighbour and in the process annihilated the Qing government's pride and joy—its modernized Beiyang Fleet then deemed to be the strongest naval force in Asia. In doing so, Japan became the first Asian country to join the previously exclusively western ranks of colonial powers. The defeat was a rude awakening to the Qing court especially when set in the context that it occurred a mere three decades after the Meiji reforms set a feudal Japan on course to emulate the Western nations in their economic and technological achievements. Finally, in December 1894, the Qing government took some concrete steps to reform military institutions and to re-train selected units in westernized drills, tactics and weaponry. These units were collectively called the New Army (新式陸軍), the most successful of which was the Beiyang Army (北洋軍) under the overall supervision and control of an ex-Huai Army commander, the Han Chinese general Yuan Shikai (袁世凱), who exploited his position to eventually become Republic president, dictator and finally abortive emperor of China.
Fall of the dynasty
By the early twentieth century, mass civil disorder had begun and continuously grown. Empress Dowager Cixi and the Guangxu emperor both died in 1908, leaving a relatively powerless and unstable central authority. Puyi, the eldest son of Zaifeng, Prince Chun, was appointed successor at age two, leaving Zaifeng with the regency. This was followed by the dismissal of General Yuan Shikai from his former positions of power. In mid 1911 Zaifeng created the "Imperial Family Cabinet", a ruling council of the Imperial Government almost entirely consisting of Aisin Gioro relatives. This brought a wide range of negative opinions from senior officials like Zhang Zhidong. The Qing Emperor Guangxu ordered a series of reforms to try to change social and institutional ills. The empress Cixi was tired of Guangxu’s power and wanted to overthrow him. She knew that if Guangxu had carried out on the 100 Days Reform then everyone would be with the plan and they would follow Guangxu.
The Wuchang Uprising succeeded on October 10, 1911, and was followed by a proclamation of a separate central government, the Republic of China, in Nanjing with Sun Yat-sen as its provisional head. Numerous provinces began "separating" from Qing control. Seeing a desperate situation unfold, the Qing government brought an unwilling Yuan Shikai back to military power, taking control of his Beiyang Army, with the initial goal of crushing the revolutionaries. After taking the position of Prime Minister (內閣總理大臣) and creating his own cabinet, Yuan went as far as to ask for the removal of Zaifeng from the regency. This removal later proceeded with directions from Empress Dowager Longyu.
With Zaifeng gone, Yuan Shi-kai and his Beiyang commanders effectively dominated Qing politics. He reasoned that going to war would be unreasonable and costly, especially when noting that the Qing Government had a goal for constitutional monarchy. Similarly, Sun Yat-sen's government wanted a Republican constitutional reform, both aiming for the benefit of China's economy and populace. With permission from Empress Dowager Longyu, Yuan began negotiating with Sun Yat-sen, who decided that his goal had been achieved in forming a republic, and that therefore he could allow Yuan to step into the position of President of the Republic. In 1912, after rounds of negotiations, Longyu issued the Imperial Edict bringing about the abdication of the child emperor Puyi.
The collapse of the Qing dynasty in 1912 brought an end to over 2,000 years of imperial China and began an extended period of instability of warlord factionalism. Obvious political and economic backwardness combined with widespread criticism of Chinese culture led to questioning and doubt about the future. China's turbulent history since the overthrow of the Qing may be understood at least in part as an attempt to understand and recover significant aspects of historic Chinese culture and integrate them with influential new ideas that have emerged within the last century.