Arabic language
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Languages
| Arabic العربية al-‘arabiyyah |
||
|---|---|---|
| al-‘Arabiyyah in written Arabic ( Naskh script): |  |
|
| Pronunciation: | /alˌʕa.raˈbij.ja/ | |
| Spoken in: | Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian territories, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates, Western Sahara, Yemen by a majority; it is also the liturgical language of Islam. | |
| Region: | Arab world | |
| Total speakers: | Estimates of native speakers between 186 and 422 million . According to Ethnologue, 246 million including second language speakers, (1999 est). | |
| Ranking: | 2 to 6 (native speakers) | |
| Language family: | Afro-Asiatic Semitic West Semitic Central Semitic Arabic |
|
| Writing system: | Arabic alphabet | |
| Official status | ||
| Official language in: | Official language of 25 countries, the third most after English and French List
|
|
| Regulated by: | Egypt: Academy of the Arabic Language in Cairo Syria: Arab Academy of Damascus (the oldest) |
|
| Language codes | ||
| ISO 639-1: | ar | |
| ISO 639-2: | ara | |
| ISO 639-3: | ara – Arabic (generic) see varieties of Arabic for the individual codes |
|
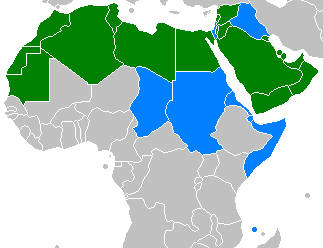 Distribution of Arabic as sole official language (green) and one of several official languages (blue) |
||
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | ||
Arabic (الْعَرَبيّة al-ʿarabiyyah or just عَرَبيْ ʿarabī) is the largest living member of the Semitic language family in terms of speakers. Classified as Central Semitic, it is closely related to Hebrew and Aramaic, and has its roots in a Proto-Semitic common ancestor. Modern Arabic is classified as a macrolanguage with 27 sub-languages in ISO 639-3. These varieties are spoken throughout the Arab world, and Standard Arabic is widely studied and known throughout the Islamic world.
Modern Standard Arabic derives from Classical Arabic, the only surviving member of the Old North Arabian dialect group, attested epigraphically since the 6th century, which has been a literary language and the liturgical language of Islam since the 7th century.
Arabic has lent many words to other languages of the Islamic world, as Latin has contributed to most European languages. And in turn, it has also borrowed from those languages, as well as Persian and Sanskrit from early contacts with their affiliated regions. During the Middle Ages, Arabic was a major vehicle of culture, especially in science, mathematics and philosophy, with the result that many European languages have also borrowed numerous words from it, especially Spanish and Portuguese due to both the proximity of European and Arab civilization and 700 years of caliphate government in the Iberian peninsula (see Al-Andalus).
Literary and Modern Standard Arabic
The term "Arabic" may refer to either literary Arabic ((al-)fuṣḥā الفصحى) or the many localized varieties of Arabic commonly called "colloquial Arabic." Arabs consider literary Arabic as the standard language and tend to view everything else as mere dialects. Literary Arabic (اللغة العربية الفصحى translit: al-luġatu l-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā "the most eloquent Arabic language"), refers both to the language of present-day media across North Africa and the Middle East and to the language of the Qur'an. (The expression media here includes most television and radio, and practically all written matter, including all books, newspapers, magazines, documents of every kind, and reading primers for small children.) "Colloquial" or "dialectal" Arabic refers to the many national or regional varieties derived from Classical Arabic, spoken across North Africa and the Middle East, which constitute the everyday spoken language. These sometimes differ enough to be mutually incomprehensible. These dialects are typically unwritten, although a certain amount of literature (particularly plays and poetry) exists in many of them. They are often used to varying degrees in informal spoken media, such as soap operas and talk shows. Literary Arabic or classical Arabic is the official language of all Arab countries and is the only form of Arabic taught in schools at all stages.
The sociolinguistic situation of Arabic in modern times provides a prime example of the linguistic phenomenon of diglossia, which is the normal use of two separate varieties of the same language, usually in different social situations. In the case of Arabic, educated Arabs of any nationality can be assumed to speak both their local dialect and their school-taught literary Arabic. This diglossic situation facilitates code switching where a speaker switches back and forth between the two varieties of the language, sometimes even within the same sentence. When educated Arabs of different nationalities engage in conversation (for example, a Moroccan speaking with a Lebanese), both switch into Literary Arabic for the sake of communication.
Like other languages, literary Arabic continues to evolve. Classical Arabic (especially from the pre-Islamic to the Abbasid period, including Qur'anic Arabic) can be distinguished from Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) as used today. Classical Arabic is considered normative; modern authors attempt (with varying degrees of success) to follow the syntactic and grammatical norms laid down by Classical grammarians (such as Sibawayh), and to use the vocabulary defined in Classical dictionaries (such as the Lisān al-Arab.) However, many modern terms would have been mysterious to a Classical author, whether taken from other languages (for example, فيلم film) or coined from existing lexical resources (for example, هاتف hātif "telephone" = "caller"). Structural influence from foreign languages or from the colloquials has also affected Modern Standard Arabic: for example, MSA texts sometimes use the format "A, B, C, and D" when listing things, whereas Classical Arabic prefers "A and B and C and D", and subject-initial sentences may be more common in MSA than in Classical Arabic. For these reasons, Modern Standard Arabic is generally treated separately in non-Arab sources.
Influence of Arabic on other languages
The influence of Arabic has been most profound in Islamic countries. Arabic is a major source of vocabulary for languages as diverse as Berber, Kurdish, Persian, Swahili, Urdu, Hindi (especially the spoken variety), Turkish, Malay and Indonesian, as well as other languages in countries where these languages are spoken. For example, the Arabic word for book (/kitāb/) is used in all the languages listed, apart from Malay and Indonesian (where it specifically means "religious book"). In addition, Spanish and Portuguese both have large numbers of Arabic loan words, and English has quite a few. Other languages such as Maltese and Kinubi derive from Arabic, rather than merely borrowing vocabulary or grammar rules.
The terms borrowed range from religious terminology (like Berber taẓallit "prayer" < salat), academic terms (like Uyghur mentiq "logic"), economic items (like English "sugar") to placeholders (like Spanish fulano "so-and-so") and everyday conjunctions (like Urdu lekin "but".) Most Berber varieties (such as Kabyle), along with Swahili, borrow some numbers from Arabic. Most Islamic religious terms are direct borrowings from Arabic, such as salat 'prayer' and imam 'prayer leader'. In languages not directly in contact with the Arab world, Arabic loanwords are often transferred indirectly via other languages rather than being transferred directly from Arabic; for example, most Arabic loanwords in Urdu entered through Persian, and many older Arabic loanwords in Hausa were borrowed from Kanuri.
Many words in English and other European languages are derived from Arabic, often through other European languages, especially Spanish and Italian. Among them are commonly-used words like "sugar" (sukkar), "cotton" (quṭn) and "magazine" ( maḫāzin). English words more recognizably of Arabic origin include "algebra", "alcohol", "alchemy", " alkali" and " zenith." Some words in common use, such as "intention" and "information", were originally calques of Arabic philosophical terms.
Arabic and Islam
Arabic is the language of the Qur'an. Traditionally, Muslims deem it impossible to translate the Qur'an in a way that would reflect its exact meaning in a different language. Some schools of thought maintain that it should not be translated at all. Arabic is often associated with Islam, but it is also spoken by Arab Christians, Arab Druze, Mizrahi Jews and Iraqi Mandaeans.
Most of the world's Muslims do not speak Arabic as their native language but can read the script and recite the words of religious texts.
History
Modern Arabic is considered to be part of the Arabo-Canaanite sub-branch of the central group of West Semitic languages. While Arabic is not the oldest of the Semitic languages, it shares many features with the common ancestor for all Semitic languages in the Afro-Asiatic group of languages: Proto-Semitic whose phonological, morphological, and syntactic features have been determined by linguists. Many linguists consider Arabic to be the most Semitic of any modern Semitic languages in terms of how completely it preserves the features of Proto-Semitic.
The earliest Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts are the Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, from the 8th century BC, written not in the modern Arabic alphabet, nor in its Nabataean ancestor, but in variants of the epigraphic South Arabian musnad. These are followed by 6th-century BC Lihyanite texts from southeastern Saudi Arabia and the Thamudic texts found throughout Arabia and the Sinai, and not in reality connected with Thamud. Later come the Safaitic inscriptions beginning in the 1st century BC, and the many Arabic personal names attested in Nabataean inscriptions (which are, however, written in Aramaic). From about the 2nd century BC, a few inscriptions from Qaryat al-Faw (near Sulayyil) reveal a dialect which is no longer considered "Proto-Arabic", but Pre-Classical Arabic.
By the fourth century AD, the Arab kingdoms of the Lakhmids in southern Iraq, the Ghassanids in southern Syria the Kindite Kingdom emerged in Central Arabia. Their courts were responsible for some notable examples of pre-Islamic Arabic poetry, and for some of the few surviving pre-Islamic Arabic inscriptions in the Arabic alphabet.
Dialects and descendants
"Colloquial Arabic" is a collective term for the spoken varieties of Arabic used throughout the Arab world, which, as mentioned, differ radically from the literary language. The main dialectal division is between the North African dialects and those of the Middle East, followed by that between sedentary dialects and the much more conservative Bedouin dialects. Speakers of some of these dialects are unable to converse with speakers of another dialect of Arabic; in particular, while Middle Easterners can generally understand one another, they often have trouble understanding North Africans (although the converse is not true, due to the popularity of Middle Eastern—especially Egyptian—films and other media).
One factor in the differentiation of the dialects is influence from the languages previously spoken in the areas, which have typically provided a significant number of new words, and have sometimes also influenced pronunciation or word order; however, a much more significant factor for most dialects is, as among Romance languages, retention (or change of meaning) of different classical forms. Thus Iraqi aku, Levantine fīh, and North African kayən all mean "there is", and all come from classical Arabic forms (yakūn, fīhi, kā'in respectively), but now sound very different.
The major groups are:
- Egyptian Arabic مصري : Spoken by about 79 million people in Egypt and perhaps the most widely understood variety, due to the popularity of Egyptian-made films and TV shows
- Maghrebi Arabic مغربي ( Algerian Arabic, Moroccan Arabic, Tunisian Arabic, Maltese and western Libyan Arabic) The Moroccan and Algerian dialects are each spoken by about 20 million people.
- Levantine Arabic شامي (Western Syrian, Lebanese, Palestinian, western Jordanian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic)
- Iraqi Arabic عراقي (and Khuzestani Arabic) - with significant differences between the more Arabian-like gilit-dialects of the south and the more conservative qeltu-dialects of the northern cities
- East Arabian Arabic بحريني (Eastern Saudi Arabia, Western Iraq, Eastern Syrian, Jordanian and parts of Oman)
- Gulf Arabic خليجي (Bahrain, Saudi Eastern Province, Kuwait, UAE, Qatar, and Oman)
Other varieties include:
- Ḥassānīya حساني (in Mauritania, Mali and western Sahara)
- Sudanese Arabic سوداني (with a dialect continuum into Chad)
- Hijazi Arabic حجازي (western Saudi Arabia)
- Najdi Arabic نجدي (Najd region of central Saudi Arabia)
- Yemeni Arabic يمني (Yemen to southern Saudi Arabia)
- Andalusi Arabic أندلسي (Iberia until 17th century)
- Siculo Arabic صقلي (Sicily, South Italy until 14th century)
- Maltese مالطي, which is spoken on the Mediterranean island of Malta, is the only one to have established itself as a fully separate language, with independent literary norms. Apart from its phonology, Maltese bears considerable similarity to urban varieties of Tunisian Arabic, however in the course of history, the language has adopted numerous loanwords, phonetic and phonological features, and even some grammatical patterns, from Italian, Sicilian, and English. It is also the only Semitic tongue written in the Latin alphabet.
Sounds
The phonemes below reflect the pronunciation of Standard Arabic. There are minor variations from country to country.
Vowels
Arabic has three vowels, with long and short forms of /a/, /i/, and /u/. There are also two diphthongs: /aj/ and /aw/.
Consonants
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Inter-dental | Dental (incl. alveolar) | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyn- geal |
Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | emphatic | |||||||||||
| Plosive | voiceless | ت t̪ | ط t̪ˁ | ك k | ق q | ء ʔ | ||||||
| voiced | ب b | د d̪ | ض d̪ˁ | ج dʒ¹ | ||||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | ف f | ث θ | س s | ص sˁ | ش ʃ | خ x | ح ħ | ه h | |||
| voiced | ذ ð | ز z | ظ ðˁ | غ ɣ | ع ʕ | |||||||
| Nasal | م m | ن n | ||||||||||
| Lateral | ل l ² | |||||||||||
| Trill | ر r | |||||||||||
| Approximant | و w | ي j | ||||||||||
See Arabic alphabet for explanations on the IPA phonetic symbols found in this chart.
- [dʒ] is pronounced as [ɡ] by some speakers. This is especially characteristic of the Egyptian and southern Yemeni dialects. In many parts of North Africa and in the Levant, it is pronounced as [ʒ].
- /l/ is pronounced [lˁ] only in /ʔalːaːh/, the name of God, i.e. Allah, when the word follows a, ā, u or ū (after i or ī it is unvelarised: bismi l-lāh /bismilːaːh/).
- /ʕ/ is usually a phonetic approximant.
- In many varieties, /ħ, ʕ/ are actually epiglottal [ʜ, ʢ] (despite what is reported in many earlier works).
- /x/ is considered to be an uvular sound (/χ/) by some linguists.
Arabic has consonants traditionally termed "emphatic" /tˁ, dˁ, sˁ, ðˁ/ are both velarized [tˠ, dˠ, sˠ, ðˠ] and pharyngealised [tˁ, dˁ, sˁ, ðˁ]. This simultaneous velarization and pharyngealization is deemed "Retracted Tongue Root" by phonologists. In some transcription systems, emphasis is shown by capitalizing the letter e.g. /dˁ/ is written ‹D›; in others the letter is underlined or has a dot below it e.g. ‹ḍ›.
Vowels and consonants can be (phonologically) short or long. Long (geminate) consonants are normally written doubled in Latin transcription (i.e. bb, dd, etc.), reflecting the presence of the Arabic diacritic mark shaddah, which marks lengthened consonants. Such consonants are held twice as long as short consonants. This consonant lengthening is phonemically contrastive: e.g. qabala "he accepted" and qabbala "he kissed".
Syllable structure
Arabic has two kinds of syllables: open syllables (CV) and (CVV) - and closed syllables (CVC), (CVVC) and (CVCC). Every syllable begins with a consonant - or else a consonant is borrowed from a previous word through elision – especially in the case of the definite article the, al- (used when starting an utterance) or _l (when following a word), e.g. baytu –l mudiir “house (of) the director”, which becomes bay-tul-mu-diir when divided syllabically. By itself, "the director" would be pronounced /al mudiːr/.
Stress
Although word stress is not phonemically contrastive in Standard Arabic, it does bear a strong relationship to vowel length, though phonemic, and syllable shape, and correct word stress aids intelligibility. The basic rules are:
- Only the last three syllables may be stressed.
- Given this restriction, the last "Superheavy" syllable (containing a long vowel or followed by two consonants for example) is stressed.
- If there is no such syllable, the pre-final syllable is stressed if 'Heavy'. Otherwise, the first allowable syllable is stressed.
- In Standard Arabic, a final long vowel may not be stressed. (This restriction does not apply to the spoken dialects, where original final long vowels have been shortened and secondary final long vowels have arisen.)
For example: ki-TAAB "book", KAA-tib "writer", MAK-tab "desk", ma-KAA-tib "desks", MAK-ta-ba "library", KA-ta-buu (MSA) "they wrote" = KA-ta-bu (dialect), ka-ta-BUU-hu (MSA) "they wrote it" = ka-ta-BUU (dialect), ka-TA-ba-taa (MSA) "they (dual, fem) wrote", ka-TAB-tu (MSA) "I wrote" = ka-TABT (dialect). Doubled consonants count as two consonants: ma-JAL-la "magazine", ma-HALL "palace".
Some dialects have different stress rules. In the Cairo ( Egyptian Arabic) dialect, for example, a heavy syllable may not carry stress more than two syllables from the end of a word, hence mad-RA-sa "school", qaa-HI-ra "Cairo". In the Arabic of Sana, stress is often retracted: BAY-tayn "two houses", MAA-sat-hum "their table", ma-KAA-tiib "desks", ZAA-rat-hiin "sometimes", mad-RA-sat-hum "their school". (In this dialect, only syllables with long vowels or diphthongs are considered heavy; in a two-syllable word, the final syllable can be stressed only if the preceding syllable is light; and in longer words, the final syllable cannot be stressed.)
Dialectal variations
In some dialects, there may be more or fewer phonemes than those listed in the chart above. For example, non-Arabic [v] is used in the Maghrebi dialects as well in the written language mostly for foreign names. Semitic [p] became [f] extremely early on in Arabic before it was written down; a few modern Arabic dialects, such as Iraqi (influenced by Persian and Turkish) distinguish between [p] and [b].
Interdental fricatives ([θ] and [ð]) are rendered as stops [t] and [d] in some dialects (such as Levantine, Egyptian, and much of the Maghreb); some of these dialects render them as [s] and [z] in "learned" words from the Standard language. Early in the expansion of Arabic, the separate emphatic phonemes [dˁ] and [ðˁ] coallesced into a single phoneme, becoming one or the other. Predictably, dialects without interdental fricatives use [dˁ] exclusively, while those with such fricatives use [ðˁ]. Again, in "learned" words from the Standard language, [ðˁ] is rendered as [zˁ] (in the Middle East) or [dˁ] (in North Africa) in dialects without interdental fricatives.
Another key distinguishing mark of Arabic dialects is how they render the original velar and uvular stops /q/, /ʤ/ ( Proto-Semitic /g/), and /k/:
- /q/ retains its original pronunciation in widely scattered regions such as Yemen, Morocco, and urban areas of the Maghreb. But it is rendered as a voiced velar stop [ɡ] in Gulf Arabic, Iraqi Arabic, Upper Egypt, much of the Maghreb, and less urban parts of the Levant (e.g. Jordan); as a voiced uvular constrictive [ʁ] in Sudanese Arabic; and as a glottal stop [ʔ] in several prestige dialects, such as those spoken in Cairo, Beirut and Damascus. Some traditionally Christian villages in rural areas of the Levant render the sound as [k], as do Shia Bahrainis. In some Gulf dialects, it is palatalized to [ʤ] or [ʒ]. Many dialects with a modified pronunciation for /q/ maintain the /q/ pronunciation in certain words (often with religious or educational overtones) borrowed from the Classical language.
- /ʤ/ retains its pronunciation in Iraq and much of the Arabian Peninsula, but is pronounced /g/ in Cairo and parts of Yemen, /ʒ/ in Morocco and the Levant, and /j/ in some words in much of Gulf Arabic.
- /k/ usually retains its original pronunciation, but is palatalized to /ʧ/ in many words in Palestine, Iraq and much of the Arabian Peninsula. Often a distinction is made between the suffixes /-ak/ (you, masc.) and /-ik/ (you, fem.), which become /-ak/ and /-iʧ/, respectively. In Sana Arabic, /-ik/ is pronounced /-iʃ/.
Grammar
Nouns in Literary Arabic have three grammatical cases ( nominative, accusative, and genitive [also used when the noun is governed by a preposition]); three numbers (singular, dual and plural); two genders (masculine and feminine); and three "states" (indefinite, definite, and construct). The cases of singular nouns (other than those that end in long ā) are indicated by suffixed short vowels (/-u/ for nominative, /-a/ for accusative, /-i/ for genitive). The feminine singular is often marked by /-at/, which is reduced to /-ah/ or /-a/ before a pause. Plural is indicated either through endings (the sound plural) or internal modification (the broken plural). Definite nouns include all proper nouns, all nouns in "construct state" and all nouns which are prefixed by the definite article /al-/. Indefinite singular nouns (other than those that end in long ā) add a final /-n/ to the case-marking vowels, giving /-un/, /-an/ or /-in/ (which is also referred to as nunation or tanwīn).
Verbs in Literary Arabic are marked for person (first, second, or third), gender, and number. They are conjugated in two major paradigms (termed perfective and imperfective, or past and non-past); two voices (active and passive); and five moods in the imperfective ( indicative, imperative, subjunctive, jussive and energetic). There are also two participles (active and passive) and a verbal noun, but no infinitive. As indicated by the differing terms for the two tense systems, there is some disagreement over whether the distinction between the two systems should be most accurately characterized as tense, aspect or a combination of the two. The perfective aspect is constructed using fused suffixes that combine person, number and gender in a single morpheme, while the imperfective aspect is constructed using a combination of prefixes (primarily encoding person) and suffixes (primarily encoding gender and number). The moods other than imperative are primarily marked by suffixes (/u/ for indicative, /a/ for subjunctive, no ending for jussive, /an/ for energetic). The imperative has the endings of the jussive but lacks any prefixes. The passive is marked through internal vowel changes. Plural forms for the verb are only used when the subject is not mentioned, or is preceding it, and the feminine singular is used for all non-human plurals.
Adjectives in Literary Arabic are marked for case, number, gender and state, as for nouns. However, the plural of all non-human nouns is always combined with a singular feminine adjective, which takes the /-ah/ or /-at/ suffix.
Pronouns in Literary Arabic are marked for person, number and gender. There are two varieties, independent pronouns and enclitics. Enclitic pronouns are attached to the end of a verb, noun or preposition and indicate verbal and prepositional objects or possession of nouns. The first-person singular pronoun has a different enclitic form used for verbs (/-ni/) and for nouns or prepositions (/-ī/ after consonants, /-ya/ after vowels).
Nouns, verbs, pronouns and adjectives agree with each other in all respects. However, non-human plural nouns are grammatically considered to be feminine singular. Furthermore, a verb in a verb-initial sentence is marked as singular regardless of its semantic number when the subject of the verb is explicitly mentioned as a noun. Numerals between three and ten show "chiasmic" agreement, in that grammatically masculine numerals have feminine marking and vice-versa.
The spoken dialects have lost the case distinctions and make only limited use of the dual (it occurs only on nouns and its use is no longer required in all circumstances). They have lost the mood distinctions other than imperative, but many have since gained new moods through the use of prefixes (most often /bi-/ for indicative vs. unmarked subjunctive). They have also mostly lost the indefinite "nunation" and the internal passive. Modern Standard Arabic maintains the grammatical distinctions of Literary Arabic except that the energetic mood is almost never used; in addition, Modern Standard Arabic sometimes drop the final short vowels that indicate case and mood.
As in many other Semitic languages, Arabic verb formation is based on a (usually) triconsonantal root, which is not a word in itself but contains the semantic core. The consonants k-t-b, for example, indicate 'write', q-r-ʾ indicate 'read', ʾ-k-l indicate 'eat', etc. Words are formed by supplying the root with a vowel structure and with affixes. (Traditionally, Arabic grammarians have used the root f-ʿ-l 'do' as a template to discuss word formation.) From any particular root, up to fifteen different verbs can be formed, each with its own template; these are referred to by Western scholars as "form I", "form II", ... up through "form XV". These forms, and their associated participles and verbal nouns, are the primary means of forming vocabulary in Arabic. Forms XI to XV are extremely rare.
Writing system
The Arabic alphabet derives from the Aramaic script (through Syriac and then Nabatean), to which it bears a loose resemblance like that of Coptic or Cyrillic script to Greek script. Traditionally, there were several differences between the Western (North African) and Middle Eastern version of the alphabet—in particular, the fa and qaf had a dot underneath and a single dot above respectively in the Maghreb, and the order of the letters was slightly different (at least when they were used as numerals). However, the old Maghrebi variant has been abandoned except for calligraphic purposes in the Maghreb itself, and remains in use mainly in the Quranic schools ( zaouias) of West Africa. Arabic, like all other Semitic languages (except for the Latin-written Maltese, and the languages with the Ge'ez script), is written from right to left. There are several styles of script, notably Naskh which is used in print and by computers, and Ruq'ah which is commonly used in handwriting.
Calligraphy
After the definitive fixing of the Arabic script around 786, by Khalil ibn Ahmad al Farahidi, many styles were developed, both for the writing down of the Qur'an and other books, and for inscriptions on monuments as decoration.
Arabic calligraphy has not fallen out of use as calligraphy has in the Western world, and is still considered by Arabs as a major art form; calligraphers are held in great esteem. Being cursive by nature, unlike the Latin alphabet, Arabic script is used to write down a verse of the Qur'an, a Hadith, or simply a proverb, in a spectacular composition. The composition is often abstract, but sometimes the writing is shaped into an actual form such as that of an animal. Two of the current masters of the genre are Hassan Massoudy and Khaled Al Saa’i.
Transliteration
There are a number of different standards of Arabic transliteration: methods of accurately and efficiently representing Arabic with the Latin alphabet. There are multiple conflicting motivations for transliteration. Scholarly systems are intended to accurately and unambiguously represent the phonemes of Arabic, generally supplying making the phonetics more explicit than the original word in the Arabic alphabet. These systems are heavily reliant on diacritical marks such as "š" for sound equivalently written sh in English. In some cases, the sh or kh sounds can be represented by italicizing or underlining them -- that way, they can be distinguished from separate s and h sounds or k and h sounds, respectively. (Compare gashouse to gash.) At first sight, this may be difficult to recognize. Less scientific systems often use digraphs (like sh and kh), which are usually more simple to read, but sacrifice the definiteness of the scientific systems. Such systems may be intended to help readers who are neither Arabic speakers nor linguists to intuitively pronounce Arabic names and phrases. An example of such a system is the Bahá'í orthography. A third type of transliteration seeks to represent an equivalent of the Arabic spelling with Latin letters, for use by Arabic speakers when Arabic writing is not available (for example, when using an ASCII communication device). An example is the system used by the US military, Standard Arabic Technical Transliteration System or SATTS, which represents each Arabic letter with a unique symbol in the ASCII range to provide a one-to-one mapping from Arabic to ASCII and back. This system, while facilitating typing on English keyboards, presents its own ambiguities and disadvantages. During the last few decades and especially since the 1990s, Western-invented text communication technologies have become prevalent in the Arab world, such as personal computers, the World Wide Web, email, Bulletin board systems, IRC, instant messaging and mobile phone text messaging. Most of these technologies originally had the ability to communicate using the Latin alphabet only, and some of them still do not have the Arabic alphabet as an optional feature. As a result, Arabic speaking users communicated in these technologies by transliterating the Arabic text using the Latin script, sometime known as IM Arabic.
To handle those Arabic letters that cannot be accurately represented using the Latin script, numerals and other characters were appropriated. For example, the numeral "3" may be used to represent the Arabic letter "ع", ayn. There is no universal name for this type of transliteration, but some have named it Arabic Chat Alphabet. Other systems of transliteration exist, such as using dots or capitalization to represent the "emphatic" counterparts of certain consonants. For instance, using capitalization, the letter "د", or daal, may be represented by d. Its emphatic counterpart, "ض", may be written as D.
Numerals
In most of present-day North Africa, the Western Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) are used. However in Egypt and Arabic-speaking countries to the east of it, the Eastern Arabic numerals (٠.١.٢.٣.٤.٥.٦.٧.٨.٩) are in use. The lowest-valued digit appears on the right, so the order of digits on the page is the same as in Latin script; this reflects the way in which Arabic numbers are traditionally read (i.e. increasing order, so 1234 is "four and thirty and two hundred and one thousand"), though this reading has declined of late. Also sequences of digits such as telephone numbers are read from left to right.
Language-standards regulators
Academy of the Arabic Language is the name of a number of language-regulation bodies formed in Arab countries. The most active are in Damascus and Cairo. They review language development, monitor new words and approve inclusion of new words into their published standard dictionaries. They also publish old and historical Arabic manuscripts.
Studying Arabic
Arabic language interests millions of non-Arabic speakers to learn it to different levels, mainly because it is the language of their holy book, the Quran, and all Islamic terms are Arabic. Arabic has been taught in many elementary and secondary schools, especially Muslim schools, worldwide. Many universities in the world today have classes for studying Arabic as a Foreign Language, as part of their foreign languages, Middle Eastern studies, religious studies, area studies departments, and even standalone Arabic language departments. Many Arabic language schools exist today to assist in gaining Arabic language skills outside academic education. Most of the Arabic language schools are located in the Arab world and some Muslim world countries. Software and books with tapes are also important part of Arabic learning, as many of Arabic learners may live in places where there are no academic or Arabic language school classes available. Radio series of Arabic language classes are also provided from some radio stations. A number of websites on the Internet provide online classes for all levels as a distance education means.
