1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Geology and geophysics
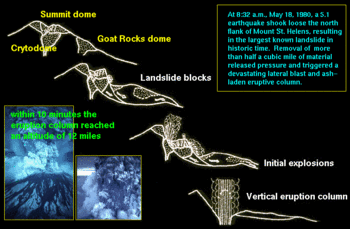
The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens, a volcano located in Washington state, in the United States, was a major volcanic eruption. The eruption was the most significant to occur in the contiguous 48 U.S. states ( VEI = 5, 0.3 cu mi, 1.2 km3 of material erupted), in terms of power and volume of material released, since the 1915 eruption of California's Lassen Peak. The eruption was preceded by a two-month series of earthquakes and steam-venting episodes, caused by an injection of magma at shallow depth below the mountain that created a huge bulge and a fracture system on Mount St. Helens' north slope. An earthquake at 8:32 a.m. on May 18, 1980, caused the entire weakened north face to slide away, suddenly exposing the partly molten, gas- and steam-rich rock in the volcano to lower pressure. The rock responded by exploding into a very hot mix of pulverized lava and older rock that sped toward Spirit Lake so fast that it quickly passed the avalanching north face.
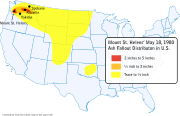
A volcanic ash column rose high into the atmosphere and deposited ash in 11 U.S. states. At the same time, snow, ice, and several entire glaciers on the mountain melted, forming a series of large lahars (volcanic mudslides) that reached as far as the Columbia River, nearly fifty miles (eighty kilometers) to the south. Less severe outbursts continued into the next day only to be followed by other large but not as destructive eruptions later in 1980. By the time the ash settled, 57 people (including innkeeper Harry Truman and geologist David A. Johnston; a full list is available here: ) and thousands of animals were dead. Hundreds of square miles were reduced to wasteland, over a billion U.S. dollars in damage had occurred ($2.74 billion in 2007 dollars), and the face of Mount St. Helens was scarred with a huge crater on its north side. At the time of the eruption, the summit of the volcano was owned by the Burlington Northern Railroad, but afterward the land passed to the United States Forest Service. The area was later preserved, as it was, in the Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument.

Buildup to the eruption

Mount St. Helens remained dormant from its last period of activity in the 1840s and 1850s, until March 1980. Several small earthquakes beginning as early as March 15, 1980, indicated that magma may have been moving below the volcano. Then on March 18 at 3:45 p.m. Pacific Standard Time (all times will be in PST), a shallow Richter magnitude 4.2 earthquake (the initial reading was 4.1), centered below the mountain's north flank, signaled the volcano's violent return from 123 years of hibernation. A gradually building earthquake swarm saturated area seismographs and started to climax at about noon on March 25, reaching peak levels in the next two days, including an earthquake registering 4.5 on the Richter scale. A total of 174 shocks of magnitude 2.6 or greater were recorded during those two days. Shocks of magnitude 3.2 or greater occurred at a slightly increasing rate during April and May with five earthquakes of magnitude 4 or above per day in early April, and 8 per day the week before May 18. Initially there was no direct sign of eruption, but small earthquake-induced avalanches of snow and ice were reported from aerial observations.
At 12:36 p.m. on March 27, at least one but possibly two nearly simultaneous phreatic eruptions (exploding groundwater-derived steam) ejected smashed rock from within the old summit crater, excavating a new crater 250 feet (76 m) wide and sending an ash column about 7,000 feet (2,100 m) into the air. By this date, a 16,000-foot (4,900 m) long, east-trending fracture system had also developed across the summit area. This was followed by more earthquake storms and a series of steam explosions that sent ash 10,000 to 11,000 feet (3,000 to 3,400 m) above their vent. Most of this ash fell within 3 to 12 miles (5 to 20 km) from its vent, but some was carried as far as 150 miles (240 km) south to Bend, Oregon, and 285 miles (460 km) east to Spokane, Washington.
A second, new crater and a blue flame was observed on March 29. The flame was visibly emitted from both craters and was probably created by burning gases. Static electricity generated from ash clouds rolling down the mountain sent out lightning bolts that were up to two miles (3 km) long. Ninety-three separate outbursts were reported on March 30, and increasingly strong harmonic tremors were first detected on April 1, alarming geologists and prompting Governor Dixy Lee Ray to declare a state of emergency on April 3.
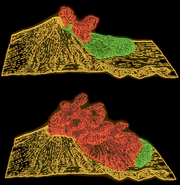
By April 7 the combined crater was 1,700 feet (520 m) long, 1,200 feet (365 m) wide and 500 feet (150 m) deep. A USGS team determined in the last week of April that a 1.5-mile (2.4 km) diameter section of St. Helens' north face was displaced out at least 270 feet (82 m). For the rest of April and early May this bulge grew 5 to 6 ft (1.5 to 1.8 m) per day, and by mid-May it extended more than 400 feet (120 m) north. As the bulge moved northward, the summit area behind it progressively sank, forming a complex, down-dropped block called a graben. Geologists announced on April 30 that sliding of the bulge area was the greatest immediate danger and that such a landslide might spark an eruption. These changes in the volcano's shape were related to the overall deformation that increased the volume of the mountain by 0.03 cubic miles (0.1 km³) by mid-May. This volume increase presumably corresponded to the volume of magma that pushed into the volcano and deformed its surface. Because the intruded magma remained below ground and was not directly visible, it was called a cryptodome, in contrast to a true lava dome exposed at the surface.
On May 7, eruptions similar to those in March and April resumed, and over the next days the bulge approached its maximum size. All activity had been confined to the 350-year-old summit dome and did not involve any new magma. A total of about 10,000 earthquakes were recorded prior to the May 18 event, with most concentrated in a small zone less than 1.6 miles (2.6 km) directly below the bulge. Visible eruptions ceased on May 16, reducing public interest and consequently the number of spectators in the area. Mounting public pressure then forced officials to allow 50 carloads of property owners to enter the danger zone on May 17 to gather whatever property they could carry. Another trip was scheduled for 10 a.m. the next morning. Since that was Sunday, more than 300 loggers would not be working in the area. By the time of the climactic eruption, dacite magma intruding into the volcano had forced the north flank outward nearly 500 feet (150 m) and heated the volcano's groundwater system, causing many steam-driven explosions (phreatic eruptions).
North face slides away
At 7 a.m. on May 18, USGS volcanologist David A. Johnston, who had Saturday night duty at an observation post about 6 miles (10 km) north of the mountain, radioed in the results of some laser-beam measurements he had made moments earlier. Mount St. Helens' activity that day did not show any change from the pattern of the preceding month. The rate of bulge movement, sulfur dioxide emission, and ground temperature readings did not reveal any unusual changes that might have indicated a catastrophic eruption.
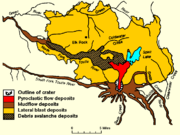
Suddenly, at 8:32 a.m., a magnitude 5.1 earthquake centred directly below the north slope triggered that part of the mountain to slide, approximately 7–20 seconds (about 10 seconds seems most reasonable) after the shock. One of the largest landslides in recorded history, the slide traveled at 110 to 155 miles per hour (175 to 250 km/h) and moved across Spirit Lake's west arm; part of it hit a 1,150-foot (350 m) high ridge about 6 miles (9.5 km) north. Some of the slide spilled over the ridge, but most of it moved 13 miles (21 km) down the North Fork Toutle River, filling its valley up to 600 feet (180 m) deep with avalanche debris. An area of about 24 square miles (62 km²) was covered, and the total volume of the deposit was about 0.7 cubic miles (2.9 km³).
Most of St. Helens' former north side became a rubble deposit 17 miles (27 km) long, averaging 150 feet (46 m) thick; the slide was thickest at one mile (1.6 km) below Spirit Lake and thinnest at its western margin. All the water in Spirit Lake was temporarily displaced by the landslide, sending 600-foot (180 m) high waves crashing into a ridge north of the lake, adding 295 feet (90 m) of new avalanche debris above the old lakebed, and raising its surface level by about 200 feet (60 m). As the water moved back into its basin, it pulled with it thousands of trees felled by a super-heated wall of volcanic gas and searing ash and rock that overtook the landslide seconds before.
Pyroclastic flows
Initial lateral blast
The landslide suddenly exposed the dacite magma in St. Helens' neck to much lower pressure causing the gas-charged, partially molten rock and high-pressure steam above it to explode a few seconds after the slide started. Explosions burst through the trailing part of the landslide, blasting rock debris northward. The resulting blast laterally directed the pyroclastic flow of very hot volcanic gases, ash, and pumice from new lava, and pulverized old rock hugged the ground while initially moving at 220 mph (350 km/h) but quickly accelerating to 670 mph (1080 km/h) (it may have briefly passed the speed of sound).
Pyroclastic flow material passed up the moving avalanche and spread outward, devastating a fan-shaped area 23 miles (37 km) across and 19 miles (30 km) long. In all, about 230 square miles (600 km²) of forest were knocked down within an 8-mile (13 km) inner-fan area, and extreme heat killed trees miles beyond the blow-down zone. At its vent the lateral blast probably did not last longer than about 30 seconds, but the northward radiating and expanding blast cloud continued for about another minute.
Superheated flow material flashed water in Spirit Lake and North Fork Toutle River to steam, creating a larger, secondary explosion that was heard as far away as British Columbia, Montana, Idaho, and Northern California. Yet many areas closer to the eruption ( Portland, Oregon, for example) did not hear the blast. This so-called "quiet zone" extended radially a few tens of miles from the volcano and was created by the complex response of the eruption's sound waves to differences in temperature and air motion of the atmospheric layers and, to a lesser extent, local topography.
Lateral blast result
Everyone in the quiet zone could see the huge ash cloud that was sent skyward from St. Helens' northern foot. The near-supersonic lateral blast, loaded with volcanic debris, caused devastation as far as 19 miles (30 km) from the volcano. The area affected by the blast can be subdivided into three roughly concentric zones:
- Direct blast zone, the innermost zone, averaged about 8 miles (13 km) in radius, an area in which virtually everything, natural or artificial, was obliterated or carried away. For this reason, this zone also has been called the "tree-removal zone." The flow of the material carried by the blast was not deflected by topographic features in this zone.
- Channelized blast zone, an intermediate zone, extended out to distances as far as 19 miles (30 km) from the volcano, an area in which the flow flattened everything in its path and was channeled to some extent by topography. In this zone, the force and direction of the blast are strikingly demonstrated by the parallel alignment of toppled large trees, broken off at the base of the trunk as if they were blades of grass mown by a scythe. This zone was also known as the "tree-down zone."
- Seared zone, also called the "standing dead" zone, the outermost fringe of the impacted area, a zone in which trees remained standing but were singed brown by the hot gases of the blast. Later studies indicated that one-third of the 0.045 cubic miles (188,000,000 m³) of material in the flow was new lava, and the rest was fragmented, older rock.
By the time this pyroclastic flow hit its first human victims, it was still as hot as 360 °C (680 °F) and filled with suffocating gas and flying angular material. Most of the 57 people known to have died in that day's eruption succumbed to asphyxiation while several died from burns. Lodge owner Harry Truman was buried under hundreds of feet (tens of meters) of avalanche material. Volcanologist David A. Johnston was one of those killed, as was Reid Blackburn, a National Geographic photographer.
Later flows
Subsequent outpourings of pyroclastic material from the breach left by the landslide consisted mainly of new magmatic debris rather than fragments of preexisting volcanic rocks. The resulting deposits formed a fan-like pattern of overlapping sheets, tongues, and lobes. At least 17 separate pyroclastic flows occurred during the May 18 eruption, and their aggregate volume was about 0.05 cubic miles (208,000,000 m³).
The flow deposits were still at about 300 °C to 420 °C (570 °F to 785 °F) two weeks after they erupted. Secondary steam-blast eruptions fed by this heat created pits on the northern margin of the pyroclastic-flow deposits, at the south shore of Spirit Lake, and along the upper part of the North Fork Toutle River. These steam-blast explosions continued sporadically for weeks or months after the emplacement of pyroclastic flows, and at least one occurred about a year later, on May 16, 1981.
Ash column grows
As the avalanche and initial pyroclastic flow were still advancing, a huge ash column grew to a height of 12 miles (19 km) above the expanding crater in less than 10 minutes and spewed tephra into the stratosphere for 10 straight hours. Near the volcano, the swirling ash particles in the atmosphere generated lightning, which in turn started many forest fires. During this time, parts of the mushroom-shaped ash-cloud column collapsed, sending additional pyroclastic flows speeding down St. Helens' flanks. Later, slower flows came directly from the new north-facing crater and consisted of glowing pumice bombs and very hot pumiceous ash. Some of these hot flows covered ice or water which flashed to steam, creating craters up to 65 feet (20 m) in diameter and sending ash as much as 6,500 feet (1980 m) into the air.
Strong high- altitude wind carried much of this material east-northeasterly from the volcano at an average speed of about 60 mph (100 km/h). By 9:45 a.m. it had reached Yakima, Washington, 90 miles (145 km) away, and by 11:45 a.m. it was over Spokane, Washington. A total of 4 to 5 inches (100 to 130 mm) of ash fell on Yakima, and areas as far east as Spokane were plunged into darkness by noon where visibility was reduced to 10 feet (3 m) and half an inch (13 mm) of ash fell. Continuing east, St. Helens' ash fell in the western part of Yellowstone National Park by 10:15 p.m. and was seen on the ground in Denver, Colorado, the next day. In time ash fall from this eruption was reported as far away as Minnesota and Oklahoma, and some of the ash drifted around the globe within about 2 weeks.
During the nine hours of vigorous eruptive activity, about 540 million tons of ash fell over an area of more than 22,000 square miles (60,000 km²). The total volume of the ash before its compaction by rainfall was about 0.3 cubic miles (1.3 km³). The volume of the uncompacted ash is equivalent to about 0.05 mile³ (208,000,000 m³) of solid rock, or about 7% of the amount of material that slid off in the debris avalanche. By around 5:30 p.m. on May 18, the vertical ash column declined in stature, but less severe outbursts continued through the night and for several days.
Mudslides flow downstream
The hot, exploding material also broke apart and melted nearly all of the mountain's glaciers along with most of the overlying snow. As in many previous St. Helens' eruptions, this created huge lahars (volcanic mudflows) and muddy floods that affected three of the four stream drainage systems on the mountain, and which started to move as early as 8:50 a.m. Lahars traveled as fast as 90 mph (145 km/h) while still high on the volcano but progressively slowed to about 3 mph (5 km/h) on the flatter and wider parts of rivers. Mudflows from the southern and eastern flanks had the consistency of wet concrete as they raced down Muddy River, Pine Creek, and Smith Creek to their confluence at the Lewis River. Bridges were taken out at the mouth of Pine Creek and the head of Swift Reservoir, which rose 2.6 feet (0.8 m) by noon to accommodate the nearly 18 million cubic yards (13 million m³) of additional water, mud, and debris.
Glacier and snow melt mixed with tephra on the volcano's northeast slope to create much larger lahars. These mudflows traveled down the north and south forks of the Toutle River and joined at the confluence of the Toutle forks and the Cowlitz River near Castle Rock, Washington, at 1:00 p.m. Ninety minutes after the eruption, the first mudflow had moved 27 river miles (43 km) upstream where observers at Weyerhaeuser's Camp Baker saw a 12-foot (3.7 m) high wall of muddy water and debris pass. Near the confluence of the Toutle's north and south forks at Silver Lake, a record flood stage of 23.5 feet (7.2 m) was recorded.
A large but slower-moving mudflow with a mortar-like consistency was mobilized in early afternoon at the head of the Toutle River north fork. By 2:30 p.m. the massive mudflow had destroyed Camp Baker, and in the following hours seven bridges were carried away. Part of the flow backed up for 2.5 miles (4 km) soon after entering the Cowlitz River, but most continued downstream. After traveling 17 miles (27 km) further, an estimated 3.9 million cubic yards (3.0 million m³) of material were injected into the Columbia River, reducing the river's depth by 25 feet (7.6 m) for a four-mile (6 km) stretch. The resulting 13-foot (4 m) river depth temporarily closed the busy channel to ocean-going freighters, costing Portland, Oregon an estimated five million US dollars. Ultimately more than 65 million cubic yards (50 million m³) of sediment were dumped along the lower Cowlitz and Columbia Rivers.
Aftermath
Direct results
The May 18, 1980, event was the most deadly and economically destructive volcanic eruption in the history of the United States. Fifty-seven people were killed and 200 homes, 47 bridges, 15 miles (24 km) of railways and 185 miles (300 km) of highway were destroyed. U.S. President Jimmy Carter surveyed the damage and stated it looked more desolate than a moonscape. A film crew was dropped by helicopter on St. Helens on May 23 to document the destruction. Their compasses, however, span in circles and they quickly became lost. A second eruption occurred the next day (see below), but the crew survived and were rescued two days after that.
In all, St. Helens released an amount of energy equivalent to 27,000 Hiroshima-sized nuclear weapons and ejected more than 1 cubic mile (4 km³) of material. A quarter of that volume was fresh lava in the form of ash, pumice, and volcanic bombs while the rest was fragmented, older rock. The removal of the north side of the mountain (13% of the cone's volume) reduced St. Helens' height by about 1,313 feet (400 m) and left a crater 1 to 2 miles (2 to 3 km) wide and 2,100 feet (640 m) deep with its north end open in a huge breach.
More than 4 billion board feet (14.6 km³) of timber was damaged or destroyed, mainly by the lateral blast. At least 25% of the destroyed timber was salvaged after September 1980. Downwind of the volcano, in areas of thick ash accumulation, many agricultural crops, such as wheat, apples, potatoes, and alfalfa, were destroyed. As many as 1,500 elk and 5,000 deer were killed, and an estimated 12 million Chinook and Coho salmon fingerlings died when their hatcheries were destroyed. Another estimated 40,000 young salmon were lost when they swam through turbine blades of hydroelectric generators when reservoir levels were lowered along the Lewis River to accommodate possible mudflows and flood waters.
Digging out
The ash fall created some temporary but major problems with transportation, sewage disposal, and water treatment systems. Visibility was greatly decreased during the ash fall, closing many highways and roads. Interstate 90 from Seattle to Spokane was closed for a week and a half. Air travel was disrupted for a few days to 2 weeks as several airports in eastern Washington shut down because of ash accumulation and poor visibility. Over a thousand commercial flights were canceled following airport closures. Fine-grained, gritty ash caused substantial problems for internal-combustion engines and other mechanical and electrical equipment. The ash contaminated oil systems and clogged air filters, and scratched moving surfaces. Fine ash caused short circuits in electrical transformers, which in turn caused power blackouts.
Removing and disposing of the ash was a monumental task for some eastern Washington communities. State and federal agencies estimated that over 2.4 million cubic yards (1.8 million m³) of ash — equivalent to about 900,000 tons in weight — were removed from highways and airports in Washington. Ash removal cost $2.2 million and took 10 weeks in Yakima. The need to remove ash quickly from transport routes and civil works dictated the selection of some disposal sites. Some cities used old quarries and existing sanitary landfills; others created dumpsites wherever expedient. To minimize wind reworking of ash dumps, the surfaces of some disposal sites were covered with topsoil and seeded with grass. In Portland, the mayor eventually threatened businesses with fines if they failed to remove the ash from their parking lots.
Cost
Early estimates of the cost of the eruption ranged from US$2–3 billion. A refined estimate of $1.1 billion ($2.74 billion in 2007 dollars ) was determined in a study by the International Trade Commission at the request of the United States Congress. A supplemental appropriation of $951 million for disaster relief was voted by Congress, of which the largest share went to the Small Business Administration, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and the Federal Emergency Management Agency.
There were also indirect and intangible costs of the eruption. Unemployment in the immediate region of Mount St. Helens rose tenfold in the weeks immediately following the eruption, and then returned to nearly normal once timber salvaging and ash-cleanup operations were underway. Only a small percentage of residents left the region because of lost jobs owing to the eruption. Several months after May 18, a few residents reported suffering stress and emotional problems, even though they had coped successfully during the crisis. Counties in the region requested funding for mental health programs to assist such people.
Initial public reaction to the May 18 eruption nearly dealt a crippling blow to tourism, an important industry in Washington. Not only was tourism down in the Mount St. Helens– Gifford Pinchot National Forest area, but conventions, meetings, and social gatherings also were canceled or postponed at cities and resorts elsewhere in Washington and neighboring Oregon not affected by the eruption. The adverse effect on tourism and conventioneering, however, proved only temporary. Mount St. Helens, perhaps because of its reawakening, has regained its appeal for tourists. The United States Forest Service and the State of Washington opened visitor centers and provided access for people to view the volcano's devastation.
Later eruptions
St. Helens produced five more explosive eruptions between May and October 1980. Through early 1990, a total of at least 21 periods of eruptive activity had occurred. The volcano remains active, with smaller, dome-building eruptions continuing into 2008.

An eruption occurred on May 25, 1980 at 2:30 a.m. that sent an ash column 9 miles (14 km) into the atmosphere. The eruption was preceded by a sudden increase in earthquake activity and occurred during a rain storm. Erratic wind from the storm carried ash from the eruption to the south and west, lightly dusting large parts of western Washington and Oregon. Pyroclastic flows exited the northern breach and covered avalanche debris, lahars, and other pyroclastic flows deposited by the May 18 eruption.
At 7:05 p.m. on June 12, a plume of ash billowed 2.5 miles (4 km) above the volcano. At 9:09 p.m. a much stronger explosion sent an ash column about 10 miles (16 km) skyward. This event caused the Portland area, previously spared by wind direction, to be thinly coated with ash in the middle of the annual Rose Festival. A dacite dome then oozed into existence on the crater floor, growing to a height of 200 feet (60 m) and a width of 1,200 feet (370 m) within a week.
A series of large explosions on July 22 broke more than a month of relative quiet. The July eruptive episode was preceded by several days of measurable expansion of the summit area, heightened earthquake activity, and changed emission rates of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide. The first hit at 5:14 p.m. as an ash column shot 10 miles (16 km) and was followed by a faster blast at 6:25 p.m. that pushed the ash column above its previous maximum height in just 7.5 minutes. The final explosion started at 7:01 p.m. and continued for over two hours. When the relatively small amount of ash settled over eastern Washington, the dome built in June was gone.

Seismic activity and gas emission steadily increased in early August, and on August 7 at 4:26 p.m., an ash cloud slowly expanded 8 miles (13 km) into the sky. Small pyroclastic flows were sent through the northern breach and weaker outpouring of ash rose from the crater. This continued until 10:32 p.m. when a second large blast sent ash high into the air. A second dacite dome filled this vent a few days later.
Two months of repose were ended by an eruption lasting from October 16 to October 18. This event obliterated the second dome, sent ash 10 miles (16 km) in the air and created small, red-hot pyroclastic flows. A third dome began to form within 30 minutes after the final explosion on October 18, and within a few days, it was about 900 feet (270 m) wide and 130 feet (40 m) high. In spite of the dome growth next to it, a new glacier formed rapidly inside the crater.
All of the post-1980 eruptions were quiet dome-building events, beginning with the December 27, 1980, to January 3, 1981, episode. By 1987 the third dome had grown to be more than 3,000 feet (900 m) wide and 800 feet (240 m) high. At that rate, assuming additional destructive eruptions do not occur, St. Helens' summit would be restored to its previous height sometime in the mid to late 22nd century.
Further eruptions occurred over a few months during 1989–1991, and the mountain became active again in late 2004.
Summary table
| Eruption Summary May 18, 1980 Eruption of Mount St. Helens |
||
|---|---|---|
| Volcano | Elevation of Summit: | Before eruption: 9,677 feet (2,950 m) After eruption: 8,363 feet (2,549 m) Total removed: 1,314 feet (401 m) |
| Crater dimensions: | East-West: 1.2 miles (1.9 km) North-South: 1.8 miles (2.9 km) Depth: 2,084 feet (635 m) |
|
| Crater floor elevation: | 6,279 feet (1,914 m) | |
| Eruption | Date: | May 18, 1980 |
| Time of initial blast: | 8:32 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time (UTC-7) | |
| Eruption trigger: | A magnitude 5.1 earthquake about 1 mile (1.6 km) beneath the volcano | |
| Landslide / Debris Avalanche |
Area covered: | 23 square miles (60 km²) |
| Volume: (uncompacted deposits) |
0.67 mi³ (2.8 km³) | |
| Depth of deposit: | Buried North Fork Toutle River to average depth of 150 feet (46 m) with a maximum depth of 600 feet (183 m) | |
| Velocity: | 70 miles per hour (113 km/h) to 150 miles per hour (241 km/h) | |
| Lateral Blast | Area covered: | 230 square miles (596 km²); reached 17 miles (27 km) northwest of the crater |
| Volume of deposit: (uncompacted deposits) |
0.046 mi³ (0.19 km³) | |
| Depth of deposit: | From about 3 feet (1 m) at volcano to less than 1 inch (2.5 cm) at blast edge | |
| Velocity: | At least 300 miles per hour (483 km/h) | |
| Temperature: | As high as 660 °F (349 °C) | |
| Energy release: | 24 megatons thermal energy (7 by blast, rest through release of heat) | |
| Trees blown down: | 4 billion board feet (9.4 million m³) of timber (enough to build about 300,000 two-bedroom homes) | |
| Human fatalities: | 57 | |
| Lahars | Velocity: | About 10 miles per hour (16 km/h) to 25 miles per hour (40 km/h) and over 50 miles per hour (80 km/h) on steep flanks of volcano |
| Damaged: | 27 bridges, nearly 200 homes. Blast and lahars destroyed more than 185 miles (298 km) of highways and roads and 15 miles (24 km) of railways. | |
| Effects on Cowlitz River: | Reduced carrying capacity at flood stage at Castle Rock from 76,000 ft³/s (2,150 m³/s) to less than 15,000 ft³/s (225 m³/s) | |
| Effects on Columbia River: | Reduced channel depth from 40 feet (12 m) to 14 feet (4 m); stranded 31 ships in upstream ports | |
| Eruption Column And Cloud |
Height: | Reached about 80,000 feet (24,400 m) in less than 15 minutes |
| Downwind extent: | Spread across U.S. in 3 days; circled Earth in 15 days | |
| Volume of ash: (based on uncompacted deposits |
0.26 mi³ (1 km³) | |
| Ash fall area: | Detectable amounts of ash covered 22,000 square miles (57,000 km²) | |
| Ash fall depth: | 10 inches (25 cm) at 10 miles (16 km) downwind (ash and pumice) 1 inch (2.5 cm) at 60 miles (97 km) downwind 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) at 300 miles (482.8 km) downwind |
|
| Pyroclastic Flows | Area covered: | 6 square miles (16 km²); reached as far as 5 miles (8 km) north of crater |
| Volume and depth: (volume based on uncompacted deposits) |
0.029 mi³ (0.12 km³); multiple flows 3 feet (1 m) to 30 feet (9 m) thick; cumulative depth of deposits reached 120 feet (37 m) in places | |
| Velocity: | Estimated at 50 miles per hour (80 km/h) to 80 miles per hour (130 km/h) | |
| Temperature: | At least 1,300 °F (700 °C) | |
| Other | Wildlife: | The Washington State Department of Game estimated nearly 7,000 big game animals (deer, elk, and bear) perished as well as all birds and most small mammals. Many burrowing rodents, frogs, salamanders, and crawfish, managed to survive because they were below ground level or water surface when the disaster struck. |
| Fisheries: | The Washington Department of Fisheries estimated that 12 million Chinook and Coho salmon fingerlings were killed when hatcheries were destroyed. Another estimated 40,000 young salmon were lost when forced to swim through turbine blades of hydroelectric generators as reservoir levels along the Lewis River were kept low to accommodate possible mudflows and flooding. | |
| Brantley and Myers, 1997, Mount St. Helens -- From the 1980 Eruption to 1996: USGS Fact Sheet 070–97, accessed 2007- 06-05; and Tilling, Topinka, and Swanson, 1990, Eruption of Mount St. Helens - Past, Present, and Future: USGS General Interest Publication, accessed 2007- 06-05. | ||
| Table compiled by Lyn Topinka, USGS/CVO, 1997 | ||