Portal:British Empire
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: British History; History; Portals
|
British Empire
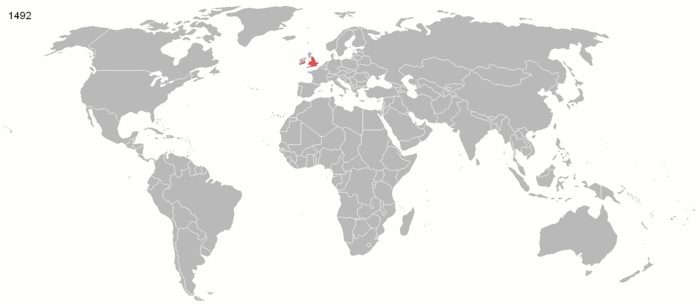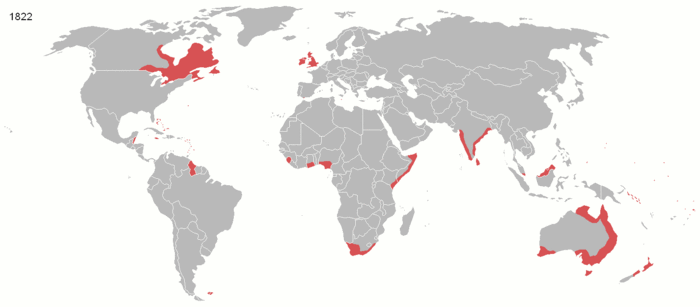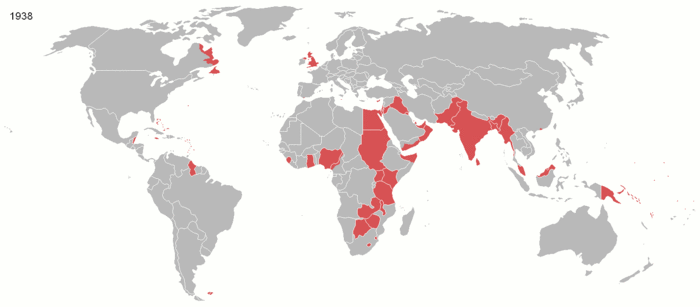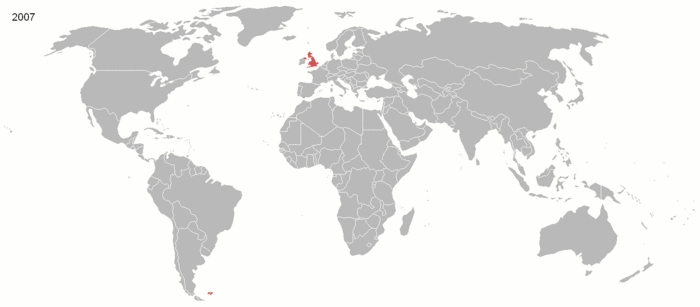
The British Empire was the largest empire in history and for a substantial time was the foremost global power. It was a product of the European age of discovery, which began with the maritime explorations of the 15th century, that sparked the era of the European colonial empires. By 1921, the British Empire held sway over a population of about 458 million people, approximately one-quarter of the world's population. It covered about 36.6 million km² (14.2 million square miles), about a quarter of Earth's total land area. As a result, its legacy is widespread, in legal and governmental systems, economic practice, militarily, educational systems, sports (such as cricket, rugby and football), traffic practices (such as driving on the left), and in the global spread of the English language. At the peak of its power, it was often said that " the sun never sets on the British Empire" because its span across the globe ensured that the sun was always shining on at least one of its numerous colonies or subject nations. During the five decades following World War II, most of the territories of the Empire became independent. Many went on to join the Commonwealth of Nations, a free association of independent states.
Selected article
The flag of Australia was chosen in 1901 from entries in a worldwide design competition held following Federation. It was approved by Australian and British authorities over the next few years, although the exact specifications of the flag were changed several times both intentionally and as a result of confusion. The current specifications were published in 1934, and in 1954 the flag became legally recognised as the "Australian National Flag". The flag is a defaced Blue Ensign: a blue field with the Union Flag in the canton (upper hoist quarter), and a large white seven-pointed star known as the Commonwealth Star in the lower hoist quarter. The fly contains a representation of the Southern Cross constellation, made up of five white stars – one small five-pointed star and four, larger, seven-pointed stars. In addition to the Blue Ensign there are several additional Australian flags, including the Aboriginal flag, the Torres Strait Islander flag and the flags of the Defence Forces. The design of the Australian flag is the subject of debate within Australia, with some advocating its redesign in connection with the republican movement. (more...) Did you know...
Selected picture
Selected biography
Major General Roger Elliott (ca. 1665 - 15 May 1714) was one of the earliest British Governors of Gibraltar. His nephew George Augustus Eliott also became a noted Governor and defender of Gibraltar. Roger Elliott was born, possibly in London but more probably in the Tangier Garrison in Morocco, to George Elliott (ca. 1636 - 1668, the Chirurgeon to the Garrison) and his wife Catherine Maxwell (ca. 1638 - 1709). George Elliott was the illegitimate son of Richard Eliot, the wayward second son of Sir John Eliot. Roger's father, George Elliott, died at the Tangier Garrison in 1668 and his widowed mother remarried there on 22 February 1670 to Robert Spotswood ( 17 September 1637 - 1680, the assistant and replacement Chirurgeon at the Garrison), and thirdly to Rev Dr George Mercer, the Garrison schoolmaster. Roger was therefore an older half-brother to Alexander Spotswood (ca. 1676 - 6 June 1740), who would become a noted Lieutenant- Governor of Virginia. (more...)
|
||